In a world where digital interactions are an integral part of daily life, securing online accounts has become more critical than ever. Whether for personal accounts or enterprise systems, ensuring that login systems are both secure and user-friendly is paramount.
Cybercrime, data breaches, and identity theft are all growing concerns, and securing login systems is the first line of defense against these threats.
To counteract these risks, best authentication methods for secure login systems are continuously evolving. With passwords becoming increasingly vulnerable and insufficient to protect sensitive information, it’s essential to adopt more advanced techniques. This article dives deep into the best authentication methods for secure login systems, offering insights into each approach, discussing their strengths and limitations, and providing practical guidance on implementation.
Let’s explore the top authentication methods that can significantly bolster your system’s security while ensuring ease of use for the user.
What Are Authentication Methods and Why Are They Important?
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system to ensure that access to a digital resource is only granted to legitimate users. It’s an essential security feature that protects user data from unauthorized access, helping to secure everything from social media accounts to enterprise systems.
In the digital age, authentication has evolved far beyond simple passwords. More sophisticated methods, such as biometric scans, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and behavioral analysis, are becoming increasingly common. These methods provide added layers of security, making it exponentially harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access.
Why Strong Authentication Matters:
- Protects Personal Information: Ensures that sensitive data such as passwords, banking details, and private conversations remain protected.
- Builds User Trust: Users feel more confident when they know that the systems they interact with prioritize their security.
- Meets Compliance Standards: Certain industries (finance, healthcare, etc.) require robust authentication to comply with data protection laws.
- Mitigates Cyber Threats: Strong authentication practices reduce the chances of successful phishing, brute-force, and credential-stuffing attacks.
Now, let’s dive into the 10 best authentication methods for secure login systems.
The 10 Best Authentication Methods for Secure Login Systems
Authentication methods come in all shapes and sizes, offering various levels of security, cost, and ease of use. Below, we’ll explore the best authentication methods for secure login systems, breaking down the strengths, weaknesses, and real-world use cases for each.
1. Password-Based Authentication
Password-based authentication has long been the most common method for securing online accounts. Users create a password that is stored securely in the system, which is then used to verify their identity. While simple, it’s increasingly vulnerable to attacks such as brute-force and phishing.
Pros:
- Easy to implement and widely recognized
- Low cost
- Universally accepted and understood by users
Cons:
- Weak passwords are easily guessed or cracked
- Users tend to reuse passwords across sites, which increases risk
- Vulnerable to brute-force, dictionary, and phishing attacks
Best Practices:
- Encourage the use of complex passwords with at least 12 characters, incorporating letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Implement password expiration policies to periodically change passwords.
- Utilize password managers to generate and store strong, unique passwords.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Easy to set up | Vulnerable to attacks | Low-security personal accounts |
| Universally understood | Often reused or weak | Non-sensitive applications |
| Low cost and simple | Potential for password fatigue | Online shopping and media services |
2. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a crucial extra layer of protection by requiring two forms of identification: something the user knows (like a password) and something the user has (like a phone or security token). This can drastically reduce the risk of account compromise.
Pros:
- Increases account security significantly
- Commonly supported by major platforms and services
- Flexible – supports SMS, email, and app-based authentication
Cons:
- Relies on a secondary device (e.g., smartphone)
- SMS-based 2FA can be intercepted by hackers
- Users may find it inconvenient if they lack access to the secondary device
Best Practices:
- Use app-based 2FA like Google Authenticator or Authy over SMS, which is more secure.
- Educate users on how to use 2FA for sensitive services (e.g., banking, email accounts).
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Adds an extra security layer | Requires secondary device | Financial services, email |
| Supported by most online platforms | Can be inconvenient | Corporate applications |
| Reduces phishing risk | Vulnerable if device is lost | High-value user accounts |
3. Biometric Authentication (Fingerprint, Facial Recognition)
Biometric authentication uses unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or even voice patterns to verify a user’s identity. It offers a high level of security and convenience.
Pros:
- Provides an almost foolproof way to verify identity
- Faster and more convenient than typing passwords
- Difficult to replicate or bypass
Cons:
- Requires specialized hardware (e.g., fingerprint sensors, cameras)
- Potential privacy concerns over biometric data storage
- May not be universally available on all devices
Best Practices:
- Use biometric authentication in combination with other methods, like PIN codes or passwords, for added security.
- Ensure biometric data is encrypted and stored securely to prevent misuse.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Highly secure | Requires specialized hardware | Personal devices (smartphones) |
| Fast and convenient | Privacy concerns | High-security applications |
| Difficult to replicate | Accessibility issues | Financial services and banking |
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to present multiple forms of verification: something they know (password), something they have (a smartphone), and something they are (biometric information). MFA is one of the most secure authentication methods, making it a preferred choice for businesses.
