In 2025, cloud gaming has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the landscape of the gaming industry and redefining the very concept of interactive entertainment. Gone are the days of expensive hardware, long downloads, and storage limitations—today, players access high-quality games instantly, from any device, with seamless performance delivered directly from the cloud.
With advancements in streaming technology, faster internet connectivity, and powerful cloud infrastructures, the barriers to entry for gamers have drastically diminished, opening doors to a more inclusive, accessible, and immersive gaming experience. As tech giants and innovative startups alike continue to push boundaries, cloud gaming is not merely a trend—it’s the future of digital entertainment, changing how we play, interact, and experience games forever.
How Cloud Gaming Works?
Your controller taps remote servers in big data centers, where graphics hardware renders each frame in a flash. Then a streaming platform sends live pixels over your internet pipe, so you can jump in on any screen.
Streaming games from remote servers
Cloud gaming streams titles from remote machines. Services like GeForce Now and Google Stadia power game streaming with servers far away. A stable internet connection carries your input to the hub and brings video back fast.
You skip downloads and tweaks and press play like flipping a switch. It feels like you own a high‑end rig without plastic or cooling fans.
NVIDIA Graphics Delivery Network runs on thirty hubs across 130 countries. This cloud platform links publishers with any 3D engine for seamless one‑click access. Powerful GPU servers encode frames in milliseconds to cut lag.
Gamers feel action in real time over fiber or 5G links. Small studios and AAA teams tap the same fast path.
Device-independent gaming experience
Gamers launch cloud gaming platforms like nvidia geforce now or google stadia on PCs, tablets, smart TVs, or a vision headset. The GDN relies on server farms and edge nodes to stream video games at up to 60 fps.
It only needs a stable internet connection of 5 Mbps per user.
Cross-platform play works without slowdown, letting players switch devices mid-match. Amazon Luna, xbox cloud gaming, and playstation now users skip high-end hardware and hard drives.
They access high-quality games on demand, enjoying low latency and high dynamic range.
Key Advantages of Cloud Gaming
Players tap into cloud streaming hubs and ditch pricey GPUs.
They jet into top‑tier games on Geforce Now or Amazon Luna with low latency.
No need for expensive hardware
By 2025, cloud gaming frees players from shelling out $1,500 on a high-end rig. Remote servers and data centers handle all the heavy lifting. Game streaming runs in real time over a stable internet connection.
Services like Nvidia GeForce Now, Google Stadia, Amazon Luna and Xbox Cloud Gaming pop up on screens from phones to smart TVs. You launch titles at once, no install or patch needed.
Game developers drop worries over user hardware. They build deeper worlds, more detailed physics, and smooth virtual reality tests, thanks to cloud infrastructure. PlayStation Now and subscription-based gaming models like Xbox Game Pass Ultimate serve thousands of live updates without compatibility tests.
This shift boosts gaming accessibility, sparks fresh ideas, and trims costs for both studios and end users.
Instant access to high-quality games
Cloud gaming loads games fast on remote servers. Google Stadia, GeForce Now, Xbox Cloud Gaming and PlayStation Now stream Control, Cyberpunk 2077 and Assassin’s Creed Odyssey in seconds.
Streaming services use remote servers in data centers across continents. Microsoft Flight Simulator taps 2.5 petabytes of Bing Maps data with 37,000 airports, two million cities, 1.5 billion buildings and two trillion trees.
Mobile phones, smart TVs and low-end PCs stream Forza Horizon 5, Halo Infinite and Bloodborne with no downloads. Players enjoy top visuals over a stable internet connection. Subscription-based gaming on Amazon Luna or Xbox Game Pass Ultimate puts choice in one library.
This setup cuts cost on high-end hardware and gives instant play.
Enhanced game security and reliability
Game servers run inside data centers. They use NVIDIA L40 cards with 48 GB memory and 142 RT cores. That gear powers ray tracing and fast load times. Virtualization layers isolate each session.
Encryption shields game files on remote servers. Publishers patch code inside secure vaults.
Stable internet links keep lag low. Fiber‑optic networks, 5G rollouts and edge computing cut delays under 20 milliseconds. Game streaming services like Google Stadia, NVIDIA GeForce Now and Xbox Cloud Gaming serve millions of players.
They let players stream high‑quality titles. Monitoring tools block hacks in real time. Gaming accessibility expands across PCs, phones and smart TVs.
The Impact of Cloud Gaming on Developers
Dev teams now zip patches through remote servers with GPU farms in edge data hubs, so players spot fixes in seconds, not days. Studios can chase fresh game ideas, instead of wrestling with console specs.
Streamlined game updates
Game update teams push code to cloud gaming data centers in minutes. GeForce Now and Stadia remote servers roll out fresh content behind the scenes. Players join the latest build on smartphones, tablets, or low‑end computers without waiting for downloads.
