New Zealand has long been a global leader in agriculture, known for its high-quality dairy, meat, and produce. However, with growing environmental concerns and increasing pressure to reduce waste, the agricultural industry is undergoing a major transformation. The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand is not just a vision but a necessary evolution toward sustainability.
Zero-waste farming aims to eliminate waste at every stage of production by utilizing innovative technologies, regenerative agriculture, and sustainable resource management.
This article explores the current state of farming waste, cutting-edge innovations, government policies, challenges, and the future prospects of zero-waste agriculture in New Zealand.
The Need for Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand
As the demand for sustainable agriculture grows, The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand is becoming increasingly crucial. Traditional farming methods generate significant waste, leading to environmental concerns and inefficiencies.
Farmers, policymakers, and environmentalists are now working toward practical solutions that minimize waste while maximizing productivity. By adopting zero-waste principles, New Zealand’s agriculture sector can maintain its competitive edge while preserving the environment for future generations.
Understanding the Agricultural Waste Problem
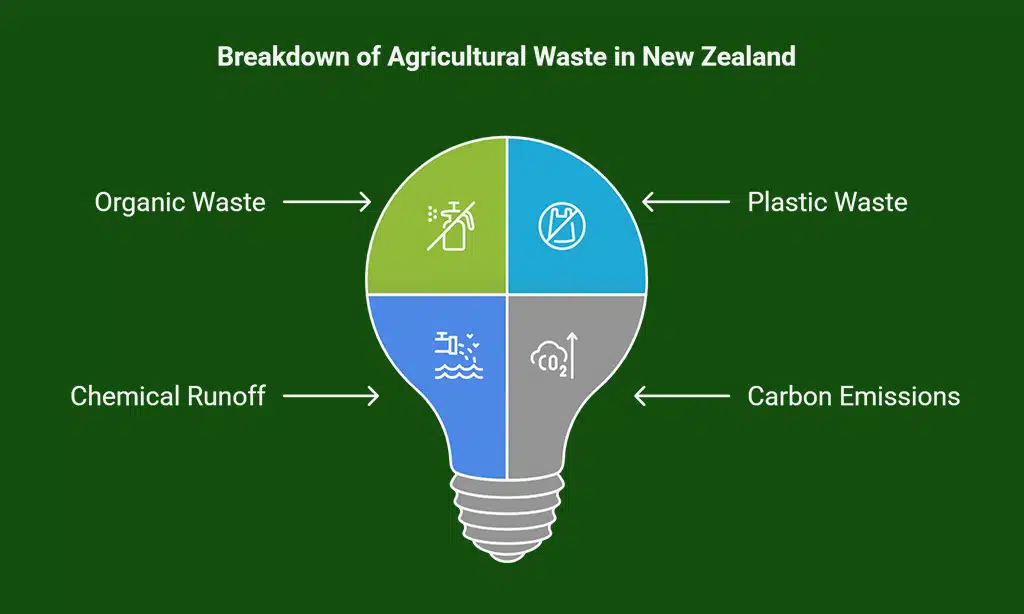
Agriculture is one of the largest contributors to waste in New Zealand. Common forms of farm waste include:
| Type of Waste | Description | Impact |
| Organic Waste | Crop residues, manure, and food waste | Increases methane emissions if not properly managed |
| Plastic Waste | Fertilizer bags, silage wrap, and irrigation tubing | Contributes to land and marine pollution |
| Chemical Runoff | Excess fertilizers and pesticides contaminating water sources | Harms aquatic ecosystems and affects water quality |
| Carbon Emissions | Methane from livestock and fuel consumption | Contributes to climate change and air pollution |
With over 40% of New Zealand’s land dedicated to farming, the environmental impact is significant. Addressing this waste problem is crucial to maintaining New Zealand’s green reputation while ensuring long-term agricultural sustainability.
How Zero-Waste Farming Solves These Challenges
As New Zealand embraces sustainability, The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand presents a pathway toward more efficient and environmentally responsible agriculture. Implementing zero-waste strategies not only reduces ecological impact but also enhances farm productivity and profitability. Farmers are increasingly turning to innovative solutions to minimize waste and make the most of available resources.
Zero-waste farming offers practical solutions to these environmental concerns:
- Reduces landfill waste by repurposing organic matter.
- Improves soil fertility with composting and regenerative techniques.
- Enhances water conservation by adopting smart irrigation.
- Lowers carbon footprint through circular agriculture and alternative energy sources.
- Encourages biodiversity by reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
By adopting zero-waste farming, New Zealand can lead the way in sustainable agriculture while maintaining profitability and productivity.
Key Innovations Shaping the Future of Zero-Waste Farming
As the agricultural sector moves towards sustainability, The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand is being shaped by a range of innovative solutions. These innovations focus on minimizing waste, enhancing resource efficiency, and ensuring long-term environmental resilience. Farmers and industry leaders are increasingly investing in new technologies and strategies that promote circular agriculture, improve waste management, and reduce ecological footprints.
1. Circular Agriculture Practices
As a cornerstone of The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand, circular agriculture focuses on repurposing farm by-products to create a self-sustaining ecosystem. This approach minimizes waste, reduces environmental impact, and enhances farm efficiency by transforming waste into valuable resources. Some key strategies include:
| Practice | Description | Benefits |
| Upcycling Crop Residues | Using leftover plant materials as animal feed or mulch | Reduces feed costs and enhances soil health |
| Manure-to-Biofertilizer | Converting livestock waste into natural fertilizers | Reduces reliance on chemical fertilizers |
| Water Recycling | Reusing irrigation and processing water | Lowers water consumption and improves sustainability |
These methods create closed-loop systems that significantly reduce waste and enhance farm productivity.
