Global trade moves faster than ever, but cross-border logistics can slow things down. Businesses face delays, high costs, and confusing regulations when shipping goods across countries.
New routes are changing the game. The seven key cross-border logistics corridors reshaping global trade cut through these challenges like a hot knife through butter. These routes connect continents, boost supply chains, and open fresh export markets.
You’ll see how smart tech and better infrastructure make shipping smoother worldwide. Keep reading to learn which corridors matter most for your business.
Stay ahead—the future of trade is rolling out now!
Key Takeaways
- The Middle Corridor boosts Asia-Europe trade, with transit volumes up 150% in 2022 and Turkish shipments to Central Asia rising 44% from 2020-2023.
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative connects Asia, Europe, and Africa through upgraded roads, rails, and ports, speeding up trade with digital tracking tools.
- USMCA fuels North American trade: Mex-Cal Truckline runs 200+ trucks and 300+ staff, while Mexico’s logistics sector grows as a key export hub by 2025.
- The Southern Corridor links the Mediterranean and Middle East, adding 10.2% to Abu Dhabi’s GDP and employing 100,000+ in logistics jobs.
- East Africa’s trade corridor uses AI and IoT to cut delays in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, but uneven rules still slow progress.
The Middle Corridor: Connecting Asia to Europe
The Middle Corridor is changing how goods move between Asia and Europe. This trade route saw transit volumes jump 150% in 2022, proving its growing role in global supply chains. It bypasses traditional paths, offering faster overland routes through Central Asia and the Caucasus.
Turkish operators are riding this wave, with a 44% surge in shipments to Central Asia from 2020 to 2023. The corridor strengthens regional integration, cutting delays at crowded ports.
Improved transportation infrastructure helps exporters reach new markets without relying solely on ocean freight. Numbers don’t lie—this isn’t just another road, it’s a game changer.
The Belt and Road Initiative: Transforming Global Trade Routes
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is China’s massive plan to boost global trade. It connects Asia, Europe, and Africa through roads, railways, and ports. Public-private partnerships speed up infrastructure projects, making trade faster and cheaper.
This network cuts through trade barriers, linking export markets and boosting economic growth.
New tech like digital tracking improves supply chain management along BRI routes. The initiative also opens doors for regional integration and foreign investment. From rare earths to liquefied natural gas, goods move smoother than ever.
It’s reshaping how countries trade, turning old routes into modern economic corridors.
The North American Corridor: Strengthening US-Mexico-Canada Trade
The North American corridor is a powerhouse for trade. It links the U.S., Mexico, and Canada under agreements like the USMCA, cutting trade barriers and boosting regional supply chains.
U.S.-Mexico border trade is set for big changes by 2025, reshaping freight forwarding and logistics services. Companies like Mex-Cal Truckline lead with 40+ years in cross-border logistics, a fleet of 200+ trucks, and 300+ skilled team members.
This route speeds up exports, from auto parts to electronics, while regional integration strengthens economic activity. Infrastructure development keeps pace, making air freight and ocean freight faster than ever.
Mexico’s role grows as a key export market, thanks to foreign direct investment fueling manufacturing hubs. Smooth customs brokerage helps goods move without bottlenecks. The Gulf Cooperation Council could learn a thing or two from North America’s playbook—it’s all about teamwork.
Economic zones thrive near borders, proving strategic planning pays off. No fancy buzzwords here—just hard roads, smart deals, and open lanes for business..
The Southern Corridor: Expanding Trade in the Mediterranean and Middle East
The Southern Corridor is boosting trade between the Mediterranean and the Middle East. It links ports, roads, and pipelines across key regions, making shipping faster and cheaper. Countries like the UAE benefit greatly, with Abu Dhabi’s logistics sector adding 10.2% to its GDP and employing over 100,000 workers.
This route strengthens regional supply chains, cuts trade barriers, and supports economic development. Major projects include LNG terminals and infrastructure upgrades, improving energy security.
The corridor also ties into broader initiatives like the Belt and Road, expanding export markets in Southeast Asia and beyond. With smoother ocean freight and better port access, businesses gain a competitive edge.
Firms using this route can move goods quicker while keeping costs low—a win for global trade.
The Trans-Siberian Corridor: A Vital Link for Eurasian Trade
The Trans-Siberian Corridor stretches over 6,000 miles, linking Asia and Europe like a steel ribbon. It speeds up trade between major hubs, cutting weeks off shipping times compared to ocean freight.
Yet high-value cargo faces risks like theft and delays due to old rails and unstable regions. Governments and businesses must pour money into upgrades to keep goods moving fast.
Tech plays a big role here. Smart tracking tools help monitor shipments in real time, avoiding costly losses. Green innovations, like electric trains, could make this route cleaner and cheaper.
With Russia’s vast gas reserves nearby, energy exports also ride these rails. Still, political clashes can freeze progress overnight. Strong partnerships between industries and nations keep the corridor alive despite the bumps.
The East African Corridor: Enhancing Trade Across the Continent
The East African Corridor is a game-changer for trade in Africa. It connects countries like Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, boosting regional supply chains and economic growth. Better roads, ports, and customs processes cut costs and speed up deliveries.
