Urban freight distribution is a critical component of modern city logistics, ensuring the seamless movement of goods to businesses and consumers. However, rapid urbanization, congestion, and environmental concerns have posed significant challenges for freight operations in U.S. cities. In response, innovative solutions leveraging technology, data analytics, and sustainable practices are transforming the way goods are transported and delivered.
From electric delivery vehicles to smart logistics hubs, cities are adopting groundbreaking strategies to enhance efficiency, reduce carbon footprints, and meet the demands of e-commerce-driven logistics. The adoption of these technologies is not only improving urban logistics but also contributing to smarter cities that are more adaptable to future mobility demands.
This article explores the top 10 Urban Freight Distribution Innovations Transforming U.S. Cities, highlighting their impact, real-world applications, and future potential in creating a more sustainable and efficient urban supply chain.
The Evolving Landscape of Urban Freight Distribution
The increasing demand for faster deliveries and growing concerns about emissions have led to a significant shift in urban freight distribution strategies.
Traditional delivery methods, often reliant on large trucks and centralized warehouses, are being replaced by more flexible, technology-driven solutions that optimize last-mile deliveries and reduce congestion.
Below, we examine the key factors driving urban freight distribution innovations transforming U.S. cities:
Key Challenges in Urban Freight Logistics:
- Traffic Congestion: Increased urban density has led to severe bottlenecks, affecting delivery speed and efficiency. Congested streets cause delays, making it difficult for businesses to maintain reliable delivery schedules.
- Environmental Concerns: Carbon emissions from freight transport contribute to air pollution and climate change. Many cities are imposing stricter emissions regulations, pushing companies to adopt greener alternatives.
- E-commerce Boom: The rise in online shopping has escalated the demand for last-mile delivery solutions. With same-day and one-hour delivery services becoming the norm, urban freight systems must keep up with growing expectations.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Aging road networks and lack of dedicated freight lanes hinder smooth operations. Many cities were not designed for high-volume freight movement, leading to inefficiencies in logistics.
Emerging Trends Shaping Urban Freight Distribution:
- Electrification of Delivery Vehicles: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels for last-mile logistics through widespread EV adoption.
- Micro-Fulfillment Centers: Establishing small, urban warehouses closer to consumers to reduce delivery times and improve logistics efficiency.
- AI & IoT in Logistics: Enhancing real-time tracking, predictive route optimization, and data-driven decision-making to improve freight movement.
- Autonomous Delivery Solutions: Using drones, robots, and self-driving vehicles for efficient, contactless deliveries.
Top 10 Urban Freight Distribution Innovations Transforming U.S. Cities
As urban populations continue to grow and consumer expectations for rapid delivery increase, cities across the U.S. are rethinking freight distribution to improve efficiency and sustainability. Traditional urban freight systems, which rely on diesel-powered trucks and centralized warehouses, contribute significantly to congestion and air pollution.
However, emerging technologies and innovative logistics solutions are revolutionizing last-mile delivery, warehouse management, and transportation networks. By leveraging automation, electrification, and data-driven strategies, urban freight operations are becoming smarter and more adaptable to the demands of modern commerce.
Below, we explore the top 10 innovations transforming urban freight distribution innovations transforming U.S. cities.
1. Electrification of Urban Delivery Fleets
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) in urban freight distribution is a game-changer for reducing emissions and improving operational efficiency. Companies such as Amazon, UPS, and FedEx are leading the charge by integrating electric vans and trucks into their fleets.
Cities like Los Angeles and New York are also supporting electrification by installing public charging stations specifically for commercial EVs.
Key Innovations:
- Adoption of electric delivery vans like Rivian and BrightDrop EV600.
- Development of charging infrastructure in urban centers to support fleet electrification.
- Government incentives and subsidies promoting EV adoption in freight logistics.
Impact:
- Reduction in carbon emissions and fuel costs, contributing to cleaner urban environments.
- Improved compliance with city emissions regulations and sustainability goals.
- Enhanced operational efficiency through lower maintenance costs and longer vehicle lifespans.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Delivery Trucks | Electric Delivery Vehicles |
| Emissions | High CO2 Output | Zero Emissions |
| Fuel Cost | High (Gasoline/Diesel) | Lower (Electric Charging) |
| Maintenance | Frequent Repairs | Lower Maintenance |
| Operating Cost | Expensive Over Time | Cost-Effective in Long Run |
2. Smart Traffic Management for Freight Optimization
Cities are deploying AI-driven traffic management systems to improve freight movement, reduce congestion, and optimize delivery routes in real time.
