On January 27, 2026, a silent revolution began. It wasn’t heralded by fireworks or a grand military parade, but by the stroke of pens in Brussels and New Delhi. What unfolded was the formal conclusion of negotiations for the India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA), a pact being hailed as the “Mother of All Trade Deals.” The India-EU trade deal marks a decisive shift in how India positions itself within global commerce and strategic alliances. This isn’t just another economic agreement; it’s a strategic masterpiece, a geopolitical chess move, and a vital lifeline for Indian industry, especially in the wake of punitive U.S. tariffs.
For too long, India’s export ambitions have been buffeted by global currents. From protectionist waves in the West to the relentless rise of competitors in Asia, the path to global market dominance has been fraught. But this deal, forged amidst a fragmented and increasingly protectionist world, offers a clear new direction. It promises to transform India’s export landscape, recalibrate global trade power balances, and subtly, yet powerfully, challenge the long shadow of U.S. tariff policy. This is not merely a news report; it’s an exploration of how one agreement could reshape destinies, ignite industries, and redefine alliances.
The Dawn of a New Export Era: Unlocking Europe’s Gates
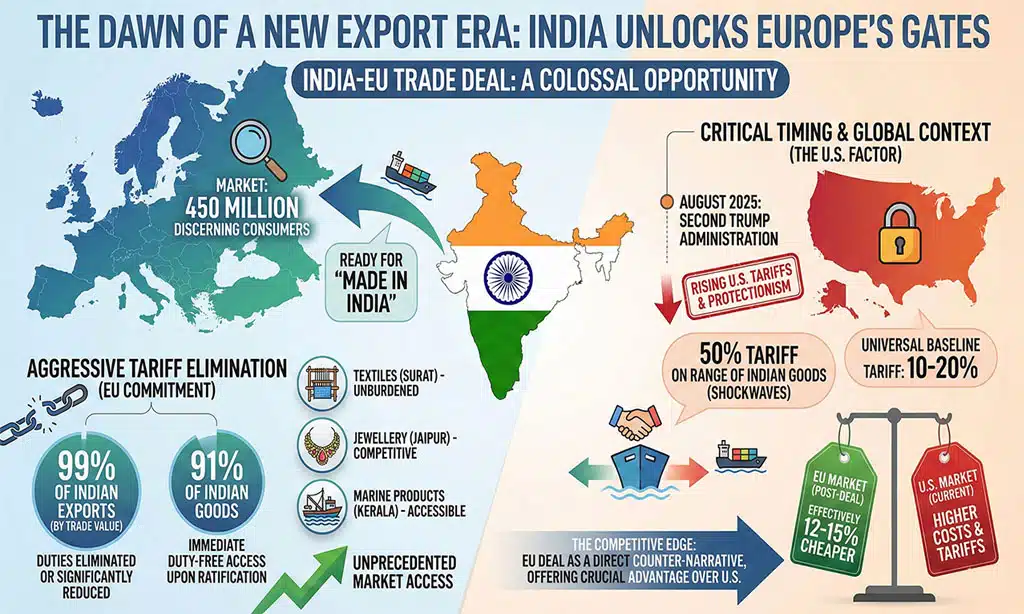
Imagine a colossal market of 450 million discerning consumers, ready to embrace “Made in India.” This is the scale of opportunity unlocked by the India-EU trade deal. This is precisely what the India-EU FTA has unlocked. The numbers are staggering, painting a picture of unprecedented market access and competitive advantage. The European Union, already India’s second-largest trading partner, is now poised to become its most accessible.
The core of this transformative agreement lies in its aggressive tariff elimination. The EU has committed to eliminating or significantly reducing duties on an astounding 99% of Indian exports by trade value. This isn’t a gradual trickle; it’s a floodgate opening. Immediately upon ratification, an estimated 91% of Indian goods will enjoy duty-free access to the EU. This means that a textile product from Surat, a piece of jewellery from Jaipur, or a consignment of marine products from Kerala will arrive in European ports unburdened by the very tariffs that previously made them less competitive.