Pros:
- Multi-layered security minimizes the risk of unauthorized access
- Can combine several methods (e.g., password, fingerprint, OTP)
- Flexible and highly customizable for different use cases
Cons:
- Can be cumbersome for users if not implemented correctly
- Requires more resources and infrastructure to maintain
- Increased friction for users in daily use
Best Practices:
- Use MFA for high-value accounts (e.g., admin access, financial accounts).
- Ensure that users have clear instructions for setup and use to reduce frustration.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Extremely secure | Can be complex for users | Corporate systems, banking |
| Flexible – combines multiple factors | Higher implementation cost | Government services |
| Great for high-risk transactions | Requires more infrastructure | High-value user accounts |
5. Smart Card Authentication
Smart card authentication uses a physical card embedded with a chip that holds encrypted data to authenticate users. This is particularly common in high-security environments, such as corporate offices and government agencies.
Pros:
- Hard to replicate or counterfeit
- Offers a very high level of security
- Often used in conjunction with PIN codes for multi-layered security
Cons:
- Requires physical card management (can be lost or stolen)
- Can be cumbersome and less convenient for everyday use
- Expensive to implement
Best Practices:
- Pair smart card authentication with biometric authentication or a PIN for added security.
- Implement policies to quickly revoke access in case of lost or stolen cards.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| High security level | Expensive to implement | Government, military, enterprise |
| Hard to replicate | Less convenient for users | Corporate access control |
| Prevents unauthorized access | Physical card management needed | High-security environments |
6. Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single sign-on (SSO) allows users to authenticate once and access multiple applications or services without needing to log in again. It’s a convenient method widely used in enterprise systems, where users need to access multiple systems throughout the day.
Pros:
- Simplifies user experience by reducing the need to remember multiple passwords
- Reduces the chances of password fatigue or reuse
- Centralized management for admins
Cons:
- If compromised, it grants access to multiple systems
- Relies heavily on centralized authentication services, which can become a single point of failure
- Complex to set up and maintain
Best Practices:
- Combine SSO with strong authentication methods like MFA to mitigate the risk of compromise.
- Ensure a robust password policy for SSO credentials.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Simplifies user experience | Single point of failure | Large enterprise systems |
| Reduces password fatigue | Risk if credentials are compromised | SaaS applications |
| Centralized management | Complex to set up | Internal systems |
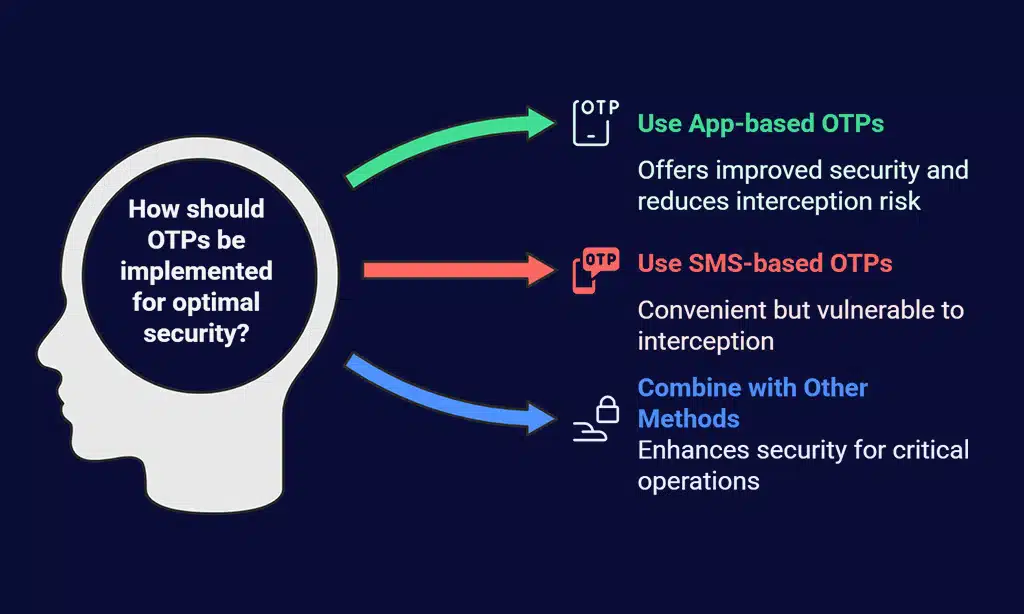
7. One-Time Passwords (OTP)
One-time passwords (OTPs) are temporary codes that can be used for a single session or transaction. OTPs are often delivered via SMS, email, or generated by an authentication app. They add a high level of security as the codes expire after use.
