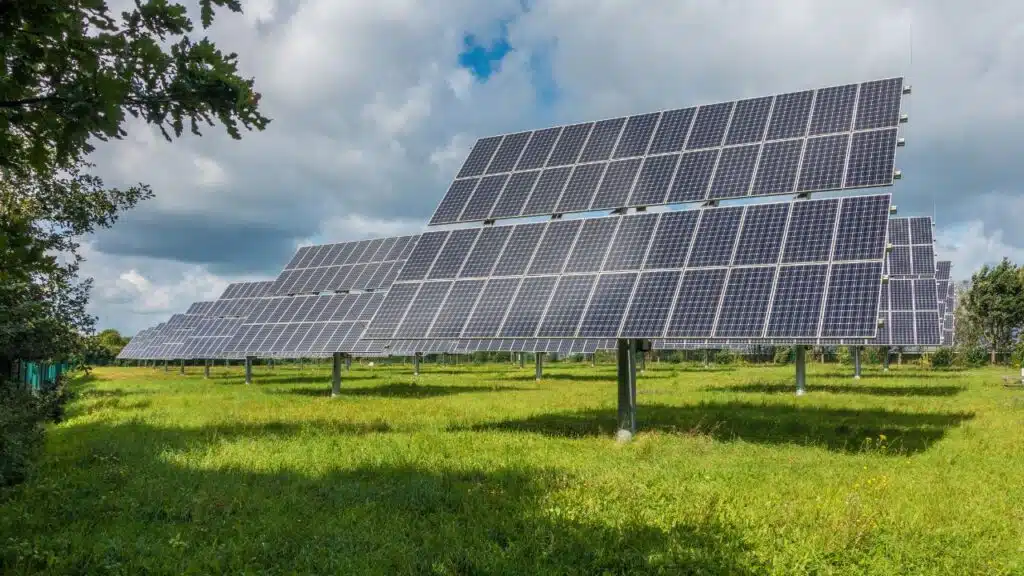
Many people worry about air pollution and climate change. You might pay high bills for electricity too. Maybe you see news about the rise of fossil fuels, or feel frustrated with how big power plants hurt green spaces and water nearby.
Here is a fact that will make you pause—solar panels work even on cloudy days because they catch light in all weather, not just sunshine. Solar energy is cleaner than oil and gas, giving us a better way to generate power.
This blog explains ten surprising ways solar panels help our planet using simple words. You will learn how these shiny rectangles lower greenhouse gases, keep water clean, create jobs, and more.
Get ready for clear facts that might just spark your curiosity!
Key Takeaways
- Solar panels cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 20 times compared to coal and 12 times less than natural gas (U.S. data, 2022). This helps fight climate change step by step.
- They do not pollute the air or use much water. Regular power plants need lots of water for cooling and produce harmful gases like CO2 and sulfur dioxide. Solar energy saves rivers, lakes, and keeps the air clean.
- Installing solar panels boosts local jobs. In 2022, over 255,000 people worked in the U.S. solar industry—a growth rate five times higher than most other fields. The Bureau of Labor Statistics expects a further 27% rise by 2031.
- Solar power makes countries less dependent on imported oil and gas. It gives more energy security since sunlight is free and long-lasting—about five billion years.
- Solar farms can go on rooftops or unused land and don’t need trees cleared or farmland taken away, helping protect nature while making electricity for homes and businesses.
Solar Panels Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Solar panels cut down greenhouse gas emissions in a big way. Fossil fuels like coal and natural gas pump huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the air during electricity generation, making up about 76% of total greenhouse gases from energy production.
Solar power flips that script with clean energy. The life-cycle emissions from solar panel systems are twelve times less than natural gas, and a whopping twenty times lower compared to coal plants.
Using renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic cells or concentrated solar power means less pollution for the planet and healthier lungs for people living near power plants. In fact, new solar farms cost less to build than keeping old coal stations running in the U.S. Grid-connected rooftop installations and large-scale solar parks deliver green energy while shrinking your household’s carbon footprint every year.
Thanks to these advances in solar technology, generating clean electricity lowers co2 emissions on a global scale—helping limit climate change step by step instead of waiting for some magic fix later down the road.
Lower Air and Water Pollution Levels
Fossil-fueled power plants like those using coal, oil, or natural gas pollute the air with CO2 and sulfur dioxide. Natural gas alone supplied 32% of America’s electricity in 2022. These plants also pump out tiny particles that can make it hard to breathe fresh air.
Solar panels cut these harmful emissions straight off the map once installed. Panels produce clean energy right on rooftops without a single puff of smoke.
Concentrated solar power and photovoltaic cells use almost no water for cooling, unlike nuclear reactors or biofuel generators that gulp gallons every hour just to stay cool. Large-scale renewable energy installations help keep rivers and lakes from running dry.
The World Wildlife Fund expects two-thirds of people worldwide might struggle with water shortages by 2025 if things do not change soon. Clean energy solutions like solar reduce strain on nature and help protect ecosystems for birds, fish, and folks alike—no need to tiptoe around muddy issues here!
Conservation of Natural Resources
Solar panels turn sunlight into electricity without burning coal, oil, or gas. Coal mines dig deep holes and leave scars on the land. Oil spills harm rivers and hurt animals that live nearby.