The timing of this agreement couldn’t be more critical. The India-EU trade deal arrives at a moment when Indian exporters are actively seeking alternatives to rising U.S. tariffs. Just months prior, in August 2025, the U.S. under the second Trump administration imposed a staggering 50% tariff on a range of Indian goods. This move sent shockwaves through Indian export sectors, threatening livelihoods and forcing a desperate search for alternative markets. The EU deal emerges as a direct counter-narrative, a stark contrast to the protectionist stance of Washington. While the U.S. has moved towards a “Universal Baseline Tariff” of 10-20% for most goods, with specific retaliatory hikes reaching 50% for India, the EU has moved decisively towards 0% for the vast majority of Indian products. This differential effectively makes Indian goods 12-15% cheaper in Europe compared to the U.S., almost overnight, offering a crucial competitive edge.
India-EU FTA vs. Current U.S. Tariff Regime – A Comparative Advantage
| Export Sector | Pre-FTA EU Tariff (Average) | Post-FTA EU Tariff (Initial) | Current U.S. Tariff (Average for Indian Goods) | Relative Advantage for Indian Exporters in EU |
| Textiles & Apparel | ~12% | 0% | ~50% (post-Aug 2025) | Significantly higher (EU offers 0% vs. U.S. 50%) |
| Gems & Jewellery | ~2-4% | 0% | ~10-20% | Substantial |
| Seafood | ~6-26% | 0% (phased) | ~10-20% | High |
| Engineering Goods | ~2-7% | 0% (phased) | ~10-20% | Moderate to High |
| Leather Goods | ~3-8% | 0% (phased) | ~10-20% | High |
This table illustrates the dramatic shift in market dynamics. For sectors like textiles, which were severely impacted by U.S. duties, the EU offers not just relief, but a genuine opportunity for revival and aggressive expansion.
Sector Spotlights: Opportunities and Risks in a New Landscape
The implications of this deal ripple across India’s diverse industrial landscape, creating both profound opportunities and nuanced challenges. Under the India-EU trade deal, these shifts are especially visible across export driven sectors.
Textiles and Apparel: A Lifeline in the Storm
The Indian textiles and apparel industry, a cornerstone of its manufacturing sector and a major employer, has been particularly vulnerable to global trade headwinds. Before the FTA, Indian apparel faced an average ~12% duty when entering the EU, a significant disadvantage compared to rivals like Bangladesh and Vietnam, which enjoyed duty-free access. This eroded India’s competitiveness in the EU’s colossal $250 billion apparel market, where India held a mere 3% share.
The FTA changes everything. With zero duties on textiles and apparel, Indian manufacturers can now compete on an equal footing, or even at an advantage, given their raw material strengths and integrated supply chains. Industry experts, particularly from the Apparel Export Promotion Council (AEPC), are projecting that exports to the EU could double within 3-4 years. This is not mere optimism; it’s a calculated projection based on a fundamental shift in cost structures.
The urgency for this shift cannot be overstated. Since October 2025, following the U.S. tariff hike, Indian textile shipments to the United States have plummeted by an alarming 50%. Factories have scaled back production, and job security has become a paramount concern. The EU deal is, for many, the only thing standing between these businesses and widespread distress. It represents a vital pivot, redirecting the flow of goods and capital towards a welcoming market.
Luxury Goods and Autos: A Two-Way Street
While the focus often falls on Indian exports, the FTA is a reciprocal agreement, meaning India has also made concessions. One of the most significant changes affects the luxury auto sector. India, long known for its prohibitive import duties on high-end vehicles, is slashing its legendary 110% import duty on luxury cars from Europe.
This duty will drop immediately to 30-40% for a specified quota of 100,000 units per year, with a plan to eventually reach 10% over a decade. For European luxury car manufacturers like Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Audi, this is a game-changer, making their vehicles significantly more affordable for India’s burgeoning affluent class. This could dramatically reshape the Indian luxury car market, increase consumer choice, and potentially stimulate competition for domestic premium brands.
However, there’s a crucial caveat: this reduced tariff primarily applies to cars priced above €15,000 (approximately ₹14 Lakhs). Mass-market Indian cars remain protected by existing duty structures, ensuring that domestic manufacturers like Maruti Suzuki and Tata Motors are shielded from a sudden influx of cheaper European alternatives. Furthermore, to protect India’s nascent electric vehicle (EV) industry, EVs are excluded from these tariff reductions for the first five years, with duties only beginning to drop after 2031. This phased approach demonstrates a strategic balance between opening markets and safeguarding nascent domestic industries.
