As the world grapples with climate change, more people are turning to sustainable living to reduce their environmental footprint. One of the most compelling solutions to this crisis is the concept of net-zero homes.
These homes not only generate enough energy to meet their own needs but also promote sustainability through design, renewable energy sources, and efficient building practices.
In this article, we explore 8 inspiring examples of net-zero homes across the globe, showcasing innovations in energy efficiency, sustainable design, and eco-friendly construction.
What are Net-Zero Homes?
Net-zero homes are buildings designed to produce as much energy as they consume on an annual basis. These homes typically incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems, and combine them with energy-efficient construction techniques to minimize energy consumption.
In essence, a net-zero home produces a balance of zero net energy—meaning the energy it generates equals the energy it uses. This makes net-zero homes an essential solution for reducing carbon footprints, lowering utility costs, and combating climate change.
The Growing Importance of Sustainability in Housing
In a rapidly urbanizing world, housing plays a significant role in global energy consumption. The construction and operation of residential buildings account for a substantial portion of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), buildings contribute to nearly 40% of global energy-related CO2 emissions. As a result, sustainable housing solutions, like net-zero homes, have become pivotal in mitigating the environmental impact of residential living. They offer an innovative way to reduce emissions, conserve natural resources, and create healthier living spaces.
Why Net-Zero Homes are the Future of Residential Living
The future of housing is undoubtedly tied to sustainability. With advancements in technology, building materials, and renewable energy sources, net-zero homes are becoming more affordable and accessible.
As governments and organizations worldwide implement stricter environmental policies and regulations, the demand for net-zero homes is expected to increase. Furthermore, these homes offer long-term financial benefits through lower energy bills, making them an attractive option for homeowners and investors alike.
Key Features of Net-Zero Homes
The backbone of a net-zero home is its energy-efficient design. These homes incorporate various features that minimize energy consumption, including high-quality insulation, energy-efficient windows, and smart thermostats.
Additionally, net-zero homes are often powered by renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind turbines, or even small-scale hydropower systems. These systems enable the home to produce more energy than it consumes, ensuring that the overall energy balance remains at zero.
Sustainable Materials and Design Practices
In addition to energy efficiency, net-zero homes are built using sustainable materials that minimize environmental impact. These materials are often locally sourced, recycled, or environmentally friendly alternatives.
For example, bamboo, reclaimed wood, and recycled metal are commonly used in the construction of net-zero homes. Design practices also prioritize the use of passive solar heating, natural ventilation, and other eco-friendly solutions that reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling.
Smart Technology Integration for Energy Management
Net-zero homes often feature smart technology that helps optimize energy consumption. These systems monitor energy use in real-time, adjusting heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy and time of day.
For instance, smart thermostats like Nest or Ecobee can be programmed to adjust the temperature when you’re away or sleeping, ensuring that energy is used only when necessary. This level of automation helps homeowners maximize their energy savings while ensuring comfort and convenience.
Waste Reduction and Water Conservation
Waste reduction and water conservation are also key components of net-zero homes. Many of these homes include rainwater harvesting systems, greywater recycling, and composting toilets to reduce water usage.
By incorporating these sustainable practices, net-zero homes help homeowners lower their water bills and minimize their environmental impact. Additionally, energy-efficient appliances and fixtures like low-flow showerheads and Energy Star-rated dishwashers help reduce both water and electricity consumption.
8 Inspiring Examples of Net-Zero Homes Across the Globe
As the demand for sustainability in housing continues to grow, the vision of net-zero homes—structures that produce as much energy as they consume—is becoming a reality. Across the globe, architects and homeowners are embracing renewable energy sources, efficient designs, and innovative technologies to reduce environmental impacts and enhance the quality of life.
These homes are not only energy-efficient but are also redefining the way we think about sustainable living.
Let’s explore eight inspiring examples of net-zero homes that demonstrate the potential for green architecture to transform residential living worldwide.
Example 1: The Solar-Powered Home in California
California, known for its abundant sunshine, is an ideal location for net-zero homes. The Solar-Powered Home in California takes full advantage of the state’s sunny climate to generate its energy needs. This home uses a rooftop solar array that produces more energy than the home consumes, allowing the owners to sell surplus power back to the grid.
Design Highlights and Energy Efficiency
The home’s design features highly efficient insulation and triple-pane windows that minimize energy loss. It also includes a geothermal heating and cooling system, which taps into the Earth’s natural temperature for energy-efficient temperature control. These elements work together to make the home as energy-efficient as possible, drastically reducing its reliance on conventional energy sources.