Luna and xCloud apply patches at the server level. Developers drop hardware limits and cut down patch fragmentation by using GPU servers and remote clusters. This process reduces lag from downloads and boosts gaming accessibility on smart TVs and PCs.
Increased creative freedom
Cloud gaming frees developers from high-end hardware. Remote servers and data centers handle rendering. Modders use sandbox games like Roblox and Minecraft to build virtual worlds in the cloud.
Unity Engine and collaboration tools let teams add custom skins, maps, and scripts. They test builds over a stable internet connection with low latency on container orchestration clusters.
Publishers cut hardware costs and boost gaming accessibility.
Subscription-based gaming services like nvidia geforce now, google stadia, amazon luna, playstation now, and xbox cloud gaming give instant feedback on new levels. Teams deploy updates via cloud infrastructures to any device, from smart TVs to web browsers.
Video-streaming services run on GPU-powered servers across data centers. Container images and continuous integration workflows speed game streaming releases. Developers focus on creative ideas, while amazon luna or xbox game pass ultimate handle heavy lifting.
The Rise of Subscription Models
Subscription plans on top cloud platforms let gamers play new hits for just a few bucks, thanks to powerful GPU servers and 5G speed. Small studios hit the jackpot with steady cash, and fans snack on new games like candy, on any screen.
Affordable gaming options
Cloud gaming cuts hardware costs for players. Game streaming platforms like Amazon Luna and Google Stadia tap remote servers to deliver high‑quality games. Gamers pay a flat fee near $15 a month to reach huge game libraries.
This model borrows from Netflix to fuel gaming on demand.
Xbox Game Pass Ultimate gives access to over 100 games for one price. PlayStation Now adds 700 titles on a similar plan. Low end PCs, phones, and smart TVs all work with these cloud services.
Data centers house Nvidia’s GPUs to cut lag and boost game security.
New revenue streams for developers
Subscription-based gaming sends steady income each month. Smaller studios reach wider audiences through streaming platforms such as Google Stadia, Nvidia GeForce Now, Xbox Game Pass Ultimate, or Amazon Luna.
It removes financial barriers for teams and players. High-end titles share billing with indie hits.
Game streaming also lets developers earn money on add‑ons and microtransactions. They share sale cuts from skins, maps, and expansion passes. Data centers in big tech hubs keep latency low, so players stay engaged.
This model boosts cash flow for studios of all sizes.
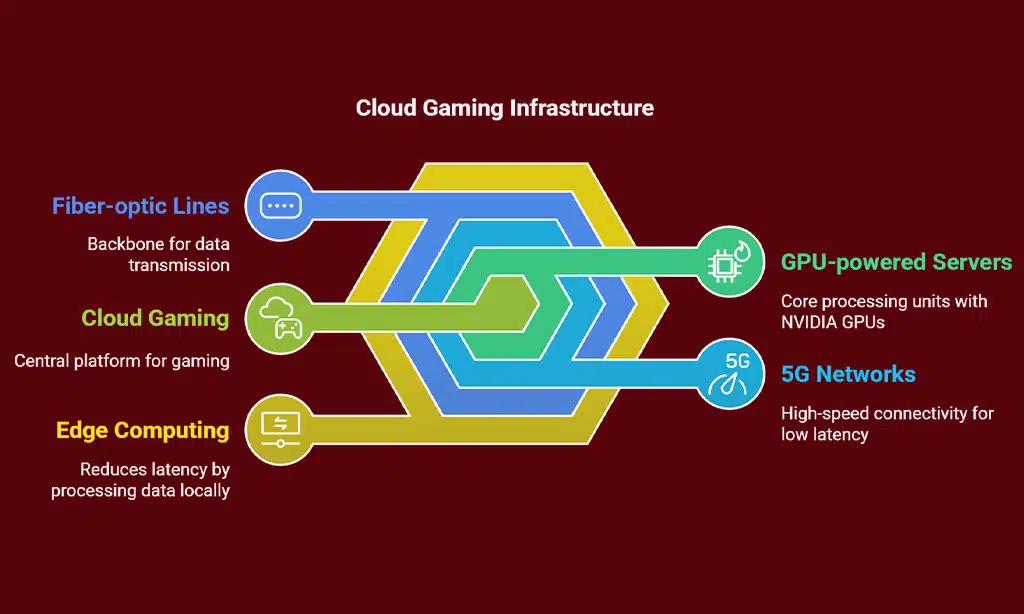
Infrastructure Behind Cloud Gaming
Server hubs behind services like NVIDIA GeForce Now and Amazon Luna stream top titles in real time. High-speed mobile links and fiber pipes cut lag, so you can hop in, not hold your breath.