Smart traffic systems analyze vehicle movements, road congestion levels, and delivery schedules to provide the most efficient routing for freight vehicles.
Key Innovations:
- AI-powered traffic signal coordination that prioritizes freight vehicles at intersections.
- Data-driven predictive analytics to identify traffic congestion hotspots and reroute trucks accordingly.
- Smart intersections equipped with vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) technology to improve communication between delivery fleets and city traffic systems.
Impact:
- Faster delivery times and improved supply chain efficiency.
- Reduced idling time, leading to lower fuel consumption and emissions.
- Enhanced safety for freight transport in urban areas by minimizing traffic conflicts.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Traffic Systems | AI-Optimized Freight Traffic |
| Route Planning | Static Schedules | Real-Time Adjustments |
| Traffic Bottlenecks | Frequent Delays | Predictive Avoidance |
| Efficiency | Lower Optimization | AI-Driven Optimization |
| Emissions Reduction | Limited | Significant |
3. Micro-Fulfillment Centers for Last-Mile Delivery
Retailers and logistics companies are establishing micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) in urban areas to shorten delivery times and improve efficiency.
MFCs allow companies to store inventory closer to customers, reducing reliance on large, distant warehouses and improving same-day delivery capabilities.
Key Innovations:
- Automated warehouses located within city limits, reducing transit times.
- AI-driven inventory management to predict demand and prevent overstocking or shortages.
- Integration with e-commerce platforms to process orders faster and more efficiently.
Impact:
- Faster delivery times with same-day or next-hour fulfillment services.
- Reduced congestion as deliveries originate closer to customers.
- Cost savings in transportation, storage, and last-mile delivery operations.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Warehousing | Micro-Fulfillment Centers |
| Location | Outside City Limits | Inside Urban Areas |
| Delivery Speed | 2-3 Days | Same-Day or Instant |
| Storage Costs | High | Lower Due to Smaller Space |
| Operational Efficiency | Moderate | Optimized for Urban Demand |
4. Cargo Bikes and Pedestrian Delivery Solutions
With increasing congestion in major cities, cargo bikes and pedestrian delivery services are emerging as viable last-mile solutions. These eco-friendly alternatives provide faster delivery in densely populated urban areas while reducing carbon emissions.
Companies like DHL, UPS, and local courier services have started integrating electric cargo bikes and walking couriers into their logistics networks.
Key Innovations:
- Expansion of bike courier networks for last-mile logistics.
- Integration of electric-assisted cargo bikes for heavier loads.
- Designation of pedestrian-only delivery zones for optimized package movement.
Impact:
- Lower carbon footprint and reduced traffic congestion.
- Faster delivery times in high-density areas where traditional vehicles face delays.
- Improved accessibility for underserved urban locations and better utilization of bike lanes.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Vans | Cargo Bikes & Pedestrian Couriers |
| Speed in Congested Areas | Slow | Faster |
| Emissions | High | Zero |
| Delivery Costs | High | Low |
| Accessibility | Limited in Pedestrian Areas | High |
5. Autonomous Delivery Robots and Drones
Autonomous delivery robots and drones are revolutionizing last-mile logistics by enabling fast, contactless deliveries. Companies like Starship Technologies and Amazon Prime Air have been deploying small robots and aerial drones to make same-day deliveries more efficient.
Key Innovations:
- Deployment of sidewalk robots capable of delivering small parcels autonomously.
- FAA-approved drone delivery services for lightweight goods.
- AI-powered navigation systems to ensure safe urban deliveries.
Impact:
- Cost reduction in labor-intensive last-mile logistics.
- Faster and more convenient delivery solutions for consumers.
- Decreased dependency on traditional vehicle-based deliveries, reducing urban congestion.
