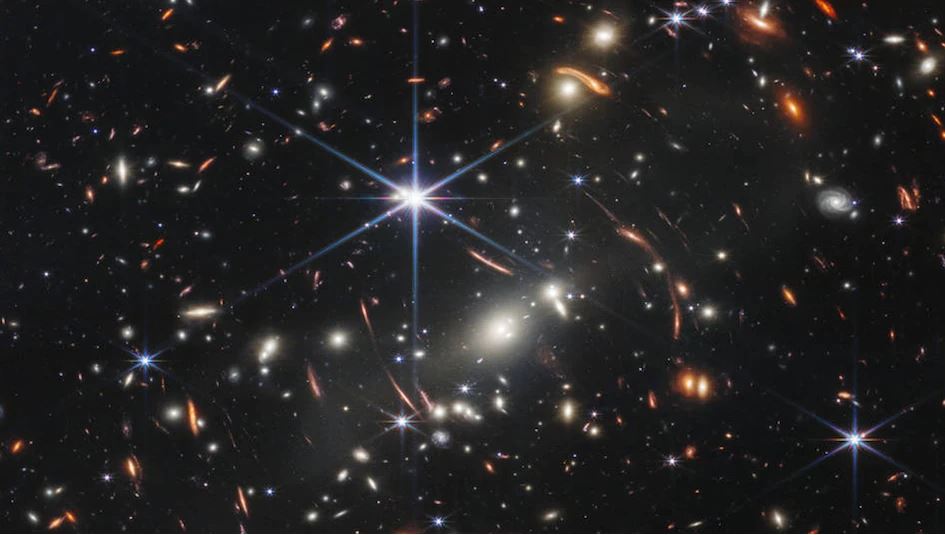
The stars, which are gaseous spheres that emit vast amounts of heat and light, have always been present among us, from leading ancient travelers through unknown places and sailing the seven seas to today assisting scholars in their studies of the Universe.
What are the stars?
As we mentioned earlier, stars are massive masses of gas and dust that emit their own light. These big hot objects that we see in various parts of the universe emit enormous amounts of energy due to a series of phases produced by nuclear fusion.
Because scientists still don’t know everything about the universe, determining the exact number of stars in the sky has been impossible until now. However, astronomers and specialists have identified some of them and calculated their influx. To give you an idea, more than three billion stars may be found in the sky with a sophisticated telescope.
You know which one is the nearest to our planet and the only one in our Solar Structure? You guessed correctly! The Sun is shining. And those closest to it are those that comprise the Alpha Centauri structure, which is more than four light years away.
Stars have varied colors depending on their temperature. In this way, we can see bluish-white stars as well as orange or reddish stars. However, due to the evolutionary cycles of the stars, their subtleties, intensity, and volume alter with time.
Each of these celestial bodies that we see in the sky emits light to varying degrees, based on their distance and the physical attributes they possess. That is why, when we observe stars that are brighter than others, it is not because they emit more energy or are bigger, but because they are closer together.
What is the process of gestation of the stars?
The stars’ vital process lasts around 1000 million years. As a result, the larger the animal, the shorter its life expectancy.
A star’s gestation period takes place within nebulae (clusters of cosmic dust composed of hydrogen). Over thousands of years, gravitational fields have assisted the collapse of compact material apertures inside the galaxy.
When a celestial body contracts one of these gaseous substances (called as protostars), the gestation period begins. A protostar is difficult to detect because the dust layers of the nebulae conceal it.
As a protostar shrinks in size, it spins faster because to the preservation of angular time (same physical magnitude exercised by professional skaters who, while turning and tightening their arms, increase speed).
The temperature rises due to the increasing stress. The stars go through what is known as the T Tauri cycle during this time period; a rather quick process.
Over the course of at least 10 billion years, the epicenter’s heat approaches 20 million degrees, triggering nuclear fusion, which ignites the epicenter and commences the star’s next life cycle, known as the main series.
The majority of stars in space (including the Sun) are categorized as main sequence stars. These are in a stable nuclear fusion state, fusing hydrogen to helium and generating X-rays. A significant amount of energy is radiated during this cycle, keeping the star’s temperature high. As a result, stars shine with enormous intensity.
