Agriculture has always been the backbone of New Zealand’s economy. With the demand for food production rising and environmental concerns becoming more critical, precision agriculture has emerged as a game-changer. One of the most significant technologies revolutionizing modern farming is Global Positioning System (GPS).
GPS technology allows farmers to optimize land use, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. From automated tractors to accurate soil mapping, GPS ensures better decision-making in farming. In this article, we will explore the role of GPS in precision agriculture in New Zealand, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
What is Precision Agriculture?
Precision agriculture, also known as smart farming, is a modern approach that utilizes technology, data, and automation to enhance crop yield and livestock management. This method enables farmers to apply the right amount of inputs (fertilizers, water, pesticides) at the right time and place, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Key Elements of Precision Agriculture
| Feature | Description |
| GPS Technology | Provides accurate positioning for farm equipment and mapping of fields. |
| IoT Sensors | Helps in monitoring soil moisture, temperature, and crop health. |
| Drones | Used for crop surveillance and pesticide application. |
| Automated Machinery | GPS-guided tractors and harvesters enhance efficiency. |
| Data Analytics | Helps farmers make informed decisions based on real-time data. |
How GPS Enhances Precision Agriculture?
1. Automated Machinery Guidance
GPS-powered autonomous tractors and machinery reduce manual labor and human error. Farmers can automate plowing, seeding, and harvesting, leading to increased efficiency and reduced fuel costs.
| Benefit | Description |
| Precision Steering | Reduces overlaps and gaps while planting and harvesting. |
| Reduced Labor | Less reliance on human operators, lowering costs. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimized paths reduce fuel consumption. |
2. Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
GPS-based variable rate application ensures that fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation are used efficiently based on specific field needs. This targeted approach reduces waste and improves crop health.
| Input Type | Optimization with GPS |
| Fertilizers | Applied only where needed, reducing environmental impact. |
| Water | Smart irrigation minimizes overwatering and conserves water. |
| Pesticides | Targeted application reduces chemical runoff. |
3. Yield Mapping and Soil Monitoring
GPS-equipped yield monitors collect real-time data on crop productivity across different field areas. This information allows farmers to adjust future planting and fertilization strategies for maximum yield.
| Feature | Benefit |
| Real-time Data | Provides immediate insights into crop performance. |
| Soil Analysis | Helps in understanding soil nutrient levels. |
| Improved Planning | Assists in future farming decisions based on past data. |
4. Geofencing and Livestock Tracking
For livestock farmers, GPS enables geofencing, allowing virtual boundaries for cattle movement tracking. Farmers receive alerts when animals stray, reducing losses and improving herd management.
| Use Case | Benefit |
| Cattle Tracking | Helps in monitoring the location of animals. |
| Virtual Fencing | Reduces the need for physical barriers. |
| Theft Prevention | Alerts farmers in case of unauthorized movement. |
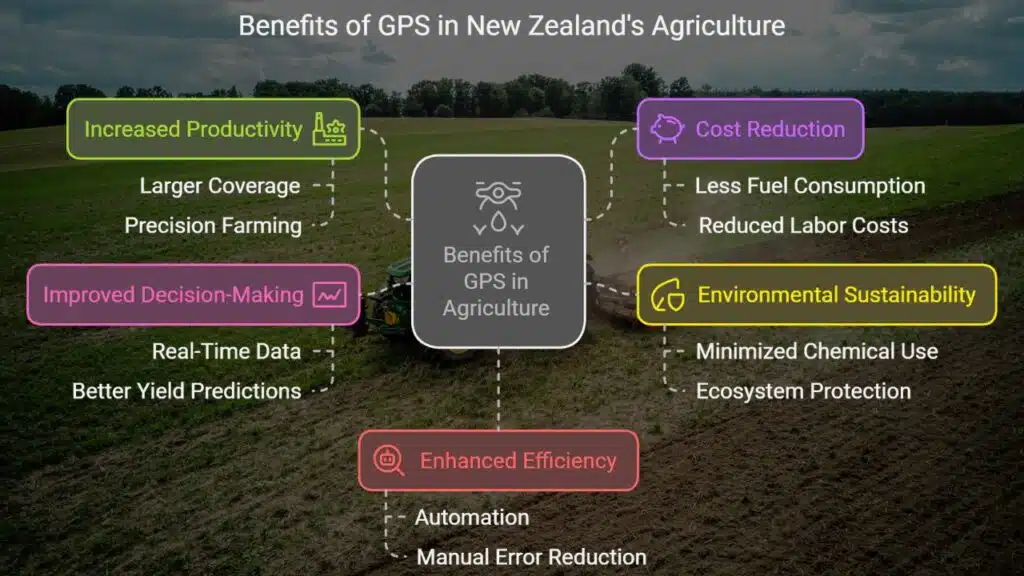
Benefits of GPS in New Zealand’s Agricultural Sector
| Benefit | Explanation |
| Increased Productivity | Farmers can cover larger areas with more precision and less effort. |
| Cost Reduction | Less fuel, labor, and resource waste lead to lower operational costs. |
| Environmental Sustainability | Minimizing excessive use of chemicals protects the ecosystem. |
| Improved Decision-Making | Real-time data helps in strategic planning and better yield predictions. |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Automation reduces manual errors and increases precision. |
Real-World Applications: GPS in New Zealand’s Farms
Case Study: Dairy Farming in Canterbury
Many dairy farms in Canterbury, New Zealand, use GPS-guided irrigation systems to ensure water is efficiently distributed. Precision irrigation has reduced water waste by up to 30%, improving sustainability and crop growth.
Case Study: Vineyards in Marlborough
New Zealand’s wine industry benefits significantly from GPS-based vineyard management. By using GPS technology, vineyards can analyze soil conditions and microclimates, leading to higher grape quality and better wine production.
Challenges and Limitations of GPS in Precision Farming
| Challenge | Explanation |
| High Initial Investment | GPS equipment and software can be costly for small farmers. |
| Connectivity Issues | Rural areas may face GPS signal and internet connectivity problems. |
| Technical Knowledge | Farmers need training to utilize GPS technology effectively. |
| Data Security | Digital data storage poses risks of cyber threats. |
Future of GPS in Precision Agriculture in New Zealand
As technology advances, the role of GPS in precision farming will continue to grow. New Zealand is investing in smart farming innovations to support sustainability and increased food production.
Emerging Trends
| Trend | Impact on Agriculture |
| AI and Machine Learning | Enhances predictive analysis for crop yield and weather patterns. |
| Autonomous Farming Equipment | Reduces reliance on human labor. |
| Blockchain in Agriculture | Ensures secure data storage and transparency. |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | Reduces water usage while maintaining crop health. |
Takeaways
GPS technology is transforming precision agriculture in New Zealand by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and promoting sustainability. Farmers can leverage automated machinery, precise mapping, and real-time data to maximize yield and profitability.
Despite some challenges, the future of GPS-powered farming looks promising. As New Zealand continues to invest in agri-tech innovations, farmers adopting GPS technology will gain a competitive advantage in sustainable and efficient farming.
Call to Action
Are you a farmer looking to integrate GPS technology into your operations? Start exploring smart farming solutions today for better productivity and profitability.