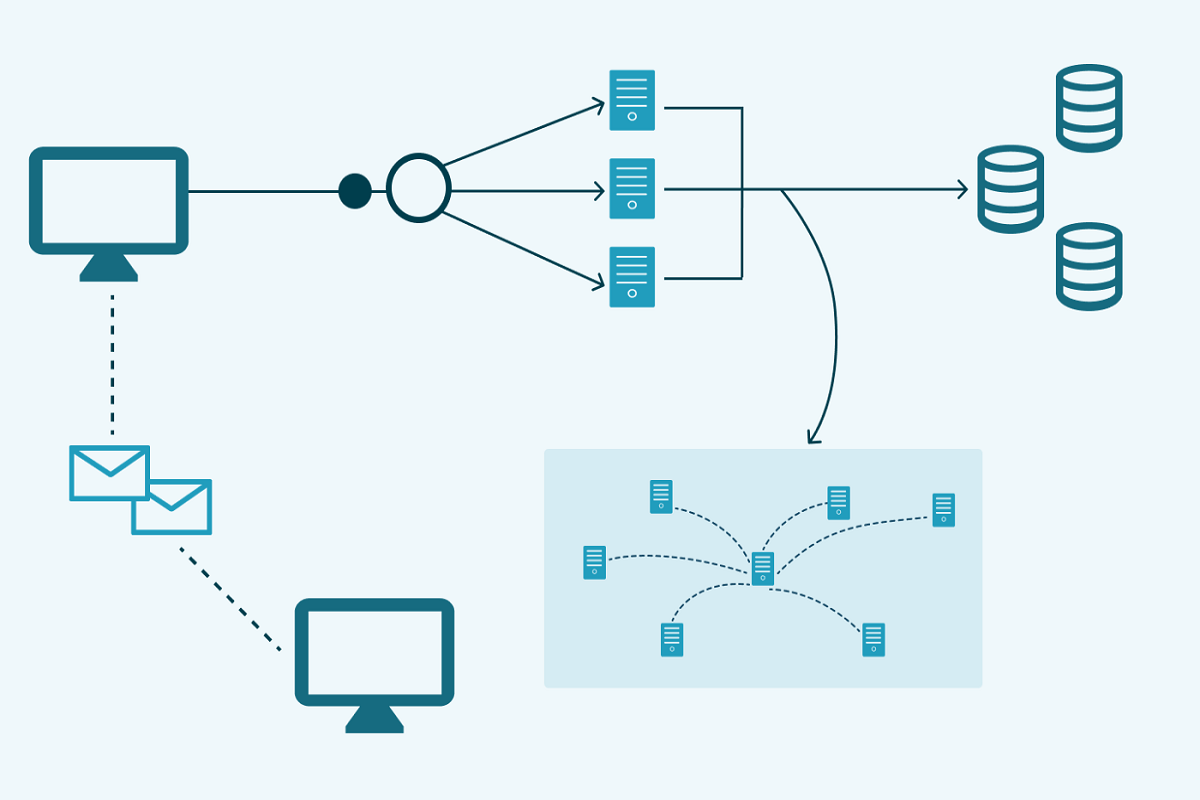
A system design software (such as Collimator) offers a high-level overview of the system architecture and human-machine interface, as well as detailed descriptions of each system software service. Its authors make the course very engaging, providing the pros and cons of each design option.
It provides a high-level overview of the system architecture
System design is the process of creating a functional system. It includes the specification of modules and their inter-relationships. It provides an overall organizational structure for the system and its components. It also explains the design and implementation of the various modules. A system is made up of many sub-systems, each with its own architecture.
The architecture of a system explains the way in which various components of the system work together and how data flows between them. It also defines the responsibilities of each component of the system. In a software solution, the system architecture should provide a high-level view of the system and its components. It should include data flow diagrams and a narrative describing the relationships between the subcomponents. Moreover, it should contain detailed descriptions of the components, including their physical and logical interactions.
System architectures should be logically layered and describe the hardware and software components. It should also provide a diagram showing how components communicate with one another and how their components are distributed in the system’s network. It should also include information on the necessary firewalls and the capacity of the network.
The 4+1 View Model provides a high-level view of a system’s architecture. It identifies the different concerns and features of a software system and enables stakeholders to understand its architecture and design. It also provides a standardized way to communicate software design documents.
System architecture is the foundation of the entire system. The architecture of an enterprise includes many different systems, each of which is connected. These systems can be distributed across many computers, and different companies may own them. A well-documented architecture can make it possible to analyze and reuse components, as well as design of different parts of the system.
A high-level system design document describes the system’s goals. It may also include the data design associated with the system, the human-machine interface, and operational scenarios. The high-level design document is then decomposed into low-level design specifications for each component. These documents serve as the primary input to the detailed design and preliminary design review phases.
It describes the human-machine interface
The human-machine interface, or HMI, is the user interface between a machine and its human operator. It includes electronic components that communicate with the industrial control systems. These systems monitor and control the operation of the machinery and associated devices. They are often designated critical infrastructure. In addition to the human-machine interface, industrial control systems have various other components, including programmable logic controllers. HMIs allow users to interact with the system by turning switches on and off, and viewing schematics, and other information.
The human-machine interface is a vital component of any system. This is why it is important to develop an HMI that emphasizes the human as a key element of the system. To do this, the SE should establish an HSI IPT within the program office. The HSI IPT should detail HSI objectives, risks, and activities. It should also include staffing for HSI.
Often, the human-machine interface is built on the basis of interaction scenarios, which describe typical maintenance situations. These scenarios are useful for defining a concrete HMI and for usability testing. These scenarios are then refined to reflect the specific requirements of each use case. They can also be used to generate a formal HMI framework and define devices.
Human-machine interfaces can be physical control panels, industrial PCs, or specialized HMI software. These interfaces enable the human operator to interact with the automated machines. This is accomplished through the use of buttons or touchscreens. The HMIs may also have physical buttons.
An HMI can provide a reference for others under development. It also enables developers to test the functionality of the interface and make improvements. This way, they can ensure that their systems work correctly and provide an optimal user experience. It is important to consider the input and output characteristics of the software.