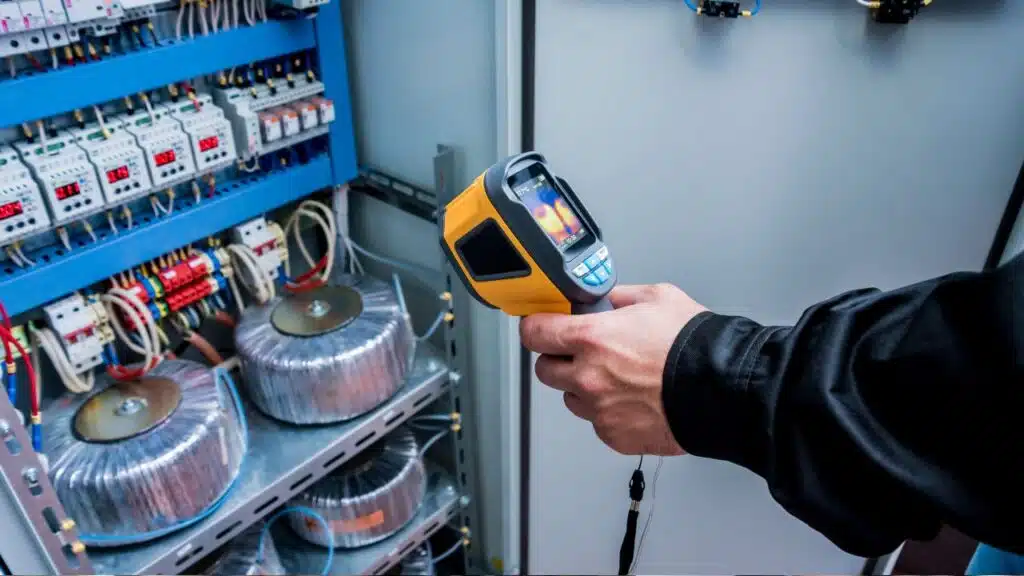
In a world increasingly driven by data and automation, the ability to measure temperature accurately and remotely is paramount. Infrared Temperature Sensors are at the forefront of this technological revolution, offering a non-contact method to monitor thermal conditions in a vast array of applications.
These remarkable devices are not just about convenience; they are fundamentally transforming industrial processes, enhancing safety protocols, and boosting operational efficiency in ways previously unimaginable. By detecting the thermal energy naturally emitted by all objects, these sensors provide instantaneous and precise temperature readings without ever making physical contact, a capability that is crucial in hazardous, fast-moving, or sterile environments.
The global demand for this technology underscores its growing importance. According to a report by Fortune Business Insights, the global temperature sensor market is projected to reach USD 14.9 billion by 2032, with a significant portion of this growth attributed to the adoption of advanced non-contact solutions like infrared sensors.
This surge is fueled by their increasing integration into sectors ranging from manufacturing and healthcare to automotive and consumer electronics, where the need for precise thermal management is critical for quality control, safety, and energy conservation.
The Science Behind the Unseen: How Infrared Temperature Sensors Work
At the heart of every Infrared Temperature Sensor lies a fundamental principle of physics: all objects with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C or 0 Kelvin) emit thermal energy in the form of infrared radiation. This radiation is part of the electromagnetic spectrum and is invisible to the human eye. The intensity of this emitted radiation is directly proportional to the object’s temperature – the hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it emits.
An infrared temperature sensor, often referred to as an IR sensor or pyrometer, is essentially a sophisticated detector of this thermal radiation. The key components of an IR sensor and their functions are:
- Optical System: A lens focuses the infrared energy emitted from the target object onto the detector. The quality of the optics is crucial for the accuracy of the measurement, especially at a distance.
- Infrared Detector: This is the core of the sensor. When the focused infrared radiation strikes the detector, it generates an electrical signal. Common types of detectors include thermopiles, microbolometers, and pyroelectric sensors.
- Signal Processing Unit: The electrical signal from the detector is then processed and converted into a temperature reading. This unit often includes an emissivity adjustment, which is a critical factor for accurate measurements. Emissivity is a measure of an object’s ability to emit infrared energy and varies depending on the material and surface finish. Modern sensors often allow for adjustable emissivity to ensure precise readings across different materials.