Switching to solar energy cuts down our need for these finite resources, protecting forests and wetlands from damage. The sun’s supply will last about 5 billion years, making it a reliable source of clean energy.
Many solar power plants use rooftops or empty fields instead of chopping down trees or taking up farmland. Thin film photovoltaic cells even blend in as rooftop tiles; pretty clever, right? Once installed, solar panels need little upkeep or replacement parts compared to fossil fuel systems.
With minimal impact on nature and much lower resource consumption, solar technology offers a brighter path for global electricity generation while conserving what nature provides us today.
Mitigation of Climate Change
Solar panels play a key role in fighting climate change. They cut CO2 emissions, which is vital for global climate initiatives. In 2023, about three-quarters of new renewable capacity came from solar energy.
This shift helps to limit warming to 2°C above pre-industrial levels, a major goal worldwide.
Solar capacity in the U.S. could top natural gas by 2026 and coal by 2027. More homes are adopting these clean technologies thanks to programs like the UK government’s Warm Homes Plan.
It invests £1.8 billion for energy-saving upgrades in homes, pushing us closer to our climate goals while reducing our carbon footprint.
Energy Independence and Sustainability
Energy independence comes from using local resources like solar energy. Solar panels help reduce the need for imported fossil fuels. In 2022, the UK got 37% of its primary energy from imports, mostly oil and gas.
This reliance adds to greenhouse gas emissions during transport. Solar power generates clean energy right at home, cutting back on these harmful effects.
Sustainability means meeting our needs without harming future generations. Solar panels make this possible with a lifespan of 25-30 years or more. The United States is seeing rapid growth in renewable energy sources like solar power.
By 2050, it could be the largest source on the grid! More solar installations mean less dependence on foreign fuel and a better carbon footprint for everyone involved.
Efficient Land Use for Solar Farms
Solar panels can go on rooftops, car parks, and other unused spaces. This helps to save habitats while still generating power. Large solar farms also fit into public lands managed by the Bureau of Land Management.
They promote smart renewable development that minimizes harm to local communities and habitats.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants use mirrors to focus sunlight. This method produces electricity even in areas with less sun. With this efficient land use, solar energy becomes a valuable resource for everyone, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Reduced Water Consumption Compared to Other Energy Sources
Conventional energy sources, like coal and gas, need a lot of water for cooling. In fact, they use huge amounts daily. This can lead to water shortages in many places. The World Wildlife Fund warns that two-thirds of the global population may face these issues by 2025.
Solar panels don’t require any water for cooling at all. They take sunlight and turn it into electricity without wasting precious resources.
Compared to other methods, solar power uses far less water. While fossil fuels suck up gallons every day, solar technology helps conserve our most vital resource: water. Plus, since solar panels operate silently, they also cut down on noise pollution around us—making them a win-win solution for the environment!
Contribution to Job Creation and Economic Growth
Solar panels create many jobs. The U.S. solar industry employed over 255,000 workers in 2022. This number is growing fast, five times faster than the overall job market. The Bureau of Labor Statistics expects a 27% growth for solar photovoltaic installers from 2021 to 2031.
Jobs in this field include manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of solar panels. There are also roles in research and development of new technology. Installing solar panels can increase a home’s value by up to 4.1%.
Additionally, these panels can reduce energy bills by up to 80%. As more people choose renewable sources like solar power, both jobs and economic growth will continue to rise across the country.
Takeaways
Solar panels do a lot for our environment. They cut down greenhouse gas emissions, helping to fight climate change. These panels also lower air and water pollution, making our planet cleaner.
Investing in solar energy boosts job creation too. With more sunshine and smarter technology, we can all enjoy a brighter and greener future!
FAQs
1. How do solar panels cut greenhouse gas emissions?
Solar panels use sunlight to make electricity. This means less need for fossil fuels like coal and oil, which lets us lower CO2 emissions and shrink our carbon footprint.
2. Can solar power really help fight climate change?
Yes, using solar energy helps combat climate change. Solar PV systems turn the sun’s light into clean energy, making it easier to meet climate goals without burning dirty fuels.
3. What makes solar panel efficiency important for the planet?
High-efficiency photovoltaic cells mean more electricity from every ray of sunshine. Better solar cell technology boosts renewable power generation, helping the world move toward a sustainable future.
4. Are rooftop solar panels just for homes in sunny places?
Not at all! Rooftop installations work in many climates thanks to new advancements in solar technologies. Even on cloudy days, they add green energy to local grids and reduce overall energy consumption from non-renewable sources.
5. Does switching to renewables like wind or solar actually make a difference globally?
Absolutely! Global electricity generation is changing fast with more renewable energy sources like wind turbines and large-scale solar plants popping up everywhere from China’s massive capacity projects to small towns across Europe under their Green Deal plans.
6. How does concentrated thermal power fit into the big picture of clean energy?
Concentrating thermal power uses mirrors or lenses at special plants called concentrating thermal stations; these gather heat from sunlight then turn it into usable electric current alongside regular photovoltaic setups—another smart way we get sustainable fuel while cutting pollution right down to size.