Impact on Local Community and Environment
The Solar-Powered Home serves as an example of how sustainable living can benefit not only homeowners but also local communities. By generating surplus energy, the home contributes to the grid and reduces the demand for fossil fuel-based power. Moreover, its environmentally friendly design sets a precedent for other homes in the area, encouraging more homeowners to adopt solar power and energy-efficient solutions.
Example 2: The Off-Grid Home in New Zealand
The Off-Grid Home in New Zealand is a true testament to the power of sustainable materials. Constructed with locally sourced timber, recycled steel, and natural stone, this home minimizes its environmental footprint from the start. The home’s design also includes large windows and skylights to maximize natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
Innovative Renewable Energy Solutions
This off-grid home is powered by a combination of solar panels, a wind turbine, and a backup generator. The energy generated is stored in batteries for use during cloudy days or periods of low wind. By utilizing these renewable energy sources, the home remains completely independent from the grid, providing the owners with true energy autonomy.
Lessons Learned and Benefits
One of the key lessons from the Off-Grid Home is the importance of resilience in remote locations. While the home is fully self-sustaining, the integration of backup power systems ensures that the residents never face energy shortages. Additionally, the home’s ability to function entirely off the grid serves as a model for other remote or rural areas looking to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels.
Example 3: The Green Rooftop Home in Berlin
In Berlin, the Green Rooftop Home offers a unique approach to energy efficiency with its green roofs. These roofs are covered with plants that help insulate the home by providing shade and reducing heat absorption. During the summer, the green roofs also help cool the building naturally, reducing the need for air conditioning.
Integration with Urban Spaces
This home is integrated seamlessly into Berlin’s urban environment. The green rooftops provide an aesthetic appeal while promoting biodiversity in the city. These eco-friendly features not only benefit the homeowners but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the urban landscape.
Performance Over Time
Over the years, the Green Rooftop Home has demonstrated significant energy savings, particularly in the areas of heating and cooling. The plants on the roof help reduce the home’s energy consumption by keeping the interior cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter.
This design proves that urban spaces can contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability.
Example 4: The High-Efficiency Home in Canada
The High-Efficiency Home in Canada is built using passive house principles, a design strategy that prioritizes energy efficiency. The home features super-insulated walls, high-performance windows, and airtight construction to minimize energy loss. This design ensures that the home maintains a comfortable temperature year-round, without relying heavily on heating or cooling systems.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Reduction
Due to its passive house design, this home uses very little energy to maintain indoor comfort. It relies on a small, efficient ventilation system to maintain air quality while recovering heat from exhaust air. This reduces the home’s carbon footprint, making it one of the most energy-efficient homes in the region.
Role in Promoting Net-Zero Housing in Cold Climates
Canada’s cold climate presents unique challenges for net-zero homes, but the High-Efficiency Home proves that even in harsh environments, energy-efficient homes can thrive. By adopting passive house principles, the home’s energy consumption is drastically reduced, making it an ideal model for other homes in cold regions.
Example 5: The Zero-Energy Eco-Home in Japan
In Japan, the Zero-Energy Eco-Home is powered by a combination of solar energy and a smart grid system that helps manage energy use efficiently. The home’s solar panels generate electricity, which is stored in a battery system for use when sunlight is limited. The integration of smart grid technology allows the homeowners to monitor and optimize their energy use, ensuring that they remain energy-independent.
Integration of Bioclimatic Architecture
The design of the Zero-Energy Eco-Home takes full advantage of Japan’s climate by incorporating bioclimatic architecture principles. The home’s orientation, shading devices, and ventilation systems are all carefully designed to maximize natural cooling and heating, reducing the need for mechanical systems.
Local and Global Impact
This home is not just a symbol of innovation for Japanese homeowners but also a model for global sustainability efforts. By adopting renewable energy and smart technology, the Zero-Energy Eco-Home showcases how high-tech solutions can be integrated into residential living to create a more sustainable future.
Example 6: The Self-Sustaining Home in Australia
Located in the outback of Australia, the Self-Sustaining Home is designed to function entirely independently from the grid. It combines a large solar array with a wind turbine, allowing it to generate all the energy it needs for daily living. The home is also equipped with an advanced battery storage system, which stores excess energy during sunny or windy periods for use when conditions aren’t ideal.