Tech plays a big role here. AI and IoT track shipments, reducing delays. But hurdles remain, like differing rules between countries. Public-private partnerships help fix these issues, making trade smoother and safer.
The goal? Stronger market access and poverty reduction through smarter logistics.
The South American Corridor: Building Connectivity in Latin America
South America’s cross-border logistics corridors are vital for moving goods and boosting the region’s economy. Countries like Brazil, Argentina, and Chile rely on these routes to connect with global markets.
Infrastructure investment is key to upgrading old transport networks and making shipping faster.
The Mercosur bloc plays a big role in regional trade, but complex rules slow things down. AI helps truckers find the best routes across borders, cutting delays. With better logistics, trade costs could drop by 15%, helping smaller businesses grow.
U.S. tariff changes have also opened doors for Mexico, putting pressure on South America to improve its supply chains fast.
Technological Innovations Supporting Cross-Border Corridors
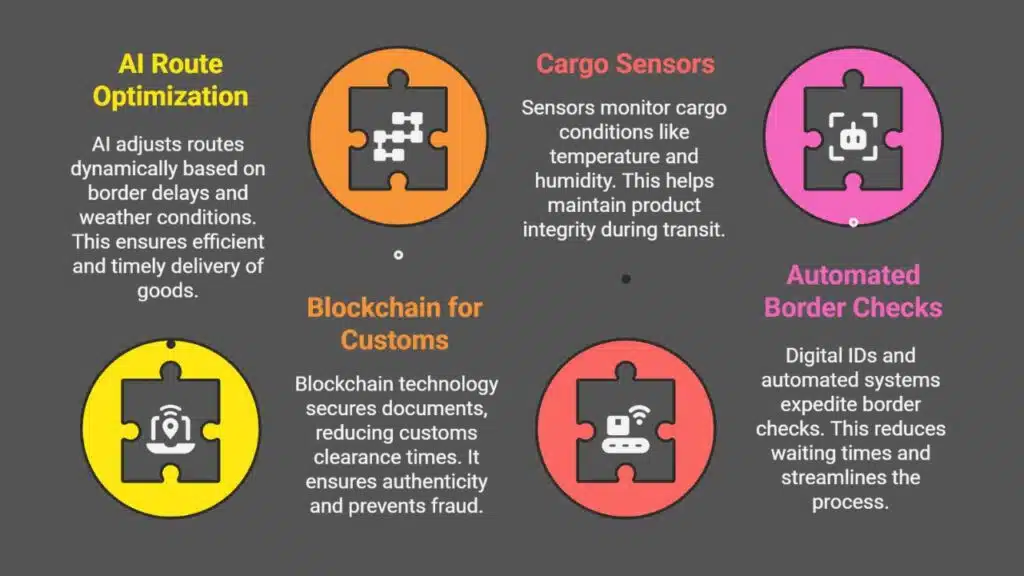
Tech is changing cross-border logistics fast. AI tweaks routes on the fly if borders slow down or storms hit. This keeps goods moving without wasting time.
Blockchain cuts customs headaches by locking in documents that can’t be faked. Sensors in cargo containers track heat, dampness, and bumps during trips. Machines now check papers at borders using digital IDs, speeding things up.
These tools help trade flow smoother across regions like Central Asia or the GCC, linking supply chains tighter than ever.
Challenges in Harmonizing Regulations Across Borders
Harmonizing trade rules between countries is no walk in the park. Different nations have their own customs laws, safety standards, and paperwork requirements. These mismatches slow down cross-border logistics, jack up costs, and frustrate businesses trying to move goods smoothly.
Picture a truck stuck at a border for days because one country demands extra inspections while another accepts simpler forms—it’s a headache for everyone involved.
Security risks like theft or terrorism add more roadblocks. Geopolitical tensions, including trade wars and sanctions, make cooperation harder too. Some regions face gaps in infrastructure or funding that delay shipments even further.
The Belt and Road Initiative tries to bridge some of these divides but still grapples with red tape across its many routes until regulations align better globally these hurdles will keep weighing down regional supply chains everywhere you look!
Takeaways
Global trade is moving faster than ever, thanks to these seven logistics corridors. From Asia to Africa, new routes are cutting costs and boosting efficiency. Businesses that tap into these networks will stay ahead of the curve.
The future of shipping is here, and it’s connected. Keep an eye on these routes—they’re changing the game.
FAQs
1. What are cross-border logistics corridors?
They are trade routes connecting countries, like the Silk Road or Panama Canal. These corridors boost regional supply chains, cut trade barriers, and speed up ocean and air freight.
2. How does China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) affect global trade?
BRI builds economic corridors, like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). It pushes infrastructure development, linking Southeast Asia to Central Asia. This pumps foreign direct investment into export markets.
3. Why is the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) important?
RCEP ties Asia together. It eases trade between members like China and ASEAN. Businesses get better access to logistics services and regional integration.
4. What role do ports like Gwadar play in trade corridors?
Ports are hubs. Gwadar, part of CPEC, handles sea freight. It connects the GCC region to Asia, slashing shipping times and costs.
5. How does digital transformation help these trade corridors?
Tech streamlines exporting. It tracks shipments, manages LTL freight, and links smallholders to global markets. Faster data means smoother regional economic development.