In today’s fast-paced world, the traditional method of education, confined to the four walls of a classroom, is no longer the only option. The increasing demand for flexible learning opportunities has led to the rise of hybrid education models blending online and in-person learning.
These models integrate the best elements of both traditional classroom instruction and digital learning platforms to create a more dynamic, accessible, and personalized learning experience. The ongoing advancements in technology have opened up new avenues for educators to cater to diverse learning styles and individual preferences.
As the education sector continues to evolve, these hybrid learning models are becoming more popular in K-12 schools, universities, and even in corporate training programs.
This article will explore ten popular hybrid education models, delving into how they work, the benefits they offer, and real-world examples of successful implementation.
Whether you’re an educator, student, or institution looking to adopt or enhance hybrid learning, this guide will provide valuable insights on how to make it work for you.
What Are Hybrid Education Models?
Hybrid education models refer to teaching and learning strategies that combine online and in-person instruction. In these models, students have access to both face-to-face classes and online learning materials, providing a more flexible and personalized educational experience.
The integration of digital tools allows students to learn at their own pace, while in-person sessions offer opportunities for deeper engagement, discussion, and hands-on activities.
The flexibility provided by hybrid models caters to different learning styles and time constraints, making it a popular choice for modern education. The key advantage of hybrid education is that it allows for a better blend of synchronous and asynchronous learning, addressing various needs and preferences of both educators and students.
The Evolution of Education: From Traditional to Hybrid
Education has been traditionally centered around in-person classes where teachers and students interact face-to-face.
However, the rise of the internet and digital technologies introduced online learning, offering students flexibility, convenience, and access to global resources. Hybrid education, therefore, is the natural progression of this digital revolution, combining the strengths of traditional methods with modern technological tools.
As educational institutions increasingly adopt hybrid models, they are able to engage a broader audience, including non-traditional learners like working adults or those in remote locations.
Hybrid education represents a fundamental shift in how learning can be delivered, offering more opportunities for accessibility, personalization, and engagement.
Benefits of Hybrid Learning for Students and Educators
The hybrid learning model offers numerous advantages for both students and educators. Below, we’ve listed some of the most significant benefits:
For Students:
- Flexibility: Students can balance schoolwork with other responsibilities, such as jobs or family care, by learning at their own pace and on their own schedule.
- Increased Engagement: The combination of online and in-person activities encourages students to engage with the content in various ways, improving understanding and retention.
- Personalization: Hybrid models allow students to focus on the areas where they need more help, taking online courses or activities that match their personal learning style.
For Educators:
- Access to a Wider Audience: Educators can reach students from around the world, allowing them to teach diverse learners.
- Efficient Use of Time: Teachers can use in-person sessions for interactive activities while relying on online platforms to deliver content, grade assignments, and monitor student progress.
- Improved Student Performance: The combination of both learning environments allows educators to tailor their teaching to the needs of each student, leading to better outcomes.
Key Components of Hybrid Education
Hybrid education is built on three main components that work synergistically to deliver an effective and comprehensive learning experience. These components—online learning, in-person instruction, and technology—serve as the backbone of any hybrid learning model.
1. Online Learning: Flexibility and Accessibility
Online learning plays a pivotal role in hybrid education. It allows students to learn at their own pace, access resources 24/7, and engage with materials that suit their learning style. Online platforms also provide access to a wealth of resources, including videos, articles, and forums for discussion.
Benefits:
- Access Anytime, Anywhere: Students can engage with content at their own pace, making it easier for those with busy schedules to keep up.
- Diverse Learning Tools: Platforms like Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard offer diverse tools such as quizzes, assignments, and multimedia that enrich the learning experience.
Challenges:
- Self-Discipline Required: Some students may struggle with time management and the lack of face-to-face accountability in online environments.
2. In-Person Learning: Interaction and Engagement
While online learning provides flexibility, in-person learning remains essential for fostering real-time collaboration, building relationships, and engaging in hands-on learning activities. In-person sessions create opportunities for deep interactions, such as discussions, group work, and practical demonstrations that enhance the learning process.
Benefits:
- Engagement: Physical classrooms allow for immediate interaction, enabling students to ask questions, clarify doubts, and participate in discussions.
- Collaboration: In-person learning allows students to work together on projects and practice skills in real-world contexts.
Challenges:
- Limited Flexibility: In-person learning requires students to be present at scheduled times, which can be challenging for those with other obligations.