Role of 5G networks
High-speed 5G links slash lag, so cloud gaming feels smooth. They push speeds above 1 Gbps, like fiber-optic connections. Edge computing shifts load to nearby nodes, cutting round trips.
The global data network runs over 30 data centers in 130 nations to keep pings low.
Network infrastructure relies on this rollout. Gaming hits no choke points with latency under 20 ms. Fiber-optic trunks back the wireless towers. This mix of 5G, fiber-optic lines, edge compute, and cloud technology lets gamers stream AAA titles on any device.
Integration of GPU-powered servers
Cloud gaming relies on cloud technology in powerful server farms packed with NVIDIA L40 graphics processors. Operators deploy these cards to handle ray tracing through 142 RT Cores and 48 GB memory.
Each compute card sits in off-site hosts near major network hubs to cut lag. This setup fuels game streaming and video streaming, boosts gaming accessibility and delivers low latency.
Gamers need just 5 Mbps to stream high-quality games on PCs, smartphones, smart TVs or Apple Vision Pro. Services like NVIDIA GeForce Now and Xbox Cloud Gaming link players to these remote cores without bulky hardware.
The result feels as smooth as silk on subscription-based gaming or pay-per-play plans. I once told a buddy, “That dynamic ray tracing glow blew my mind,” and he nodded in awe.
The Future of Cloud Gaming
New data centers will beam games to your smart TV with low lag, thanks to fast 5G waves and beefy graphics cards. AI sidekicks will tweak your quests in real time while VR goggles sweep you into wild worlds, and you can jump in on any gadget you like.
Advancements in virtual reality and AI integration
Cloud gaming extends into VR environments, letting players slip into cyberpunk scenes on a headset. AI tools adapt scenarios in real time, so each run feels fresh and alive. Data centers host the code, while remote servers stream the view with low latency and high-quality frames.
Roblox and Minecraft follow suit, letting creators build live experiences with voice chat and motion tracking.
5G networks cut lag and boost frame rates for VR kits, giving crisp visuals on Oculus Quest or Valve Index. NVIDIA GeForce Now and Google Stadia fine‑tune AI routines that scale graphics on demand, thanks to remote servers in major data centers.
Amazon Luna adds voice controls, allowing users to shift scenes with a single word. Players stay immersed in worlds that react to each move.
Expanding accessibility across devices
Using cloud gaming services, players log in on a laptop, a phone, or a smart TV. 5G networks and fiber lines deliver low latency, so you feel every jump and shot in real time. Data centers with GPU-driven servers push graphics to screens in seconds.
I once joined Fortnite’s Metallica: Fuel. Fire. Fury concert on my living room set, then switched to my phone during a coffee break without missing a beat.
Subscription-based services drop the need for high-end hardware. Remote servers host titles in vast libraries, and you hit play like you tune into a show. ZenOS hosted a VR watch party for the 2023 League of Legends Worlds, and players joined on budget headsets or PCs.
Now gaming on demand spans solid-state drives to wireless handsets, making discs look like fossils.
Takeaways
Cloud gaming shakes up how we play. Gamers stream heavy titles from remote servers on phones, tablets, even smart TVs. Developers dream bigger when they skip hardware limits at data centers.
A 5G link and GPU cluster cut lag to almost zero. Subscription plans from big-name streaming services offer full libraries for a flat fee. Players and makers both stand to win in this new game era.
FAQs
1. What is cloud gaming and how does it work in 2025?
Cloud gaming uses remote servers in huge data centers to run games. It does game streaming, like video streaming, over a stable internet connection. Your device just shows the video, no need for dvds or gaming consoles. Services like google stadia, xbox cloud gaming, playstation now, and a library service lead the shift.
2. How does cloud gaming improve gaming accessibility?
It cuts out the need for high-end hardware. You can jump into Cyberpunk 2077 on your laptop, phone, or smart tvs. It feels like a live show in your home if you have a stable internet connection. It opens the gaming industry to more players.
3. Do I need a powerful console or high-end hardware?
Nope, not really. All heavy work runs on a GPU-powered service in the cloud. Your device just streams the video, like watching a movie on netflix. A good high-speed internet connection and a simple controller do the trick.
4. What role do data centers and remote servers play?
They form the core gaming infrastructure. They host game engines, manage low latency, and push out high-performance streaming. Think of them as magic puppet masters, sending your moves to the game, and beaming back high-quality games in real time.
5. How do subscription-based gaming services work?
You pay a subscription fee to access a game library. You can try xbox game pass ultimate or other subscription services, and play gaming on demand. No need to buy dvds or single titles. You just pick and play.
6. What does the future of the video game industry look like with cloud tech?
It feels boundless, like a rocket to new worlds. Game publishers will speed up video game development, roll out updates on the fly. We may see cross-platform multiplayer, augmented reality, even whatsapp-style social hubs. The future of gaming on the web is full of immersion and surprises.