The legal system is divided into two primary categories: civil cases and criminal cases
While both involve disputes and legal proceedings, they serve different purposes, follow distinct procedures, and have unique consequences. Understanding these 8 key differences between civil and criminal cases is crucial for individuals, businesses, and anyone navigating the legal landscape.
Whether you are dealing with a lawsuit, facing charges, or simply trying to grasp the fundamentals of law, this guide will break down the most critical distinctions between these two types of cases. From the burden of proof to legal penalties, we will cover everything you need to know in an easy-to-understand manner.
What Are Civil and Criminal Cases?
Understanding the 8 key differences between civil and criminal cases begins with knowing their fundamental definitions. Legal cases fall into these two primary categories, each with its distinct processes, parties involved, and consequences.
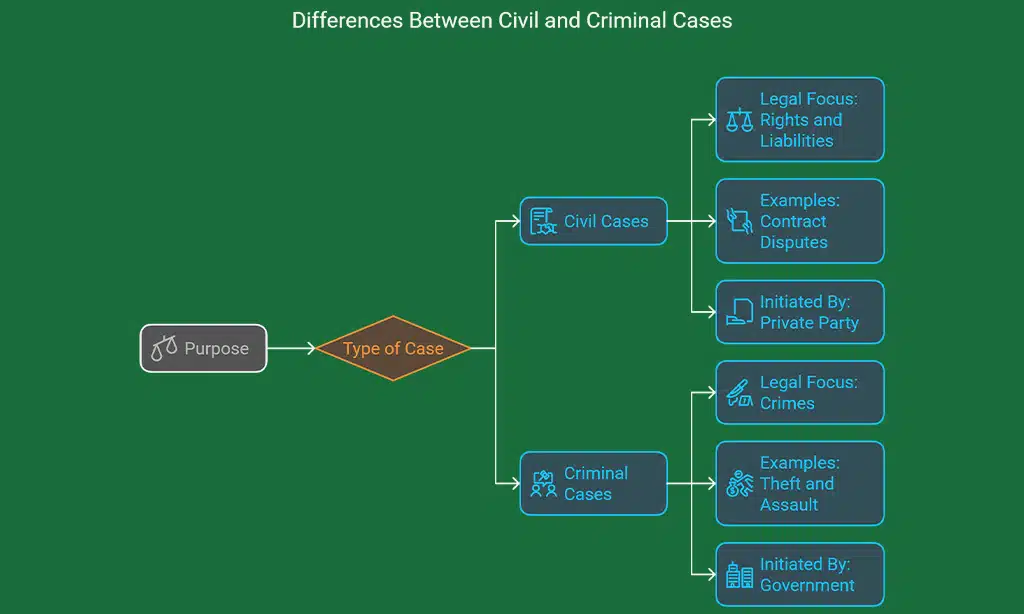
Civil cases primarily deal with disputes between individuals or organizations, while criminal cases focus on offenses against society or the state. Below, we explore their definitions and provide examples to clarify these differences.?
What Is a Civil Case?
A civil case is a legal dispute between two or more private parties—either individuals or organizations. The objective is typically to resolve conflicts and award monetary compensation or other forms of relief rather than to punish wrongdoing. Civil cases aim to protect personal rights and provide remedies for violations rather than impose penalties.
Common Examples of Civil Cases:
- Contract Disputes – Breach of agreement between businesses or individuals.
- Property Disputes – Landlord-tenant issues, boundary disputes.
- Family Law Cases – Divorce, child custody, alimony.
- Personal Injury Claims – Car accidents, medical malpractice.
- Employment Disputes – Workplace discrimination, wrongful termination.
What Is a Criminal Case?
A criminal case involves an offense against the state, government, or society as a whole. The government (prosecutor) initiates the case against an individual (defendant) accused of violating the law. Criminal cases seek to uphold justice by punishing offenders to deter future crimes.
Common Examples of Criminal Cases:
- Theft and Burglary – Stealing property, breaking into homes.
- Assault and Battery – Physical harm or threats.
- Drug Offenses – Possession, trafficking, or manufacturing illegal drugs.
- White-Collar Crimes – Fraud, embezzlement, identity theft.
- Homicide – Murder or manslaughter cases.
8 Key Differences Between Civil and Criminal Cases
Understanding the 8 key differences between civil and criminal cases starts with recognizing their fundamental nature. Civil cases revolve around disputes between individuals or organizations, often seeking financial compensation or legal remedies.
In contrast, criminal cases involve actions that are deemed offenses against the state or society, with the primary goal of punishment and deterrence.
1. Nature of the Case
Civil and criminal cases differ fundamentally in their nature and purpose. Civil cases focus on resolving disputes between individuals or organizations, typically over contracts, property, or personal injury. The goal is to provide remedies such as monetary compensation or specific performance. In contrast, criminal cases address actions that are considered offenses against society. The state prosecutes offenders to enforce laws and maintain order.