Comparison Table:
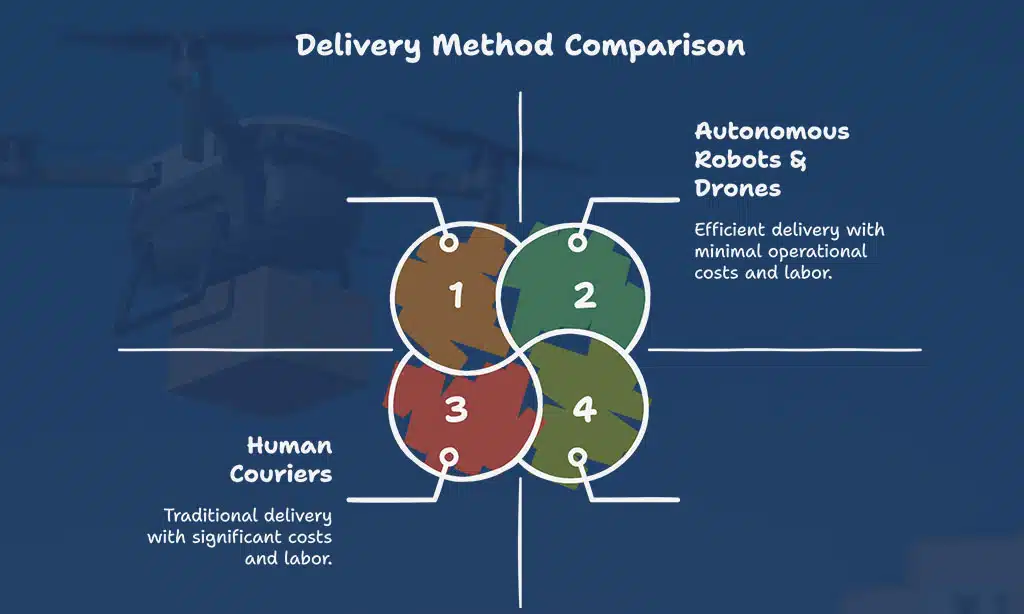
| Feature | Human Couriers | Autonomous Robots & Drones |
| Delivery Speed | Moderate | Faster for Small Packages |
| Cost | High | Lower Over Time |
| Labor Requirements | High | None |
| Traffic Congestion | Adds to Road Traffic | Reduces Road Usage |
6. Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing urban freight distribution by enhancing supply chain transparency, security, and operational efficiency. As urban logistics become more complex, the need for verifiable and immutable data has increased, making blockchain an ideal solution for tracking shipments, reducing fraud, and automating transactions.
This innovation ensures that all transactions and deliveries are traceable, minimizing errors and improving accountability. Major logistics companies such as FedEx, Maersk, and UPS are implementing blockchain-based tracking systems to streamline operations and boost customer confidence.
Additionally, governments are exploring blockchain integration for regulatory compliance and emissions tracking, further reinforcing its role in the future of sustainable urban freight logistics.
Key Innovations:
- Distributed ledger systems for tracking shipments in real-time.
- Smart contracts to automate payment processing and reduce fraud.
- Integration with IoT sensors to improve transparency.
Impact:
- Increased trust between suppliers, carriers, and customers.
- Enhanced security and fraud prevention.
- Improved efficiency in last-mile logistics.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Supply Chains | Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chains |
| Transparency | Limited visibility | End-to-end tracking |
| Security | Prone to fraud | Immutable records |
| Payment Processing | Manual and delayed | Automated via smart contracts |
7. Underground and Overhead Freight Transport Systems
To reduce surface-level congestion, cities are exploring underground tunnels and aerial drone highways for freight movement. These alternative freight corridors allow for efficient and uninterrupted deliveries, bypassing heavily congested urban roads.
Major cities like Los Angeles and Chicago are investing in underground tunnel prototypes, while companies like Amazon and UPS are testing aerial drone highways to improve last-mile logistics.
By shifting a portion of freight traffic below and above city streets, urban areas can achieve faster deliveries, reduced emissions, and improved transportation efficiency.
Key Innovations:
- Hyperloop-style underground freight transport systems.
- Drone highways designed for urban package delivery.
- Pneumatic tube systems for lightweight goods transportation.
Impact:
- Reduced urban congestion by shifting freight movement underground and above ground.
- Faster, more efficient deliveries with minimal road traffic interference.