Marine and Seafood Exports: Swimming Ahead
India is a major global player in marine and seafood exports, but faces significant tariff barriers in the EU, often up to 26% on products like shrimp and processed fish. These duties made it challenging to compete with countries like Vietnam and Ecuador, which often enjoyed preferential access or lower cost structures.
With the phased elimination of these tariffs under the FTA, Indian marine and seafood exporters are poised to significantly enhance their competitiveness. This allows them to target the lucrative premium segments of the European supermarket chains and hospitality sector, previously difficult to penetrate due to price disadvantages. The quality and variety of Indian seafood, combined with zero tariffs, could see a substantial boost in market share and revenue.
Strategic Diversification in a Protectionist World
The India-EU FTA is far more than an economic agreement; it’s a strategic pivot in the evolving architecture of global trade. The India-EU trade deal reflects India’s broader push for strategic autonomy in an increasingly protectionist world. In a world increasingly defined by protectionism, supply chain vulnerabilities, and geopolitical tensions, India and the EU are actively seeking to reduce their overdependence on single markets, particularly the United States.
The U.S. imposition of 50% tariffs on Indian goods was a stark reminder for New Delhi of the risks associated with putting too many eggs in one basket. With the new EU preferential access, India is effectively diversifying its export destinations, building resilience, and potentially shielding key industries from future unilateral U.S. trade actions. This repositioning is a core tenet of India’s long-term economic strategy, aimed at fostering “strategic autonomy” in its trade relations.
Expert voices emphasise the significance of this shift. According to trade policy analysts, the deal signals India’s determination to chart its own course in global commerce rather than allowing any single nation’s trade policy to dictate its economic future. With the EU also seeking to diversify away from excessive dependence on China and navigate a more protectionist United States, India is increasingly seen as a natural strategic partner in this realignment.
This deal also sends a powerful message about the viability of multilateralism and bilateral agreements in an era where global trade bodies like the WTO often struggle to reach consensus. It highlights a pragmatic approach where like-minded economies are forging direct alliances to create predictable and favorable trade environments.
Geopolitical Implications: The “Ukraine Twist”
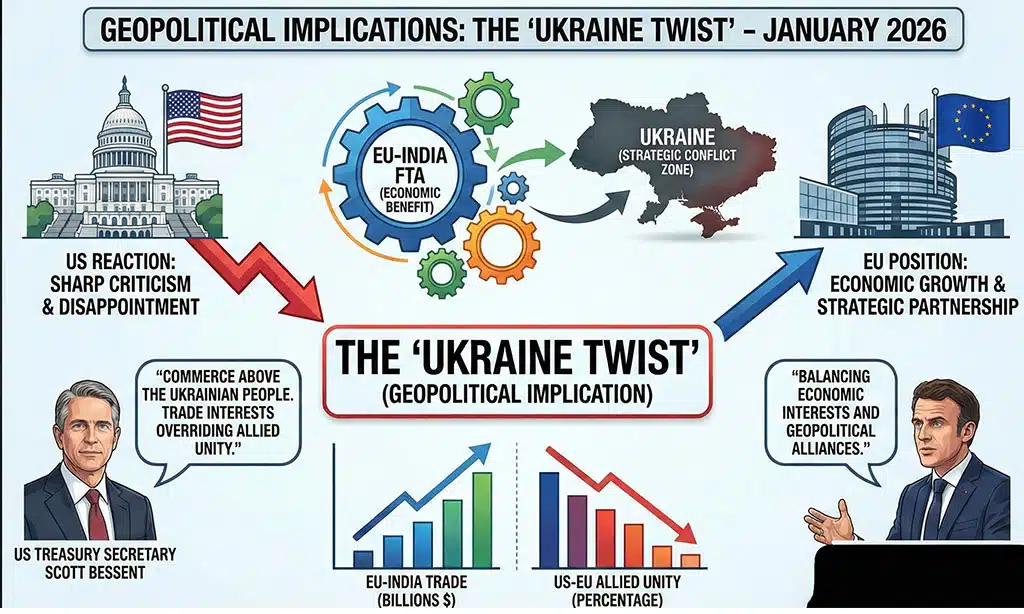
The story of the India-EU FTA cannot be told without acknowledging its profound geopolitical undercurrents, particularly the reaction from the United States. While the deal is economically beneficial for both India and the EU, it has triggered sharp criticism from Washington, adding a complex diplomatic layer to the narrative.