Key Differences Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Purpose | Resolve disputes, provide remedies | Punish offenders, deter crime |
| Legal Focus | Rights, liabilities, and compensation | Crimes, law enforcement, justice |
| Examples | Contract disputes, family law, personal injury | Theft, assault, murder, drug offenses |
| Initiated By | Private party (Plaintiff) | Government (Prosecutor) |
For instance, if someone owes you money and refuses to pay, you can file a civil lawsuit. However, if someone commits fraud, the government may press criminal charges.
2. Legal Standards and Burden of Proof
Civil and criminal cases require different levels of proof. In civil cases, the burden of proof lies with the plaintiff, who must prove their case by a preponderance of evidence, meaning their claim is more likely true than not. In criminal cases, the prosecution must establish guilt beyond a reasonable doubt, the highest legal standard, to ensure that innocent individuals are not wrongly convicted.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Burden of Proof | Preponderance of the evidence | Beyond a reasonable doubt |
| Who Must Prove | Plaintiff | Prosecutor |
| Risk of Error | Defendant may pay damages | Defendant may face imprisonment |
Why This Matters
Criminal defendants benefit from a stronger presumption of innocence, ensuring that only those truly guilty are convicted. In civil cases, a slight probability of truth in the plaintiff’s favor may lead to a judgment.
3. Parties Involved in the Case
- Civil Case: Involves a plaintiff (the one who files the case) and a defendant (the one being sued).
- Criminal Case: Involves a prosecutor (representing the government) and a defendant (accused of a crime).
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Who Files the Case | Plaintiff (individual/entity) | Prosecutor (government) |
| Who is Accused | Defendant (another party) | Defendant (alleged offender) |
| Legal Representation | Not guaranteed | Right to a public attorney |
For example, in a personal injury lawsuit, the injured person (plaintiff) sues the responsible party. In a criminal case, the government charges the person accused of harming someone.
4. Possible Outcomes and Penalties
Civil and criminal cases have vastly different consequences. In civil cases, the defendant may be required to pay damages, return property, or fulfill specific obligations but does not face imprisonment. In criminal cases, penalties can include fines, community service, probation, or incarceration, depending on the severity of the crime.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Possible Outcome | Monetary compensation, injunctions | Fines, imprisonment, probation |
| Punishment | No jail time | Possible incarceration |
| Impact on Record | No criminal record | Criminal record may affect life choices |
5. Role of Intent and Negligence
Intent plays a major role in criminal cases but is less significant in civil cases. Civil cases often involve negligence, meaning a party failed to exercise reasonable care. Criminal cases, on the other hand, usually require intent or recklessness for a conviction.
Example:
- A person who accidentally causes an injury due to negligence can be sued in a civil case for damages.
- If the same person intentionally harms another, they may face a criminal case for assault.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Focus | Negligence, breach of duty | Intent, recklessness |
| Example | Car accident due to carelessness | Assault with intent to harm |
6. Legal Representation and Rights
Defendants in criminal cases have the right to legal representation, even if they cannot afford an attorney. In civil cases, there is no guaranteed right to an attorney, meaning individuals must hire their own legal representation.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Right to an Attorney | Not guaranteed | Guaranteed by law |
| Who Provides It? | Self-funded | Court-appointed if necessary |
7. Trial Process and Jury Involvement
Civil and criminal trials differ in their processes and jury involvement. Civil cases may be heard by a judge or a jury, whereas criminal cases typically involve a jury to ensure a fair trial.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Trial Type | Judge or jury trial | Usually a jury trial |
| Pre-Trial Settlement | Common | Less common |
| Jury Requirement | Optional | Often required |
For example, a personal injury case may be decided by a judge if both parties agree, while a murder case almost always involves a jury to ensure impartiality.
8. Consequences of the Verdict
- Civil Cases: The defendant may be required to pay damages or comply with a court order but will not face criminal punishment.
- Criminal Cases: Convictions can result in prison time, fines, probation, or even capital punishment in severe cases.
Verdict Outcome Table:
| Aspect | Civil Cases | Criminal Cases |
| Potential Penalty | Monetary damages, injunctions | Fines, imprisonment, probation |
| Impact on Record | No criminal record | Criminal record may impact life |
| Repercussions | Financial burden | Loss of freedom, job limitations |
A person sued for breach of contract may only need to pay restitution, while someone convicted of theft could face jail time and a permanent criminal record.
Wrap Up
The 8 key differences between civil and criminal cases highlight the contrasting roles, procedures, and consequences of these legal proceedings. While civil cases resolve disputes between private parties, criminal cases address offenses against society.
Understanding these differences is essential for anyone dealing with the law, whether as a business owner, an individual seeking justice, or someone facing legal charges. If you’re unsure about your legal situation, consulting an attorney is always recommended.
Have you ever been involved in a legal case? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below!