3. The Role of Technology in Hybrid Learning
Technology underpins the entire hybrid learning model, facilitating both online and in-person learning. Learning management systems [LMS], virtual classrooms, and collaboration tools enable instructors and students to communicate, share resources, and track progress. Innovations like artificial intelligence [AI] and data analytics also allow for personalized learning experiences, where students receive tailored recommendations based on their learning behaviors and performance.
Benefits:
- Efficiency: Technology streamlines administrative tasks, such as grading, tracking progress, and managing assignments.
- Personalization: AI-powered tools can adapt the curriculum to individual learning styles and needs, helping students learn more effectively.
Challenges:
- Digital Divide: Access to technology is still a barrier for some students, particularly in underserved communities.
10 Hybrid Education Models Blending Online and In-Person Learning
Let’s explore 10 prominent hybrid education models that blend online and in-person learning. Each of these models has its own set of benefits, and they can be tailored to suit various educational contexts.
1. Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model is one of the most widely recognized hybrid approaches. In this model, students first engage with new material online through videos, readings, or interactive tutorials. In-person classes are then used for discussions, group work, and application of the material.
How It Blends Online and In-Person Learning:
- Online: Students learn theoretical content asynchronously.
- In-Person: The focus is on active learning, problem-solving, and interaction with peers and instructors.
Example:
- Case Study: A high school science teacher uses video lectures and online quizzes for students to review before class. In-person sessions are then used for lab work and group discussions.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Promotes active learning | Requires high student discipline for pre-class engagement |
| Maximizes in-class time | May be difficult for younger students to adapt to self-paced learning |
| Encourages deeper understanding | Initial setup of resources can be time-consuming for instructors |
2. Blended Learning with Rotation
In this model, students rotate between online learning, in-person classes, and possibly independent study. The rotation schedule is pre-determined, and students may engage in online activities, attend face-to-face classes, and then move on to individual work at home or in a learning center.
What is the rotation model?
- Online: Students can work on lessons or projects at their own pace.
- In-Person: Face-to-face sessions can focus on collaboration, discussion, and assessments.
- Independent: Students can complete assignments or reviews independently.
Example:
- Case Study: A college language class rotates between online vocabulary drills, in-person conversation practice, and homework assignments in a set weekly schedule.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Helps cater to different learning preferences | Requires significant planning and coordination |
| Provides structure and flexibility | Potential confusion with schedule transitions for students |
3. Self-Paced Learning with Virtual Support
In this model, students learn course materials at their own pace using online resources such as videos, tutorials, and quizzes. Virtual support from instructors and peers is provided via email, online forums, and chat tools. In-person support may also be available through scheduled office hours or collaborative sessions.
How Virtual Support Enhances Self-Paced Learning:
- Online: Self-paced learning through digital resources.
- Virtual Support: Students can access live chat sessions, email assistance, or even peer study groups for guidance.
Example:
- Case Study: A professional development course allows participants to complete lessons on their own time, while instructors host weekly virtual office hours for real-time Q&A.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Maximum flexibility for students | Lack of face-to-face interaction might feel isolating |
| Allows for personalized pacing | Can create a sense of disconnection if virtual support is not timely |
4. Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning Blend
This model combines synchronous [real-time] and asynchronous [on-demand] learning. Students attend live virtual or in-person classes for scheduled lectures or discussions while completing independent assignments and activities online at their own pace.
How It Works:
- Synchronous: Real-time classes via video conferencing or in-person sessions.
- Asynchronous: Self-paced assignments and learning activities that can be accessed anytime.
Example:
- Case Study: A university course in business administration combines weekly live online lectures with self-paced readings, case studies, and quizzes that students complete on their own time.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides flexibility while maintaining structure | May be difficult for students to keep up with deadlines |
| Enhances student collaboration | Not all students thrive in a blend of scheduled and self-paced learning |
5. Project-Based Learning with Hybrid Support
Project-based learning [PBL] emphasizes students working on real-world problems and projects over an extended period of time. When combined with hybrid education, students can collaborate on projects both online and in person, using digital tools for research, communication, and collaboration, while meeting in person for presentations, group work, and practical activities.
How It Works:
- Online: Students use digital tools for research, planning, and collaboration, such as Google Drive, Slack, or Trello, which allow for virtual teamwork.
- In-Person: Students meet for group discussions, to present progress, and to engage in hands-on learning activities related to their projects.