- Lower environmental footprint compared to traditional delivery methods.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Road Freight | Underground & Overhead Freight |
| Traffic Impact | High Congestion | Minimal Surface Disruption |
| Delivery Speed | Slower in Cities | Faster, Direct Routes |
| Infrastructure Cost | Lower | High Initial Investment |
8. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics for Logistics
AI-driven predictive analytics is transforming urban freight logistics by providing real-time insights into demand forecasting, route optimization, and fleet management. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI helps logistics companies predict peak delivery times, optimize resource allocation, and minimize delays.
This technology is particularly valuable in cities where traffic congestion and unpredictable demand fluctuations create challenges for timely deliveries.
Major logistics providers like FedEx, UPS, and Amazon are investing heavily in AI-powered logistics solutions to enhance last-mile delivery efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Key Innovations:
- Machine learning algorithms for demand forecasting.
- Real-time traffic and weather data integration.
- AI-based fleet management and route optimization.
Impact:
- Reduced delivery delays and congestion-related inefficiencies.
- Improved supply chain resilience with proactive decision-making.
- Enhanced cost savings and fuel efficiency for logistics providers.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Logistics | AI-Powered Logistics |
| Demand Forecasting | Based on Historical Data | Real-Time Predictive Modeling |
| Route Planning | Manual Adjustments | AI-Optimized Routes |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High |
9. Shared Urban Distribution Networks
Collaborative freight networks are transforming urban logistics by allowing multiple businesses to share delivery infrastructure, significantly reducing costs, congestion, and environmental impact.
These networks involve shared urban distribution hubs, joint-use delivery vehicles, and cooperative warehousing, streamlining logistics operations for companies of all sizes.
Cities like New York, London, and Paris are actively encouraging such initiatives to optimize last-mile logistics while reducing redundant trips.
By integrating data-sharing platforms and advanced route optimization, businesses can achieve seamless coordination, improving both delivery efficiency and sustainability.
Key Innovations:
- Urban freight consolidation centers to combine shipments.
- Multi-business last-mile delivery hubs.
- Shared delivery vehicle programs to optimize load efficiency.
Impact:
- Lower logistics costs through shared infrastructure.
- Reduced traffic congestion with fewer vehicles on the road.
- Enhanced sustainability by minimizing redundant deliveries.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Individual Logistics Operations | Shared Distribution Networks |
| Delivery Costs | Higher | Lower Through Shared Resources |
| Traffic Congestion | Higher | Reduced with Fewer Vehicles |
| Environmental Impact | Higher Emissions | Lower Carbon Footprint |
10. 3D Printing for On-Demand Manufacturing
3D printing is revolutionizing urban freight logistics by enabling localized manufacturing, reducing the reliance on long-distance transportation of goods. By leveraging additive manufacturing, companies can produce parts and products on demand, minimizing the need for large-scale warehouses and extensive supply chains.
This shift is particularly beneficial for industries such as healthcare, automotive, and retail, where rapid production and customization are crucial.
Cities like New York and San Francisco are seeing an increase in urban micro-factories that use 3D printing to produce everything from medical implants to consumer electronics, reducing freight volume and ensuring just-in-time manufacturing.
The adoption of this technology is streamlining logistics, cutting costs, and significantly lowering environmental impact by eliminating excess packaging and transportation emissions.
Key Innovations:
- Localized 3D printing hubs for rapid production.
- Just-in-time manufacturing models reducing warehousing needs.
- Integration with urban micro-fulfillment centers.
Impact:
- Lower transportation and storage costs.
- Faster product availability and reduced supply chain dependencies.
- Reduced environmental impact by minimizing long-distance freight movement.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Traditional Manufacturing | 3D Printing for Urban Logistics |
| Production Speed | Longer Lead Times | Faster, On-Demand |
| Warehousing Needs | Large Storage Facilities | Minimal Storage Required |
| Supply Chain Dependency | High | Lower Due to Localized Production |
Takeaways
Urban freight distribution is undergoing a major transformation, driven by technology, sustainability initiatives, and the need for greater efficiency. The innovations outlined above demonstrate how cities and logistics providers are rethinking traditional supply chain models to create smarter, greener, and more resilient urban freight systems.
As urban populations grow and consumer demands evolve, continued investment in smart logistics, electrification, and autonomous delivery solutions will be crucial.
By embracing these cutting-edge strategies, U.S. cities can achieve a more seamless, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly freight distribution network that benefits businesses, residents, and the planet alike.
Stay tuned as we explore the next wave of freight innovations shaping the future of city logistics.