If the star’s core runs out of hydrogen, the nuclear fusion phase will be disrupted, destabilizing your center and causing it to heat up. The volume of the heavenly body will lead its evolution to take distinct pathways in this section. However, as previously said, as your volume expands, your standard of living will decrease.
Evolution of the stars
Main series stars (similar to the Sun) can classify their evolution as follows:
Stars of the same magnitude as the Sun
- Red giant: When transforming hydrogen into helium, it will go directly to the center; which will cause the heat to increase and its outer crust to dilate and cool.
- White dwarf: As the red giant cools little by little, its magnitude will decrease, until it reaches a level called white dwarf. These originate from celestial bodies of small volume.
- Black Dwarf: When the white dwarf no longer generates more energy and radiates light and heat; will turn into a black dwarf.
Stars of greater magnitude than the Sun
- Red supergiant: They have a larger volume than the red giants. Also, they are cooler than the Sun.
- Supernova: The center of the star reaches the point of destabilization and explodes, forming a supernova that dispenses amazing energy discharges; They can last for days or even months. This would lead, in theory, to the death of the star.
The neutron stars
They are particles left over from supernova explosions, where electrons fuse to become neutrons. Pulsars are neutron stars that spin at high speeds and emit radiation at specific periods.
Black voids
If the collapsed supernova’s epicenter was part of a vast and gigantic celestial body, it may create a tremendously thick black hole with such a powerful gravitational field that no piece of matter or luminosity could get rid of it.
Star characteristics
- They are primarily composed of helium and hydrogen.
- They do not spread equally throughout the Universe, but rather clump together until they form a gas and molecular constellation. Due to the pull of gravity, some stars are isolated and others are close, resulting in stellar formations.
- Binary star formations consist of two stars.
- Three or more stars form multiple stellar formations. Three, four, five, six, seven, or even more stars are possible.
- They produce radiation as a result of nuclear fusion, which occurs when two or more atomic epicenters collide, creating a new, more charged atomic epicenter. As a result, an electromagnetic emission is produced, causing the stars to emit light and generate energy discharges.
- Their colors are determined by the degree of heat in their outer shells: Stars turn reddish in extremely cold temperatures. However, if the temperature is really high, they turn a bluish color.
- As part of their life cycle, celestial bodies are born and die. As a result, the material from which they are made takes on a new form. Stars have ages ranging from one to ten billion years.
How the stars are classified?
In 1885, cosmologist Edward Pickering would launch the first photographic analyses of sidereal images from the Harvard College Observation Center, a project that would culminate with the astronomer Annie Cannon.
According to the degree of intensity in some filtration lines, such scientific studies would lead to the discovery that stellar images are enrolled in a sequential chain. These studies provide information on the ages and rates of growth of numerous stars.
The numerous cycles in the sequential chain of images are labeled with the letters A, B, F, G, K, M, and O, completing the star categorization. The subcategories, which range from zero to nine, are used to denote the series in each hierarchy’s pattern.
Nitrogen, helium, hydrogen, and oxygen lines are classified as type O. They are celestial bodies with high temperatures, ranging from those that produce images of incandescent helium and hydrogen lines to those that show black lines of the same components.
Type B helium lines that are brightest in the B2 sub-order and gradually fade to white in higher sub-orders. In every sub-orders, the strength of the hydrogen lines grows continually. The star Epsilon Orionis determines this set.
Type A hydrogen stars have pictures that have been treated to hydrogen filtering lines. Sirius is a prominent celestial body in this constellation.
F-type
The so-called H and K lines of calcium, as well as the representative lines of hydrogen, stand out in this category. Delta Aquilae is a well-known F-type star.
G-type
It includes stars with strong calcium H and K lines as well as stars with weaker hydrogen lines. It also features depictions of other metals, particularly iron. Because the Sun is a part of this group, the celestial body G is referred to as a “solar class star.”
K-type
Celestial bodies with strong calcium lines and others that suggest the existence of other metals. In this set, he is referred to as Arthur.
Type M
Images submitted by groups that depict the appearance of metal oxides, particularly titanium oxide. The last violet portion of the image is weaker than the K stars. This grouping is distinguished by the celestial body Betelgeuse.