Example:
- Case Study: A high school environmental science class uses the hybrid model for a project on sustainable urban development. Students collaborate online to research and develop their proposals, while in-person meetings allow them to build prototypes and present their findings to local stakeholders.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Encourages practical, real-world problem-solving | Requires strong coordination among students |
| Fosters collaboration and communication skills | May require additional resources for hands-on activities |
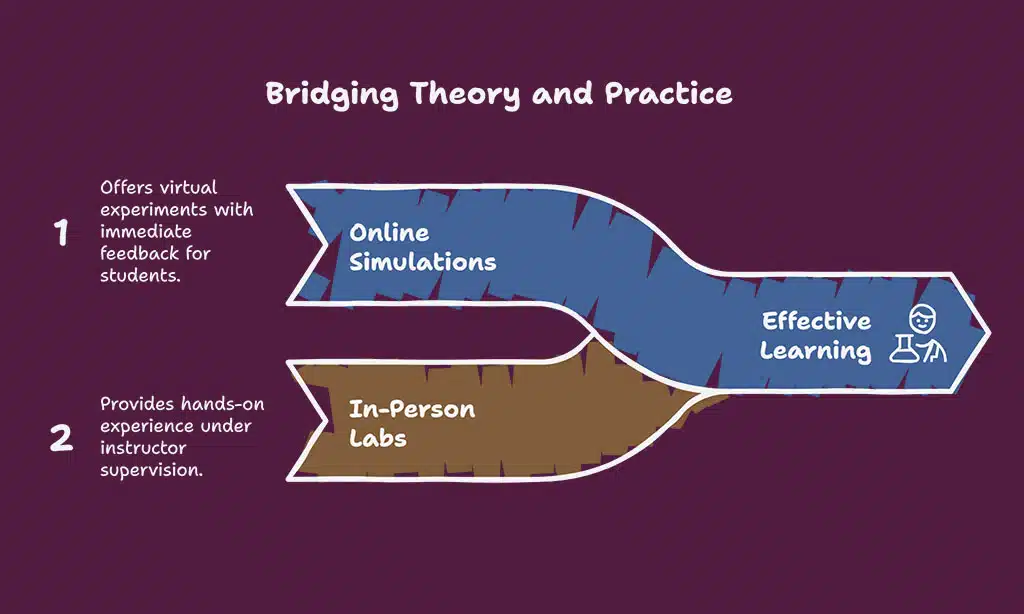
6. Virtual Labs with In-Person Support
For subjects that require hands-on experimentation—such as science, engineering, or art—hybrid education can integrate virtual labs with in-person guidance and assessment. In this model, students can complete virtual lab exercises online, practicing theoretical concepts in a simulated environment before coming together in person for hands-on, real-world application.
How It Works:
- Online: Students conduct experiments in virtual labs or through simulations, receiving immediate feedback from digital tools.
- In-Person: Students work in physical labs under the supervision of instructors to apply the skills they learned in virtual settings.
Example:
- Case Study: An engineering course uses virtual simulations for circuit design before having students meet in person to assemble physical circuits in the lab.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides safe, cost-effective practice opportunities | Not all disciplines can be easily simulated online |
| Bridges the gap between theory and practice | Can be challenging to recreate the full lab experience virtually |
7. Competency-Based Hybrid Learning
Competency-based education [CBE] focuses on mastering specific skills or knowledge areas rather than completing a set number of hours or assignments. In a hybrid setting, students can progress through material at their own pace, using both online modules and in-person assessments or skill demonstrations.
How It Works:
- Online: Students work through modules and assessments that test their mastery of specific competencies.
- In-Person: Students meet for skill demonstrations, one-on-one coaching, or practical assessments that validate their mastery of the competencies.
Example:
- Case Study: A medical school uses a competency-based hybrid model where students complete online coursework in anatomy and pathology at their own pace, while in-person labs focus on clinical practice and skill validation.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Personalized learning experience | Requires careful design of assessments and competencies |
| Students can progress at their own pace | May be challenging to ensure all students meet required standards |
8. Corporate Hybrid Training Programs
Hybrid education is not limited to traditional educational institutions; it is also an effective model for corporate training programs. In these models, employees combine online training courses with in-person workshops, seminars, and collaborative team projects to develop new skills and knowledge relevant to their roles.
How It Works:
- Online: Employees take part in e-learning courses or webinars that provide theoretical knowledge and skill development.