The non-contact nature of this technology is its most significant advantage. Unlike traditional contact thermometers like thermocouples or resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), IR sensors can measure the temperature of moving objects, objects in a vacuum, and those in hazardous or hard-to-reach locations.
A Double-Edged Sword: Boosting Efficiency and Ensuring Safety
The impact of Infrared Temperature Sensors on both industrial efficiency and workplace safety is profound and multifaceted. Their ability to provide real-time, non-contact temperature data empowers businesses to optimize processes and protect their personnel in ways that were previously challenging or impossible.
Driving Operational Efficiency
The integration of IR sensors into industrial processes leads to significant gains in efficiency, productivity, and cost savings.
- Process Optimization and Quality Control: In manufacturing, precise temperature control is often the key to product quality. For instance, in the plastics industry, IR sensors monitor the temperature of plastic films to ensure uniform thickness and strength. In the steel industry, they are used to monitor the temperature of molten metal, ensuring it is at the perfect temperature for casting. By providing continuous and accurate temperature data, these sensors allow for real-time adjustments, minimizing defects and waste.
- Predictive Maintenance: Overheating is a common early indicator of equipment malfunction. By continuously monitoring the temperature of critical machinery such as motors, bearings, and electrical panels, Infrared Temperature Sensors can detect abnormal temperature rises before a catastrophic failure occurs. This predictive maintenance approach allows for scheduled repairs, reducing costly unplanned downtime and extending the lifespan of the equipment. A study by Senseye, a leading predictive maintenance provider, highlights that unplanned downtime can cost industrial manufacturers an estimated $50 billion annually.
- Energy Savings: In energy-intensive processes like heating and drying, even small deviations from the optimal temperature can lead to significant energy waste. IR sensors enable precise temperature control, ensuring that energy is used efficiently. For example, in industrial ovens, they can maintain the exact temperature required for a process, preventing over-heating and reducing energy consumption.
A Shield Against Hazards: Enhancing Workplace Safety
The non-contact nature of Infrared Temperature Sensors makes them an invaluable tool for enhancing workplace safety.
- Monitoring Hazardous Environments: In industries such as chemical processing and power generation, workers often need to monitor equipment operating at extreme temperatures or in hazardous environments. IR sensors allow them to take accurate temperature readings from a safe distance, eliminating the risk of burns, exposure to dangerous substances, or electrical shocks.
- Fire Prevention: The early detection of overheating is crucial for fire prevention. IR cameras and sensors can continuously scan large areas for hot spots, providing an early warning of a potential fire hazard. This is particularly important in warehouses, data centers, and facilities that handle flammable materials.
- Health Screening: The COVID-19 pandemic brought the use of non-contact infrared thermometers for fever screening to the forefront. This application highlights their ability to quickly and safely measure body temperature without physical contact, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination in healthcare settings and public spaces. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized non-contact thermometers as a useful tool for initial temperature screening.
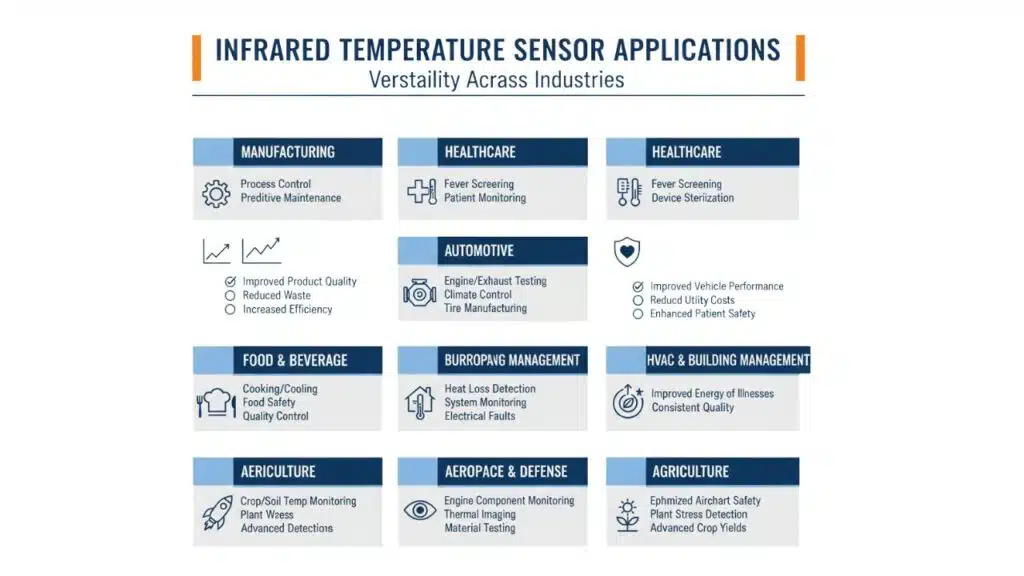
A World of Applications: Where Infrared Temperature Sensors Make a Difference
The versatility of Infrared Temperature Sensors has led to their adoption across a wide spectrum of industries.