If you are interested
You can also read Entertainment, Numerology, Tech, and Health-related articles here: OnePlus 9RT Review, Netflix October 2022 Schedule, Summer Podcasts on Movistar, Best Cycling Simulator Games, MyShopify, Ben Affleck Net Worth, Filmymeet, 5Movies, September 8 Zodiac, Kengan Ashura Season 3, iPhone 14 Plus Release Date, High School DxD Season 5, How Gautam Adani Emerged World’s Third Richest Man, Jeezy Net Worth, Historical Series on HBO Max, F2Movies, Best Travel Movies of All Time, Vikings Season 7, How to Watch Artemis I Launch Attempt, Best Kitchen Gadgets for Home Cooks, September 2 Zodiac, Hubble’s Law and Age of Universe, New Movies on Disney Plus September 2022, Amazon Prime Release Date September 2022, Steps for Casual Look, Daredevil Season 4, Tinyzone, Elon Musk Mother sleeps in Garage, Lady Gaga All movies, Virgo,
Does TikTok Spy on You, Thank You in Spanish, Openload, Invention of Antibiotics, Subnautica, Knives Out 2, Best Basketball Anime, 13 Regions for Astronauts to Land on the Moon, Red Bottom Shoes, StoriesDown, Meaningful Learning, E-learning 2022, She-Hulk release date, Overlord Season 5, Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 4 Review, Feogi, Laal Singh Chaddha Review, Baki Season 5, Bflix, Leonardo DiCaprio Sneakers, Hurawatch, Salman Rushdie,
Accessibility Apps for Android, Best Jobs in the Metaverse, QueenslandMax, Shower Standing Handle, August 11 Zodiac, How to pass a drug test, How to Roll a Joint, iFun, Emerald Chat, How to Play Mancala, August 8 Zodiac, OnePlus 10T Review, Jilo Virals, August 4 Zodiac, Findsnap, Tomb Raider Anime, Netflix August 2022 Schedule, Animixplay, Upcoming Marvel Movies 2022, July 31 Zodiac, Best Lily Collins Movies, Notepadqq, Flaxseeds with Milk Benefits, Imginn, Snaptik, Picuki, Alexis Clark Net Worth, Black Panther 2,
Apart from the above articles, you can read more
Marvel Echo Release Date, Frozen Fruit Recipes, Black Tourmaline, Webtoon XYZ, Fastest VPN for Android, IFVOD, XXXX Dry Review, Highest Grossing Indian Movies of all Time, Highest Grossing Movies of All Time, Rush Limbaugh net worth. Gotham Season 7, Parag Agrawal Net Worth, Tara Reid Net Worth, Blonde Trailer, Fastest VPN for PC, Highest Paid CEO in India 2022, Highest paid athletes 2022, My5 TV Activate, Kissmanga, Highest Paid CEO 2022, Grey’s Anatomy Season 19, Alexa.com Alternatives, The Resident Season 6, Kraven The Hunter, One Punch Man season 3, The Resident Season 5, Yellowstone season 5, Ozark season 4 part 2, How to Remove Bookmarks on Mac,
Outer Banks Season 4, How to watch NFL games for free, DesireMovies, 6streams, 4Anime, Moviesflix, 123MKV, MasterAnime, Buffstreams, GoMovies, VIPLeague, How to Play Music in Discord, Vampires Diaries Season 9, Homeland Season 9, Brent Rivera Net Worth, PDFDrive, SmallPDF, Knightfall Season 3, Crackstream, Kung Fu Panda 4, 1616 Angel Number, 333 Angel Number, 666 Angel Number, 777 Angel Number, 444 angel number, Bruno Mars net worth, KissAnime, Jim Carrey net worth, Bollyshare, Afdah, Prabhas Wife Name, Project Free TV, Kissasian, Kickassanime, Moviezwap, Jio Rockers, Dramacool, M4uHD, Hip Dips, M4ufree, Fiverr English Test Answers, Fiverr SEO Skill Test, NBAstreamsXYZ, Highest Paid CEO, The 100 season 8, and F95Zone.
Thanks for reading. Stay tuned!