Water Collection and Recycling Systems
Australia is known for its dry conditions, and this self-sustaining home incorporates innovative water conservation practices. It features a rainwater harvesting system, which collects water from the roof and stores it for use in the home. The water is then filtered and purified, providing clean water for drinking, bathing, and irrigation. Additionally, greywater recycling is used to repurpose water from sinks, showers, and laundry, reducing water consumption and promoting sustainability.
Long-Term Viability of the Design
The Self-Sustaining Home is designed with long-term durability and resilience in mind. The combination of renewable energy generation and water conservation practices ensures that it can remain off-grid indefinitely. This makes it an excellent example of a sustainable home that can thrive in challenging environments. Furthermore, the design serves as a proof of concept for other homes in remote or arid regions around the world, where water and energy are limited resources.
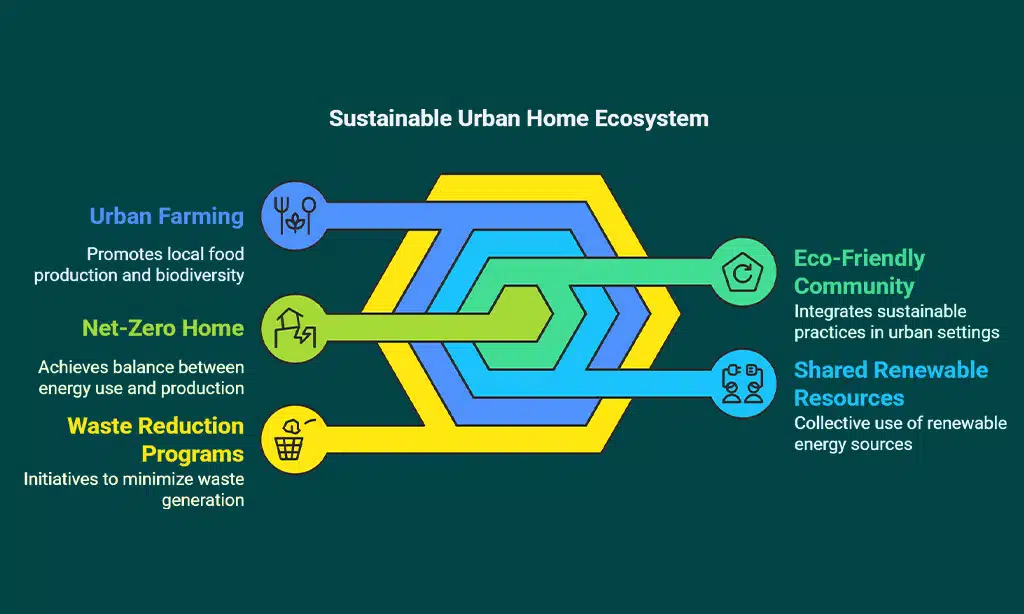
Example 7: The Sustainable Urban Home in Denmark
In Denmark, the Sustainable Urban Home is part of an eco-friendly community designed to integrate net-zero homes into urban spaces.
The home is located in a development that prioritizes green living, featuring shared renewable energy resources, urban farming, and waste reduction programs. The home itself is equipped with solar panels, efficient insulation, and energy-saving appliances, which help it achieve net-zero status.
Collaboration with Local Authorities
This sustainable development is the result of close collaboration between local authorities, architects, and urban planners. Denmark’s government has long been committed to sustainability, and this project exemplifies how municipal planning can contribute to achieving net-zero goals. The project serves as a model for other cities looking to promote green urban living.
Impact on City Sustainability
The Sustainable Urban Home is part of a larger initiative to reduce the carbon footprint of urban areas. By incorporating renewable energy, energy-efficient building techniques, and sustainable design, the project reduces the environmental impact of city living. Furthermore, it promotes a more sustainable way of life for urban dwellers, inspiring other cities to adopt similar practices.
Example 8: The Earth-Sheltered Home in Iceland
The Earth-Sheltered Home in Iceland is designed to blend seamlessly with the natural environment. Built into the earth itself, the home is naturally insulated, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling. Iceland’s abundant geothermal energy is harnessed to heat the home, making it an entirely self-sufficient, energy-efficient structure.
Challenges in Remote Locations
Building a net-zero home in a remote location like Iceland presents unique challenges. The Earth-Sheltered Home’s construction required careful planning to ensure that it could withstand harsh weather conditions while maintaining energy efficiency. The site’s geothermal energy resources were carefully tapped to ensure the home could remain comfortable year-round, even during the coldest winters.