Pros:
- Temporary nature makes them very secure
- Difficult for attackers to reuse or intercept
- Often used for high-risk transactions
Cons:
- Can be inconvenient if delivery methods are slow (e.g., SMS)
- Vulnerable to interception if sent via insecure channels
Best Practices:
- Use OTPs in conjunction with other forms of authentication for critical operations like financial transactions.
- Encourage users to use app-based OTPs rather than SMS for improved security.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Secure and temporary | Delivery may be slow | Financial transactions |
| Difficult to intercept | Vulnerable to interception | Online banking and payments |
| Reduces replay attack risk | Requires access to delivery channel | Sensitive data access |
8. Behavioral Biometrics Authentication
Behavioral biometrics authentication focuses on identifying users based on patterns in their behavior, such as typing speed, mouse movements, and even how they interact with the device. This method is often used in conjunction with other authentication techniques to add an extra layer of security, especially in high-risk environments.
Pros:
- Continuous and passive authentication, ensuring security throughout the session
- Difficult for attackers to mimic behavioral traits
- Non-intrusive for users; no extra steps required
Cons:
- Requires sophisticated algorithms and data analysis tools
- Might have accuracy issues, especially with new users or unusual behaviors
- Privacy concerns regarding the collection and analysis of personal data
Best Practices:
- Use behavioral biometrics alongside other methods like MFA to enhance security without significantly affecting user experience.
- Regularly update and refine the algorithms to ensure accurate detection of abnormal behavior.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Continuous, seamless security | Requires advanced technology | Banking apps, enterprise systems |
| Passive and non-intrusive | Accuracy may vary with user patterns | Fraud detection systems |
| Difficult to replicate | Privacy concerns with behavior data | High-value transaction systems |
9. CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart)
CAPTCHA is a challenge-response test designed to distinguish human users from bots. It’s a commonly used method to prevent automated attacks like brute force and credential stuffing, often appearing during registration or login processes.
Pros:
- Simple and effective for preventing bot-based attacks
- Free and easy to implement on most platforms
- Adds minimal friction for genuine users
Cons:
- Can cause inconvenience to users if overly complex
- May not be fully effective against advanced bots powered by AI
- Can be a barrier for users with disabilities (e.g., vision impairments)
Best Practices:
- Use CAPTCHA for registration and login forms, but avoid using it excessively in the user experience to minimize friction.
- Implement reCAPTCHA v3, which is less intrusive and uses machine learning to detect suspicious behavior automatically.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Prevents bot-based attacks | Can be difficult for users | Login and registration forms |
| Simple and low cost | May frustrate legitimate users | Preventing automated attacks |
| Easy to integrate | Not effective against AI-driven bots | Websites with high user traffic |
10. Hardware Tokens
Hardware tokens are physical devices used to authenticate users by generating a one-time passcode or acting as a USB key. These tokens are often used in high-security environments and are typically employed for secure access to networks, servers, and critical systems.
Pros:
- Highly secure because physical tokens are difficult to replicate
- Resistant to phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks
- Can be used in conjunction with other authentication methods like PINs
Cons:
- Can be lost or stolen, which could result in access being compromised
- Requires users to carry an additional physical device
- Expensive and difficult to manage at scale for large organizations
Best Practices:
- Implement hardware tokens for access to highly sensitive accounts or systems.
- Use backup methods, like a recovery PIN or biometric authentication, in case the hardware token is lost or stolen.
| Pro | Con | Best Use Case |
| Extremely secure | Risk of losing the device | Corporate networks, admin access |
| Difficult to duplicate | Requires additional hardware | Financial institutions |
| Resistant to phishing attacks | Management of tokens can be complex | High-security government applications |
Wrap Up
The best authentication methods for secure login systems vary based on the needs of the user or organization. From the simplicity of password-based systems to the advanced capabilities of biometric authentication, each method has its strengths and weaknesses.
The key is to select the appropriate level of security based on the sensitivity of the data being protected and the ease of use for the end users.
As the digital landscape evolves and cyber threats become more sophisticated, authentication methods will continue to adapt. Combining multiple authentication techniques, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and behavioral biometrics, can provide layered security that minimizes risks. Ultimately, the best approach is one that balances security with user convenience, ensuring that systems remain both protected and user-friendly.
For organizations looking to strengthen their security posture, adopting the best authentication methods for secure login systems—in combination with regular security audits, user education, and the latest encryption protocols—will go a long way toward mitigating the risks of unauthorized access and cybercrime.
Final Recommendations:
- Always assess the risk level associated with the type of system or data you’re protecting.
- Consider a layered approach, combining multiple authentication methods to provide defense in depth.
- Ensure that users are educated on the importance of strong passwords and security practices.
By implementing the right authentication methods and staying current with trends and technologies, organizations and users can build a robust defense against potential security breaches.