U.S. officials have openly expressed disappointment, framing the EU-India deal as a case where “trade interests are overriding allied unity on strategic issues such as Ukraine policy.” This sentiment was succinctly articulated by US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent in January 2026, who publicly slammed the agreement, accusing the EU of putting “commerce above the Ukrainian people.”
Geopolitical Reactions & Underlying Dynamics
| Actor | Stance on India-EU FTA | Core Argument/Motivation | Broader Geopolitical Context |
| EU | Enthusiastic | Economic growth, diversification, strategic partnership with India, secure supply chains. | Seeking to reduce reliance on China, stable partners amidst U.S. protectionism. |
| India | Highly Positive | Economic growth, export diversification, strategic autonomy, counter to U.S. tariffs. | Asserting independence, balancing great powers, domestic economic imperatives. |
| U.S. | Critical/Disappointed | EU prioritizing trade over Ukraine solidarity, indirect support for Russia via India’s oil imports. | Pressuring allies on Russia sanctions, maintaining global leadership, concerns about China. |
| Russia | Neutral/Beneficiary | Continued Indian oil imports, potential for India to become a hub for re-export of refined products to Europe. | Seeking to circumvent Western sanctions, maintaining economic ties with key partners. |
The core of the U.S. concern revolves around India’s continued robust trade relationship with Russia, particularly its purchase of discounted Russian Urals crude oil. Washington argues that by deepening trade with India, the EU is indirectly subsidizing the Russian war machine. The logic is that India buys Russian oil, refines it, and then sells petroleum products (like diesel or jet fuel) back to Europe. While technically within sanctions rules, the U.S. views this as a loophole that dilutes the impact of its own sanctions regime against Russia.
For New Delhi, however, this deal is a masterclass in “Strategic Autonomy.” Prime Minister Modi’s government has consistently maintained that India will pursue its national interests, which include securing affordable energy for its vast population and diversifying its trade relationships. By signing this FTA, India is signaling that it will not be bullied by U.S. tariff threats or forced to pick sides in the Ukraine conflict to the detriment of its own economic development. This positioning strengthens India’s role as an independent voice on the global stage, capable of balancing relationships with multiple great powers.
Implementation Challenges and Compliance Reality
While the headlines are celebratory, the real-world success of the India-EU FTA will depend on how effectively Indian exporters navigate the practicalities and challenges of implementation. For the India-EU trade deal, execution will matter as much as intent. Policy proclamations are one thing; compliance reality is another.
Rules of Origin (RoO): The Gatekeepers of Tariff Preference
One of the most crucial elements exporters must master is the Rules of Origin (RoO). These are designed to ensure that only goods genuinely originating from India (or the EU) benefit from the preferential tariffs, preventing third countries (like China) from simply routing their products through India to gain duty-free access.
The EU has imposed strict “Value Addition” rules. This typically means that a significant portion, often 35-40% of a product’s ex-factory value must be added within India. For complex products with global supply chains, proving origin can be intricate and demanding, requiring meticulous documentation and robust internal processes. Exporters who fail to meet these stringent RoO requirements will find their goods subject to the standard MFN (Most Favoured Nation) tariffs, effectively negating the benefits of the FTA.
Compliance with EU Standards: A Higher Bar
The EU is renowned for its high product standards, encompassing everything from environmental safety and health to technical specifications and labour practices. Indian exporters, particularly SMEs, must understand and adhere to these regulations. This includes:
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures: Crucial for agricultural and marine products, ensuring food safety and animal/plant health.
- Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT): Specific product standards, labeling requirements, and certification processes.
- Chemical Regulations (e.g., REACH): Strict rules on the use of certain chemicals in manufactured goods.
- Data Protection (GDPR): Relevant for service providers and any business handling European customer data.