Future of Earth-Sheltered Net-Zero Homes
The Earth-Sheltered Home in Iceland is a promising example of how net-zero homes can be adapted to extreme climates and remote locations. With the right resources, earth-sheltered homes can be incredibly energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. As more regions look for sustainable housing solutions, this type of design may become increasingly popular in areas with abundant geothermal energy and harsh climates.
Benefits of Living in a Net-Zero Home
One of the most significant benefits of living in a net-zero home is the reduction in energy costs. By generating your own energy through renewable sources, you can eliminate or drastically reduce your electricity bills.
In many cases, net-zero homes also incorporate energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and other technologies that further lower operational costs. Over time, these savings can add up, making net-zero homes a wise investment for the future.
Minimal Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
Net-zero homes are designed to have a minimal environmental impact. By relying on renewable energy sources and sustainable building materials, these homes significantly reduce carbon emissions. They also promote a more sustainable lifestyle, encouraging homeowners to conserve resources, recycle, and reduce waste.
Improved Health and Comfort Through Better Air Quality
Net-zero homes are built with health and comfort in mind. Energy-efficient designs include superior insulation, which helps maintain stable temperatures and reduces drafts. Additionally, many net-zero homes include ventilation systems that provide fresh, filtered air, improving indoor air quality and reducing allergens. These features contribute to a healthier living environment and a higher quality of life.
Resilience Against Natural Disasters and Climate Change
Net-zero homes are often designed to be more resilient to natural disasters and the effects of climate change. Their energy-efficient designs help them remain functional during power outages, while their sustainable materials and renewable energy systems ensure they can continue operating under adverse conditions. In addition, their designs often incorporate flood-resistant or fire-resistant materials, providing further protection.
Challenges and Considerations for Building Net-Zero Homes
While net-zero homes offer significant long-term savings, the initial investment can be higher than that of conventional homes. The costs of renewable energy systems, energy-efficient appliances, and sustainable building materials can add up.
However, there are a variety of government incentives, tax rebates, and green financing options that can help offset these costs. Additionally, as demand for net-zero homes grows, construction costs are expected to decrease.
Technological and Design Barriers
Building a net-zero home requires careful planning and the integration of various technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy-efficient heating and cooling systems.
The complexity of these designs may pose challenges, particularly in areas with limited access to specialized contractors or resources. However, as the industry continues to grow, these technologies are becoming more widely available, making it easier to build a net-zero home in various locations.
Regulatory and Zoning Challenges
In some regions, local building codes and zoning regulations may pose challenges for constructing net-zero homes. These regulations may limit the use of renewable energy systems or restrict certain design features.
However, many cities and countries are revising their building codes to promote sustainability, making it easier to build net-zero homes. It’s important for homeowners to work with local authorities and architects to ensure their projects comply with regulations.
Maintaining Efficiency Over Time
While net-zero homes are designed to be energy-efficient, maintaining their performance over time requires ongoing attention.
Regular maintenance of renewable energy systems, insulation, and appliances is necessary to ensure the home continues to operate efficiently. Homeowners should be prepared to monitor energy usage, conduct periodic checks, and replace components as needed.
The Future of Net-Zero Homes: Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, renewable energy systems will become more efficient and affordable. Advances in solar panel technology, energy storage systems, and wind turbines will allow homeowners to generate more energy with fewer resources. Additionally, emerging technologies like smart grids and energy-sharing networks will enable net-zero homes to interact more effectively with the broader energy infrastructure.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and IoT in Energy Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to play a significant role in the future of net-zero homes. Smart devices and AI-powered energy management systems can optimize energy use, reduce waste, and improve efficiency.
For example, AI can predict energy consumption patterns and automatically adjust heating, cooling, and lighting systems to minimize energy use without sacrificing comfort.
Collaborative Efforts for Global Net-Zero Housing Solutions
As the need for sustainable housing grows, governments, architects, and developers are coming together to create solutions that will make net-zero homes more accessible and affordable.
Collaborative efforts, such as building green-certified communities and creating new financing models, will help scale the adoption of net-zero homes worldwide. With global cooperation, the transition to net-zero housing could become a reality for millions of people around the globe.
Wrap Up
The 8 inspiring examples of net-zero homes across the globe showcase the immense potential of sustainable, energy-efficient living. These homes demonstrate that it is possible to reduce our environmental footprint, save money, and create healthier, more resilient living spaces.
As technology advances and the demand for eco-friendly homes grows, net-zero homes will continue to shape the future of residential living.
Whether you’re looking to build a new home or retrofit your existing one, the lessons from these inspiring examples can help you make more sustainable choices and contribute to a greener, more sustainable world.