Effective pasture management in Australia is essential for ensuring the health of your land, livestock, and the broader ecosystem.
By implementing effective pasture management in Australia, you can address challenges like variable climates and soil conditions while boosting productivity and sustainability.
This article offers actionable insights and strategies tailored to Australian conditions to help you achieve long-term success.
Understanding Pasture Management Basics
What Is Pasture Management?
Pasture management involves the strategic planning and maintenance of grazing lands to ensure sustainable productivity.
This includes monitoring soil health, selecting suitable pasture species, and implementing grazing techniques that promote recovery and growth. For effective pasture management in Australia, understanding local environmental factors and challenges is crucial.
Example: In northern Queensland, where rainfall is inconsistent, rotational grazing combined with native grass species has shown a 30% improvement in forage availability over five years.
Why Pasture Management Matters in Australia?
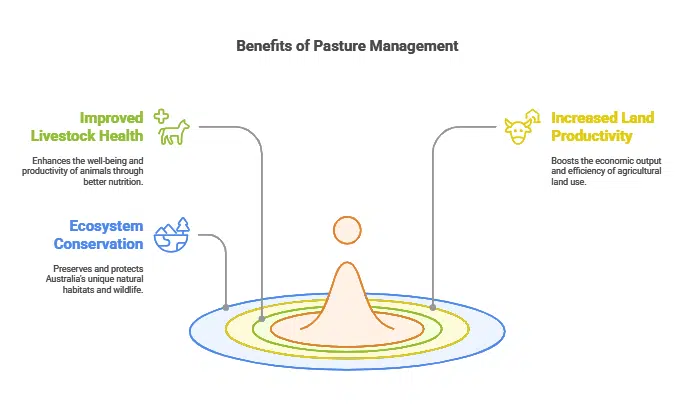
Australia’s agricultural sector faces unique challenges, such as drought, soil salinity, and invasive species. Proper pasture management supports:
- Improved livestock health through better-quality forage.
- Increased land productivity and profitability.
- Conservation of native ecosystems and biodiversity.
Quick Overview Table:
| Key Benefits of Pasture Management | Description |
| Improved Forage Quality | Ensures healthy and nutritious feed for livestock. |
| Enhanced Soil Health | Boosts fertility and supports biodiversity. |
| Sustainable Practices | Minimizes environmental impact and supports long-term productivity. |
Preparing Your Pasture for Success
Let’s get straight into it!
1. Assessing Soil Health
Conducting a Soil Test
Testing soil health is a fundamental step in pasture management. Soil tests provide insights into pH levels, nutrient availability, and organic matter content. Follow these steps:
- Collect soil samples from multiple locations across your pasture.
- Use a soil testing kit or send samples to a laboratory.
- Analyze results to identify deficiencies or imbalances.
Practical Tip: Conduct soil tests annually to monitor changes and adjust management practices as needed.
Real-Life Insight: Farmers in the Murray-Darling Basin have successfully reduced salinity levels by integrating gypsum into their soil improvement practices, resulting in a 15% yield increase.
Improving Soil Quality
- Organic Amendments: Use compost or manure to boost organic matter.
- Inorganic Options: Apply lime to adjust pH or fertilizers to address nutrient gaps.
Soil Amendments and Their Benefits
| Amendment | Benefit | Recommended Use |
| Compost | Boosts organic matter and fertility | Spread during autumn and spring. |
| Lime | Neutralizes acidic soils | Apply during soil preparation. |
| Gypsum | Reduces soil compaction | Suitable for high-clay soils. |
2. Choosing the Right Pasture Species
Selecting the appropriate pasture species is crucial for long-term success. Consider these factors:
- Climate Adaptation: Choose species suited to your region’s rainfall and temperature.
- Purpose: Focus on grazing, hay production, or soil improvement.
- Examples: Kikuyu and Rhodes grass for warmer climates; ryegrass and clover for cooler regions.
Common Pasture Species for Australia
| Species | Climate Suitability | Key Benefits |
| Kikuyu Grass | Warm climates | Drought-resistant, high biomass. |
| Ryegrass | Cool climates | High nutritional value. |
| Lucerne | Variable climates | Deep roots, improves soil health. |
Implementing Effective Grazing Strategies
3. Rotational Grazing
Rotational grazing involves dividing pastures into sections and moving livestock systematically to allow recovery. This practice is a cornerstone of effective pasture management in Australia, particularly in regions prone to overgrazing and drought.
Benefits:
- Prevention of overgrazing.
- Improved forage regrowth and quality.
- Enhanced soil fertility through better manure distribution.
Implementation Tips:
- Divide pastures into paddocks using fencing.
- Set grazing durations based on pasture recovery rates.
- Monitor livestock behavior and adjust schedules as needed.
Case Study: A sheep farm in Victoria reduced feed costs by 20% after implementing rotational grazing, as it allowed natural regrowth of clover-rich pastures.