Compliance often requires significant investment in upgrading production processes, quality control, testing, and certification. While challenging, meeting these standards can also elevate the overall quality and competitiveness of Indian products globally, not just in the EU.
CBAM: The Carbon Tax Conundrum
Perhaps the most significant non-tariff barrier for certain Indian industries is the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). This mechanism effectively places a carbon price on imports of certain carbon-intensive goods (initially iron & steel, aluminum, cement, fertilizers, hydrogen, electricity). Even with 0% import duties, Indian steel or aluminum could face substantial carbon taxes if their production processes are “dirtier” (i.e., generate more carbon emissions per unit of product) than those in the EU.
Key Challenges and Mitigation Strategies for Indian Exporters
| Challenge | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
| Rules of Origin (RoO) | Stringent requirements (e.g., 35-40% local value addition) to qualify for preferential tariffs. | Detailed documentation, supply chain mapping, investment in local sourcing. |
| EU Standards (SPS, TBT) | High product safety, health, environmental, and technical specifications. | Quality upgrades, certifications (e.g., CE marking), invest in R&D and testing. |
| CBAM (Carbon Tax) | Carbon pricing on imports of carbon-intensive goods (e.g., steel, aluminum). | Decarbonization of production, investment in green technologies, energy efficiency. |
| Labor & Sustainability Clauses | Legally binding clauses on human rights, labour laws, environmental protection. | Ethical sourcing, fair labor practices, environmental management systems, transparent reporting. |
| Ratification Process | The deal must be ratified by individual EU member states and Indian Parliament. | Stay updated on legislative developments, engage with industry associations. |
| Logistics & Infrastructure | Efficient transportation, customs clearance, port facilities. | Investment in logistics, digital trade solutions, training for customs brokers. |
CBAM poses a unique challenge because it requires Indian companies to accurately measure and report their embedded emissions, something many are not yet equipped to do. It pushes Indian industry towards decarbonization, which, while beneficial long-term, represents a significant short-term cost and compliance hurdle.
Labour and Sustainability Clauses: The Ethical Dimension
The EU has consistently integrated “legally binding” labour and environmental standards into its trade agreements. The India-EU FTA is no exception. These clauses mean that India commits to upholding international labour laws, human rights, and environmental protection standards. If India is found to be in violation, for instance, through documented cases of child labour or severe environmental degradation, the EU can potentially suspend the trade benefits for specific sectors. This pushes Indian businesses towards more ethical and sustainable practices, aligning with global best practices but also adding another layer of compliance.
The Road to Ratification
Finally, it’s important to remember that the conclusion of negotiations is not the final step. The deal must still undergo a rigorous ratification process. This involves approval by the European Parliament, potentially individual EU member states (depending on its scope), and the Indian Parliament. While ratification is widely expected given the strategic importance for both sides, it’s a procedural reality that means the full benefits of the agreement won’t kick in until early 2027.
A Special Story for a New Era
The India-EU Free Trade Agreement is more than an economic blueprint; it is a narrative of resilience, strategic foresight, and the relentless pursuit of opportunity. The deal stands as one of the most consequential economic realignments of this decade. It signifies India’s growing confidence on the global stage, its willingness to forge new partnerships, and its determination to insulate its economy from the vagaries of unilateral protectionism.
For Indian exporters, it’s a moment of immense potential, promising market access and competitive advantage that could fundamentally reshape their fortunes. For the global economy, it’s a powerful signal that despite fragmentation, pathways to deeper integration and shared prosperity can still be found.
As the ink dries on this monumental agreement, the world watches. Will India seize this moment to cement its place as a global export powerhouse? Will this deal truly rebalance global commerce and challenge the established order? The answers lie not just in policy documents, but in the factories, ports, and boardrooms across India, as a new era of trade dawns. This isn’t just a story; it’s a testament to the evolving dynamics of global power and the enduring spirit of commerce.
Read Part 1: China’s Invisible Hand in the India-EU Trade Deal
Read Part 3: From Growth to Jobs: How the India-EU Trade Deal Turns Trade Into Employment
Read Part 4: Beyond Borders: How the India-EU Trade Deal Reshapes Supply Chains and Tech