- In-Person: Workshops, seminars, or team-building exercises are held to reinforce online learning and provide practical experience.
Example:
- Case Study: A large tech company offers hybrid training for employees. Workers complete online courses about new software and then attend in-person training sessions to practice using the software with hands-on projects.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Efficient use of time and resources | Scheduling in-person sessions can be difficult for a distributed workforce |
| Flexible learning options for employees | May be hard to measure the effectiveness of the online portion |
9. Flipped Mastery Learning Model
The flipped mastery model takes the flipped classroom concept a step further by allowing students to progress through materials at their own pace, only moving on to more advanced content once they have mastered the current material. This model heavily relies on online learning to provide flexibility and self-paced progression, with in-person time used for mastery checks and applying learning.
How It Works:
- Online: Students review content, take quizzes, and complete assignments at their own pace.
- In-Person: Instructors assess mastery, provide additional help where needed, and guide students through advanced concepts or projects once mastery is achieved.
Example:
- Case Study: A high school math class uses the flipped mastery model, where students learn foundational concepts through online tutorials and videos. Only once they pass a mastery check do they move on to more complex topics during in-person sessions.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ensures students master content before advancing | Requires frequent assessments and can be time-intensive for instructors |
| Allows for personalized pacing and support | Students may feel frustrated if they do not progress quickly enough |
10. Global Learning Partnerships [Hybrid]
Global learning partnerships use hybrid models to allow students from different geographic locations to collaborate and learn together. These partnerships often involve combining online platforms for global collaboration with in-person sessions for local students. This model is particularly popular in universities and for global internships or exchange programs.
How It Works:
- Online: Students from around the world engage in online courses, discussion forums, and joint projects.
- In-Person: Local students meet in person with faculty or local peers for discussions, fieldwork, or internships that complement online learning.
Example:
- Case Study: A university in the U.S. partners with institutions in Europe and Asia, using hybrid learning to enable students from various locations to work on collaborative research projects, combining virtual meetings with on-site research.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Facilitates international collaboration | Time zone differences can pose scheduling challenges |
| Increases cultural awareness and global perspectives | May require significant logistical coordination |
Key Benefits of Blending Online and In-Person Learning
There are several reasons why hybrid learning models are gaining traction in educational institutions across the world. Let’s explore the key benefits of blending online and in-person learning.
1. Flexibility in Scheduling and Learning Styles
Hybrid education allows students to learn at their own pace, making it easier to balance their academic workload with other responsibilities.
2. Enhanced Accessibility for Diverse Learners
Hybrid learning ensures that students from different backgrounds and geographical locations and with various learning needs can access quality education.
3. Improved Learning Outcomes and Engagement
The combination of online resources and in-person engagement has been shown to improve student learning outcomes and retention rates.
4. Cost Efficiency for Educational Institutions
Hybrid education can help institutions reduce overhead costs, such as physical infrastructure, while still providing high-quality education.
Key Takeaways and Future of Hybrid Learning Models
The hybrid education models blending online and in-person learning offer unique opportunities to enhance the educational experience for students and educators alike. These models allow for increased flexibility, greater accessibility, and improved engagement, catering to a wide range of learning preferences and schedules.
Each of the 10 models explored in this article presents a different way of blending online and in-person learning, offering something for a diverse set of educational needs.
The future of hybrid education is promising, as it offers students more autonomy, enables educators to experiment with innovative teaching methods, and provides institutions with the tools to reach a broader audience.
As hybrid learning evolves, it will be essential for educators to continue experimenting with and refining these models, ensuring that they remain relevant and effective for both students and instructors in the long term.
By adopting hybrid learning strategies, educational institutions can prepare students for the future workforce, where flexibility, adaptability, and digital literacy are key skills. The transition to hybrid education may require careful planning and ongoing support, but the rewards in terms of student success, engagement, and global collaboration will make it well worth the effort.
Takeaways
The Hybrid Education Models Blending Online and In-Person Learning represent the future of education, one that is more adaptable, inclusive, and aligned with modern technological advances.
By incorporating both online and in-person elements, these models offer the best of both worlds—providing flexibility for students while also maintaining the richness of face-to-face interactions.
Whether you are a student, educator, or institution, embracing these hybrid learning models will ensure that you are prepared to meet the demands of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
The possibilities are vast, and the benefits are clear—hybrid education is more than just a trend; it’s the future of learning.