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
| Manufacturing | Process control (plastics, steel, glass), quality assurance, predictive maintenance of machinery. | Improved product quality, reduced waste, minimized downtime, increased efficiency. |
| Healthcare | Non-contact fever screening, patient monitoring, medical device sterilization. | Reduced risk of cross-contamination, rapid screening, enhanced patient safety. |
| Automotive | Engine and exhaust system testing, climate control system monitoring, tire manufacturing. | Improved vehicle performance and safety, enhanced manufacturing quality. |
| Food and Beverage | Monitoring cooking and cooling temperatures, ensuring food safety, quality control. | Prevention of foodborne illnesses, consistent product quality. |
| HVAC and Building Management | Identifying heat loss in buildings, monitoring HVAC system performance, detecting electrical faults. | Improved energy efficiency, reduced utility costs, enhanced building safety. |
| Aerospace and Defense | Monitoring engine components, thermal imaging for surveillance, testing of materials at extreme temperatures. | Enhanced safety and reliability of aircraft, advanced surveillance capabilities. |
| Agriculture | Monitoring crop and soil temperatures, detecting stress in plants. | Optimized irrigation, improved crop yields. |
The Evolving Landscape: Types and Advancements in Infrared Sensing
The field of Infrared Temperature Sensors is constantly evolving, with new technologies and advancements leading to more accurate, versatile, and affordable devices.
Types of Infrared Temperature Sensors
There are several types of IR sensors, each suited for different applications:
- Spot Pyrometers: These are the most common type of handheld IR thermometers. They measure the temperature of a single spot on a surface.
- Line Scanners: These sensors scan a line across a moving object, creating a temperature profile. They are ideal for monitoring processes on conveyor belts.
- Thermal Imagers (Infrared Cameras): These devices create a two-dimensional thermal image, or thermogram, of a scene. They are invaluable for identifying hot spots and temperature variations over a large area.
- Fiber Optic Infrared Sensors: These sensors use a fiber optic cable to transmit infrared radiation from the target to the detector, making them suitable for use in high-temperature or electromagnetically noisy environments.
Recent Advancements and Future Trends
The future of Infrared Temperature Sensors is bright, with ongoing research and development focused on:
- Miniaturization and Integration: Sensors are becoming smaller and more integrated, allowing for their inclusion in a wider range of devices, including smartphones and wearables.
- Improved Accuracy and Resolution: Advancements in detector technology are leading to more accurate and higher-resolution thermal imaging.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms is enabling more sophisticated data analysis, such as automated defect detection and predictive maintenance alerts. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the AI in manufacturing market is expected to grow significantly, with thermal imaging and sensor data analysis being a key application area.
- Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imaging: These advanced techniques capture thermal data across multiple infrared wavelengths, providing more detailed information about the composition and properties of objects.
In conclusion, Infrared Temperature Sensors have emerged as a transformative technology, offering a powerful combination of efficiency and safety benefits. Their ability to provide accurate, non-contact temperature measurements has made them indispensable in a wide range of industries.
As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications that will further enhance our ability to monitor and control the thermal world around us, leading to smarter, safer, and more efficient operations. The continued growth of the Infrared Temperature Sensors market is a testament to their critical role in the modern industrial and technological landscape.