Listen to the Podcast:
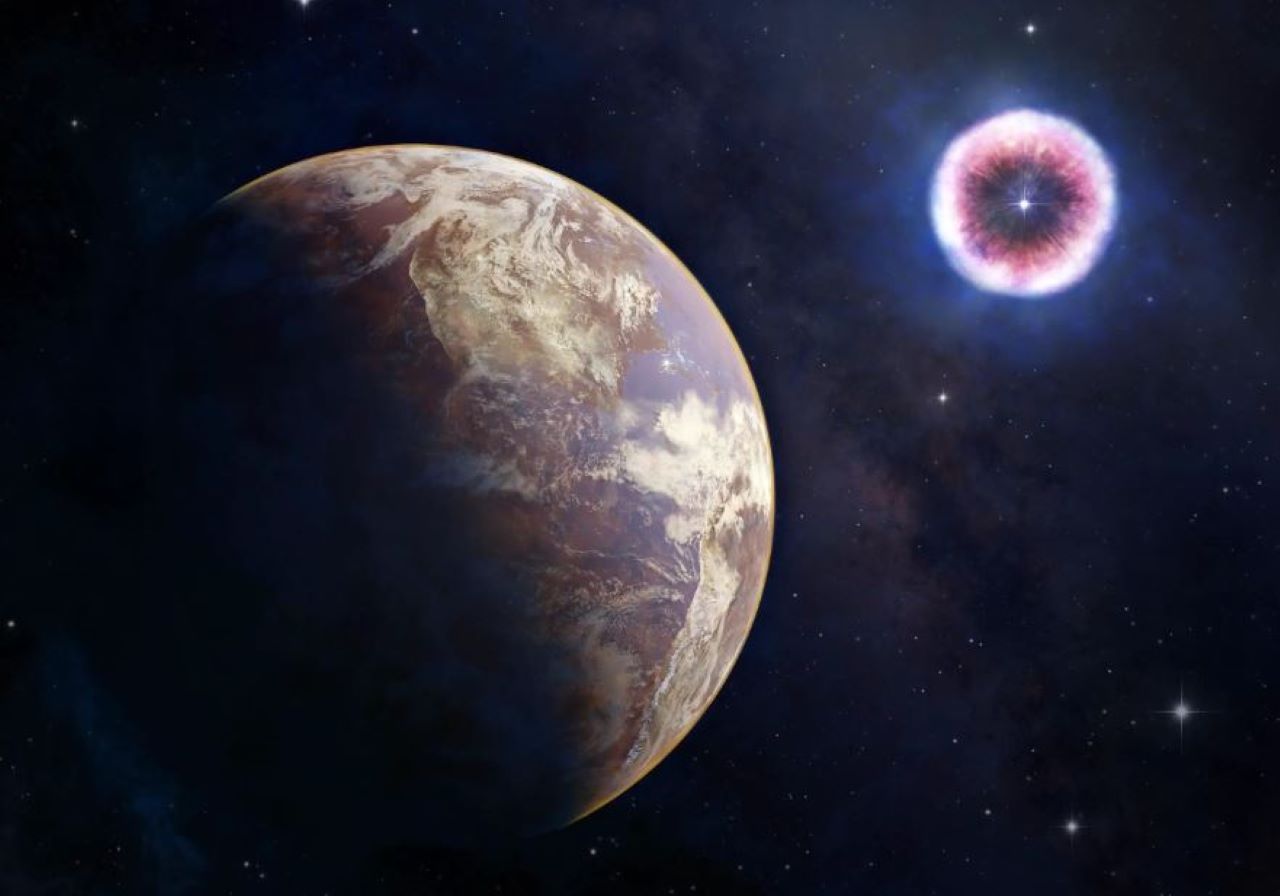
Astronomers have found a new danger to life on planets like Earth by looking at data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and other space telescopes. During a certain phase, strong X-rays from exploding stars can reach planets more than 100 light-years away. This finding has an effect on how we study other planets and whether or not they can support life.
This new danger comes from the collision of a supernova’s blast wave with dense gas around the exploded star, as shown in the upper right corner of our artist’s illustration. When this happens, it can send a lot of X-rays to a planet like Earth (shown in the lower left, lit by its mother star, which is out of view to the right). These X-rays can reach the planet months or years after the explosion and may last for decades. So much exposure could cause a mass extinction in the world.
Based on X-ray observations of 31 supernovae and their aftershocks — mostly from NASA‘s Chandra X-ray Observatory, Swift and NuSTAR missions, and ESA’s XMM-Newton — a new study says that planets can get lethal doses of radiation from as far away as 160 light-years. Four of the supernovae in the study—SN 1979C, SN 1987A, SN 2010jl, and SN 1994I—are shown in the supplemental pictures below as composite images with Chandra data. These are SN 1979C, SN 1987A, SN 2010jl, and SN 1994I.
Before this, most study on the effects of supernova explosions focused on two types of danger: the intense radiation a supernova releases in the days and months after the explosion, and the energetic particles that arrive hundreds to thousands of years later.
If a lot of X-rays hit a close planet, they could change the chemistry of the planet’s atmosphere in a big way. On a planet like Earth, this process could destroy a lot of the ozone that saves life from the harmful ultraviolet radiation of its star. It could also kill a lot of creatures, especially marine ones that are at the bottom of the food chain, which could lead to an extinction event.
After years of being killed by X-rays from a supernova and UV rays from a star that hosts a planet like Earth, a lot of nitrogen dioxide may be made, which causes a brown haze in the atmosphere, as shown in the picture. Damage to plants could also lead to a “de-greening” of large areas of land.
A different artist’s impression shows that the same world like Earth was full of life at the time of the nearby supernova, which was years before most of the X-ray’s effects were felt.
SN 2010jl has given off the most X-rays of the four supernovae in the set of pictures. The authors think it sent out enough X-rays to kill life on worlds like Earth that were less than 100 light-years away.
There is a lot of proof that supernovae happened close to Earth between 2 million and 8 million years ago. For example, a radioactive type of iron has been found in different places around the world. Scientists think that these supernovae were between 65 and 500 light-years from Earth.
Even though the Earth and the rest of the Solar System are not in a place where a supernova could happen, many other worlds in the Milky Way are. The Galactic Habitable Zone, which is part of the Milky Way galaxy where conditions are good for life as we know it, would shrink because of these high-energy events.
Because there aren’t many X-ray studies of supernovae, especially those that interact strongly with their surroundings, the authors suggest keeping an eye on interacting supernovae for months and years after they explode.
“X-Ray-luminous Supernovae: Threats to Terrestrial Biospheres” by Ian R. Brunton, Connor O’Mahoney, Brian D. Fields, Adrian L. Melott, and Brian C. Thomas, published in The Astrophysical Journal on April 19, 2023.
The paper about this finding is in the issue of The Astrophysical Journal from April 20, 2023. Ian Brunton, Connor O’Mahoney, and Brian Fields from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Adrian Melott from the University of Kansas, and Brian Thomas from Washburn University in Kansas are the other people who wrote the study.
The Chandra program is run by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Center is in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and it is there that science operations and flying operations are run.