4. Stocking Rates and Balancing Pastures
Balancing stocking rates is critical to maintaining healthy pastures. Overstocking can lead to degradation, while understocking wastes resources. Calculating appropriate stocking rates is an integral part of effective pasture management in Australia.
Calculating Stocking Rates
| Factor | Description |
| Pasture Yield | Measure of forage available per hectare. |
| Livestock Feed Demand | Average daily intake per animal. |
| Stocking Density | Number of animals per hectare. |
Water Management for Thriving Pastures
5. Irrigation Systems for Australian Farms
Efficient irrigation is vital for effective pasture management in Australia, especially in arid regions. Popular systems include:
- Drip Irrigation: Ideal for targeted watering.
- Sprinkler Systems: Suitable for larger areas.
- Flood Irrigation: Cost-effective for flat terrains.
Pros and Cons Table:
| Irrigation System | Advantages | Limitations |
| Drip | Water-efficient, precise | Higher initial cost. |
| Sprinkler | Covers large areas effectively | Potential for water loss via evaporation. |
| Flood | Low setup cost | Requires flat, leveled terrain. |
6. Water Conservation Techniques
Conserving water helps reduce costs and environmental impact. Techniques include:
- Installing rainwater tanks for storage.
- Using mulch to retain soil moisture.
- Employing contour plowing to minimize runoff.
Current Data: Studies show that implementing water conservation techniques can reduce irrigation needs by up to 25% in semi-arid Australian regions.
Monitoring and Maintaining Pasture Health
7. Identifying Weeds and Pests
Weeds and pests can compromise pasture productivity. Common Australian weeds include:
- Paterson’s curse
- African lovegrass
Control Methods:
- Manual removal or mowing.
- Applying targeted herbicides.
- Introducing biological controls, such as specific insects.
Weed Control Techniques
| Method | Pros | Cons |
| Manual Removal | Environmentally friendly | Labor-intensive. |
| Herbicides | Effective for large areas | Potential environmental impact. |
| Biological Control | Sustainable solution | Limited to specific weed types. |
8. Evaluating Pasture Performance
Regular monitoring ensures that pastures remain productive. Key performance indicators include:
- Forage growth rates.
- Nutrient levels in the soil.
- Livestock health and weight gain.
Example: A beef farm in Western Australia used NDVI satellite imagery to monitor forage health, increasing yields by 10%.
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Productivity
9. Managing Drought Conditions
Drought is a frequent challenge in Australia. Strategies to mitigate its impact include:
- Planting drought-tolerant forage species like kikuyu grass.
- Creating water reserves through dams and rainwater harvesting.
- Using rotational grazing to allow pastures to recover during dry periods.
Fact: Research indicates that farms employing drought-resilient strategies report up to 30% higher forage retention during prolonged dry spells.
10. Enhancing Biodiversity in Pastures
Biodiversity can improve ecosystem resilience and pasture productivity. Practices include:
- Introducing mixed-species pastures to reduce disease and pest pressure.
- Encouraging native plants to attract beneficial insects and pollinators.
- Establishing wildlife corridors to support ecological balance.
Example: A mixed-pasture farm in New South Wales recorded a 15% reduction in pest outbreaks after integrating wildflower strips around paddocks.
Tools and Technology for Modern Pasture Management
Precision Agriculture Tools
Modern technologies can revolutionize effective pasture management in Australia:
- Drones for aerial monitoring.
- GPS mapping for efficient paddock planning.
- Apps to track soil health and grazing patterns.
Example: In South Australia, drones equipped with NDVI sensors helped farmers identify overgrazed areas, allowing for targeted reseeding efforts.
Automated Livestock Tracking
Livestock tracking systems provide valuable data on animal behavior and movement, helping optimize grazing efficiency.
Key Technologies for Pasture Management
| Technology | Application |
| Drones | Monitoring pasture condition. |
| GPS Mapping | Optimizing paddock layout. |
| Livestock Trackers | Analyzing grazing patterns. |
Building a Pasture Management Calendar
Seasonal Tasks and Priorities
Developing a calendar helps you stay on top of essential tasks. A pasture management calendar is a practical tool for achieving effective pasture management in Australia:
- Summer: Irrigation and pest control.
- Autumn: Soil testing and planting cover crops.
- Winter: Resting paddocks and monitoring livestock.
- Spring: Rotational grazing and fertilization.
Seasonal Pasture Management Checklist
| Season | Key Activities |
| Summer | Irrigation, weed and pest control. |
| Autumn | Soil testing, planting cover crops. |
| Winter | Resting paddocks, monitoring health. |
| Spring | Grazing rotation, fertilization. |
Final Tips
Effective pasture management in Australia requires a strategic approach tailored to local conditions.
By focusing on soil health, sustainable grazing practices, and advanced technologies, you can ensure your pastures remain productive and resilient for years to come.
Start implementing these tips today to see transformative results on your farm.