2. Advanced Composting and Waste Management Systems
As one of the critical pillars of The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand, advanced composting and waste management systems play a crucial role in reducing agricultural waste while enhancing soil health. By adopting these sustainable waste solutions, farmers can turn organic matter into valuable resources that benefit both the environment and their productivity.
Composting organic waste is an essential component of zero-waste farming. Technologies such as:
- Aerobic composting (oxygen-based) accelerates decomposition and reduces methane emissions.
- Anaerobic digesters convert manure and food waste into biogas for energy production.
- Vermicomposting using earthworms to create nutrient-rich soil amendments.
| Method | Process | Key Benefit |
| Aerobic Composting | Uses oxygen to break down organic matter | Produces high-quality compost with fewer emissions |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Breaks down waste without oxygen, generating biogas | Provides renewable energy and reduces greenhouse gases |
| Vermicomposting | Uses worms to decompose organic waste | Enhances soil fertility naturally |
3. Sustainable Water and Resource Management
Efficient water management is at the heart of The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand. As climate change intensifies and water resources become increasingly scarce, farmers must adopt innovative solutions to ensure sustainability. Implementing zero-waste water strategies not only conserves this vital resource but also enhances productivity and resilience against environmental challenges.
Water is a valuable resource in farming. Zero-waste practices ensure its efficient use through:
- Drip irrigation systems that minimize water wastage.
- Rainwater harvesting to supplement irrigation.
- Hydroponics and aquaponics that reduce soil degradation and improve water efficiency.
- Precision water monitoring using AI and sensors to optimize irrigation.
| Technique | Application | Benefits |
| Drip Irrigation | Directs water to plant roots efficiently | Reduces evaporation and water waste |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Collects and stores rainwater for irrigation | Provides an alternative water source |
| Hydroponics | Grows plants in nutrient-rich water instead of soil | Uses 90% less water than traditional farming |
4. Technology-Driven Solutions for Waste Reduction
Technology is playing a transformative role in The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand. From artificial intelligence to blockchain, cutting-edge innovations are helping farmers optimize resource use, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
These advancements not only promote sustainability but also enhance profitability by reducing input costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Emerging technologies are transforming zero-waste farming:
- AI-driven precision farming to optimize fertilizer and water use.
- IoT sensors that monitor soil health in real-time.
- Blockchain technology for supply chain transparency and waste reduction.
- Automated food waste tracking to minimize surplus and enhance efficiency.
5. Eco-Friendly Packaging and Zero-Waste Supply Chains
As sustainability becomes a priority, The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand also extends to packaging and distribution. Reducing waste at this stage is crucial for achieving a fully sustainable agricultural system. By embracing innovative packaging solutions and optimizing supply chains, farmers can significantly cut down on environmental impact while maintaining product integrity.
Reducing packaging waste is a key focus for sustainable farming:
- Biodegradable and compostable packaging reduces plastic waste.
- Local food distribution models cut down on transportation emissions.
- Minimalist packaging strategies lower production costs and waste.
- Reusable packaging models allow consumers to return packaging for reuse.
Future Prospects of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand
The agricultural landscape is rapidly evolving, and The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand presents an exciting shift towards more sustainable, resilient, and profitable farming methods. As climate change pressures and global sustainability goals drive innovation, New Zealand is poised to become a leader in waste-free agriculture.
By embracing emerging trends, farmers can reduce environmental impact while ensuring economic stability and long-term food security.
Predicted Trends and Growth Opportunities
The future of zero-waste farming is promising, with key trends including:
- Increased adoption of regenerative agriculture to enhance soil fertility.
- Expansion of vertical and urban farming to reduce land use.
- Greater collaboration between farmers and tech companies to develop AI-driven waste reduction solutions.
- Growing consumer demand for sustainable produce encouraging more farms to transition to zero-waste methods.
How Farmers Can Prepare for a Zero-Waste Future
As zero-waste farming gains momentum, New Zealand’s farmers must take proactive steps to adapt. The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand depends on strategic adoption of sustainable practices, technological advancements, and market-driven approaches. By gradually integrating these solutions, farmers can not only reduce waste but also enhance productivity and profitability.
To stay ahead, farmers should:
- Invest in sustainable technologies like AI and IoT-driven farming.
- Participate in government training programs on waste management.
- Partner with eco-conscious brands to market sustainably grown produce.
- Implement small-scale zero-waste practices before transitioning fully.
Takeaways
The shift towards zero-waste farming is not just a trend—it is a necessity for New Zealand’s agricultural future. By adopting circular agriculture, smart technology, and sustainable waste management, farmers can increase profitability while reducing environmental impact.
Governments, businesses, and consumers all have a role to play in driving The Future of Zero-Waste Farming in New Zealand. With innovation, collaboration, and policy support, New Zealand can set a global benchmark in sustainable farming.
Call to Action: Are you a farmer or an agricultural business looking to adopt zero-waste farming? Start today by exploring grants, training programs, and eco-friendly solutions that align with sustainability goals.