New Zealand has long been recognized as a powerhouse in agricultural exports. With its rich natural resources, high-quality produce, and commitment to sustainability, the country plays a vital role in global food markets.
However, in today’s interconnected world, simply having quality agricultural products is not enough. Trade agreements have become a crucial tool for expanding market access, reducing tariffs, and strengthening New Zealand’s agricultural economy.
This article explores how trade agreements are boosting Kiwi agriculture exports, examining the role of international trade deals, their impact on key agricultural products, the challenges they pose, and the future outlook for New Zealand’s agribusiness sector.
Real-world examples, current market trends, and data-driven insights will provide a comprehensive understanding of this vital topic.
Understanding Trade Agreements and Their Role in Agriculture
Trade agreements are legally binding arrangements between countries that establish terms for trade relations. These agreements can be bilateral (between two nations) or multilateral (involving multiple countries) and are designed to enhance trade efficiency by reducing barriers such as tariffs and import restrictions. They help countries foster economic cooperation, promote investment, and facilitate smoother supply chains across borders.
Key Benefits of Trade Agreements:
| Benefit | Explanation |
| Lower Tariffs | Reduces costs for exporters, making products more competitive. |
| Improved Market Access | Grants entry to new and high-demand markets. |
| Increased Foreign Investment | Encourages investors to support agricultural growth. |
| Quality & Safety Standards | Ensures compliance with global food regulations. |
Key Trade Agreements Affecting Kiwi Agriculture
New Zealand has actively engaged in trade negotiations to secure favorable conditions for its exporters. Some of the most impactful trade agreements include:
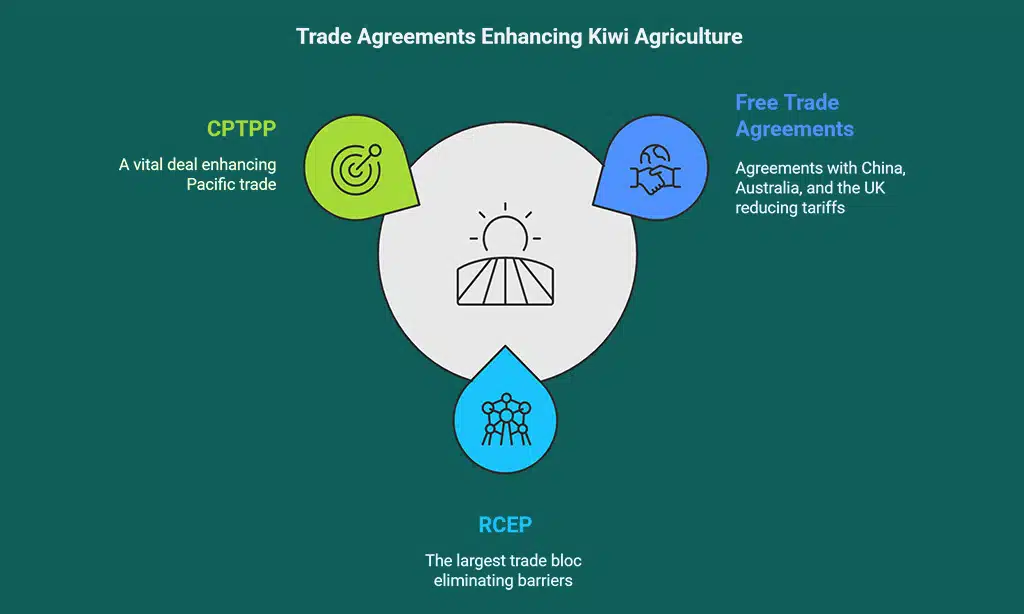
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) – These agreements, such as those with China, Australia, and the UK, have opened doors for seamless exports of Kiwi agricultural products, reducing tariffs and enhancing product competitiveness.
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) – The world’s largest trade bloc, covering 15 Asia-Pacific nations, significantly benefits New Zealand’s exporters by eliminating barriers and boosting trade efficiency.
- Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) – A vital deal that enhances trade opportunities across the Pacific region, including Japan and Canada, ensuring smoother and faster trade relations.
How Trade Agreements Are Boosting Kiwi Agriculture Exports?
One of the primary ways how trade agreements are boosting Kiwi agriculture exports is through increased market access. New Zealand has secured preferential trade terms with some of the world’s biggest economies, reducing barriers and creating lucrative opportunities for farmers and exporters.
Tariff Reductions on Key Products:
| Agricultural Product | Tariff Before Agreement | Tariff After Agreement | Export Growth (%) |
| Dairy (Milk, Cheese) | 10-25% | 0-5% | 30% |
| Kiwi Fruit | 15% | 0% | 40% |
| Beef & Lamb | 20% | 0-5% | 25% |
These tariff reductions directly enhance the competitiveness of New Zealand’s agricultural exports in international markets, providing Kiwi exporters with a significant advantage.
Strengthening Export Opportunities for Key Agricultural Products
New Zealand’s dairy industry is one of the biggest beneficiaries of trade agreements. The country’s high-quality milk, butter, and cheese are in high demand worldwide. Agreements like the China-New Zealand FTA and CPTPP have significantly increased dairy exports to Asia and North America.
Case Study: China-New Zealand FTA
Since the signing of the Free Trade Agreement in 2008, dairy exports to China have surged by over 400%, making China New Zealand’s largest dairy export market.
Expansion of the Kiwi Fruit Market
New Zealand’s kiwi fruit industry has flourished under favorable trade terms, particularly with Japan, China, and the European Union. Trade agreements ensure smooth entry into these markets with minimal trade barriers.
Key Statistics for Kiwi Fruit Exports:
| Year | Export Value (NZD) | Top Markets |
| 2018 | 1.5 Billion | China, Japan, Europe |
| 2022 | 2.8 Billion | China, Japan, Europe |
Meat and Seafood Exports
New Zealand is a global leader in premium grass-fed beef, lamb, and seafood exports. Trade deals with the EU, UK, and Asian nations have created greater demand, ensuring higher profits for Kiwi farmers and exporters.
Challenges and Risks in Trade Agreements
While trade agreements provide opportunities, they also come with stringent food safety, environmental, and labor standards that Kiwi exporters must meet. These compliance challenges often require investment in technology and best practices to maintain export eligibility.
Competition from Other Exporting Nations
New Zealand competes with major agricultural exporters like Australia, the US, and Canada. Ensuring product differentiation and premium quality is key to maintaining market leadership.
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Increased exports must be balanced with sustainable farming practices. Striking this balance is critical for long-term success, with an emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and promoting ethical sourcing.
Future of New Zealand’s Agriculture Exports in Global Trade
| Proposed Agreement | Potential Benefits |
| India-New Zealand FTA | Unlocks access to a massive consumer market. |
| Expansion of CPTPP | More member countries could mean wider reach. |
Strategies for Farmers and Exporters to Maximize Benefits
- Embracing Technology & Innovation – Smart farming, AI-driven supply chain management, and digital trade platforms to optimize efficiency.
- Strengthening Branding & Marketing – Promoting New Zealand’s agricultural excellence on global platforms and leveraging country-of-origin branding.
- Investing in Sustainable Practices – Ensuring long-term growth with environmentally responsible farming, including water conservation and organic production.
Takeaways
Trade agreements play a pivotal role in how trade agreements are boosting Kiwi agriculture exports by reducing tariffs, increasing market access, and strengthening economic growth. New Zealand’s agricultural industry stands to gain even more as global trade continues to evolve.
By staying competitive, embracing innovation, and adhering to sustainability standards, New Zealand’s agriculture sector will remain a key player in international markets for years to come.
The future of Kiwi agriculture exports is promising, with ongoing trade negotiations and a global push for high-quality, sustainable food sources driving further growth.