Many homes trap stale air, dust, and odors. Volatile organic compounds drift in, from paints and glues, and hurt indoor air quality. Clay plaster can pull toxins from the air, via gas adsorption, absorb humidity, and block mold.
This post lists eight earthen plasters, like clay plaster, lime plaster, and fiber-infused plaster, that clean indoor air, control moisture, and add natural color. You will get mixing tips, prep tricks, and real home examples.
Keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- American Clay Earth Plasters test at zero toxins, adsorb CO2, and slash VOCs to fight mold.
- Lime plaster cures by taking in CO2 and turning it to calcium carbonate, making walls strong for up to 100 years.
- Fiber-infused mixes of clay or lime with sand and hemp strands cut heating and cooling energy by up to 20% and use local, low-carbon materials.
- Craftspeople in New Hampshire and Vermont have spread 10,000 sq. yd. of earthen plaster in 10 years to boost indoor air quality.
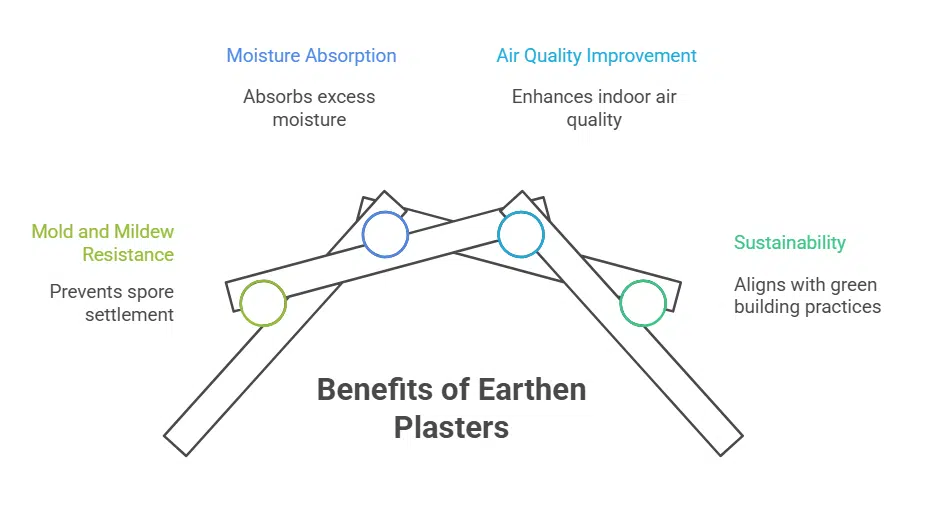
Benefits of Earthen Plasters for Indoor Air Quality
Clay plaster draws out carbon dioxide and checks humidity swings, so rooms stay fresh, not muggy. Gas chromatography tests reveal slashed TVOC levels on these walls—read on to see how your home can breathe easier.
Carbon dioxide absorption
Lime plaster, one type of earthen plaster, cures by absorbing CO2. It draws carbon dioxide from the air. Such reactions form calcium carbonate crystals over years, making walls strong and durable in sustainable building materials.
This process can last up to a century.
Many clays adsorb gases and dust. They give off negative ions, offsetting electronics’ positive ions. These plasters use open porosity to trap small molecules. Gas chromatography tests show they lower volatile organic compounds indoors and boost indoor air quality.
Regulation of indoor humidity
Clay plasters make rooms warm in winter and cool in summer. They pull in moisture as air heats up, then give it back as it cools, smoothing spikes in relative humidity. This action cuts mold growth and boosts indoor air quality.
Earthen plasters act like tiny sponges to adsorb water. Walls mix clay minerals and natural fibers, not chemicals. Their hygroscopic action rivals molecular sieves and active carbon.
Builders prize these low embodied energy materials, key sustainable building materials, for moisture control without a primer coat.
Non-toxic and chemical-free properties
American Clay Earth Plasters avoid harsh chemicals and protect indoor air quality. Tests by high pressure liquid chromatography and a mass selective detector show zero volatile organic compounds or semi-volatile organic compounds.
Lab reports show no toxins, no plasticizers, no adhesives in each batch.
Artisans apply an earthen plaster blend of slaked lime, clay plaster and sand. They add cactus juice or linseed oil for mild water resistance, not polymer sealers. Homeowners gain mold-resistant walls that breathe and stay fresh in the indoor environment.
Builders prefer this mix over gypsum plaster or cement plasters to cut embodied energy and use sustainable building materials.
Resistance to mold and mildew
Earthen plasters form a tight barrier against mold and mildew. Clay and lime plaster absorb extra moisture thanks to high hygroscopicity. This action stops spores from settling. Tests show lime plaster remains free of bacteria and mold.
Makers note that lime plaster feels caustic on the skin. Workers wear gloves while they spread it with a hand tool on brick or timber walls.
Natural plasters avoid volatile organic compounds and harsh chemicals. They make indoor air quality healthier in kitchens and bathrooms. A clay mineral helps drain excess humidity.
Each layer fights mildew even in high humidity. These plastering materials match sustainable building materials for green homes.
Types of Earthen Plasters
Homes can sport clay minerals, lime and straw-fiber blends, each binder grabs moisture and tames VOCs, and we even test them with a chromatogram—read on to find your best match.
Clay Plaster
People can dig clay plaster from local sub-soils or buy it in bags. Craftsmen mix smectite clay or kaolinites with water and natural fibers to form a smooth coat. It fights mold and stands up to heat without budging.
This earthen plaster drapes rooms in earthy tones and demands little upkeep.
Clay plaster soaks up moisture like a sponge, and it traps volatile organic compounds for better indoor air quality. Homeowners use it to steady humidity swings, dodging stale air and dry skin.
Local materials cut embodied energy, and the fireproof formula adds a safety layer near stoves. Natural plasters like this fit well into zero-energy building plans.
Lime Plaster
Lime plaster comes from heating limestone at about 900°C to form quicklime (calcium oxide) and then adding water to yield slaked lime (calcium hydroxide). Craftspeople spread this earthy mix with a trowel and use a hawk to hold the material.
The damp layer absorbs carbon dioxide and cures into a strong finish. A well-applied coat can last up to 100 years on interior walls, making it a key sustainable construction choice.
Natural plasters like this boost indoor air quality by capturing volatile organic compounds and balancing humidity. Installers mix slaked lime with sand and natural fibers for breathability without toxic binders.
Many homeowners praise the warm hues and smooth textures, while mold and mildew cannot thrive on the alkalinity of lime plasters.
Sand-Plaster Mix
Sand-plaster mix uses three main parts. The binder can use clay plaster, lime plaster or gypsum plaster. Local sand supplies the structure and fine silicon dioxide grains. Natural fibers like hemp or straw add strength and control cracking.
Builders mix small batches in a container with a mixing tool and a plaster tool. Earthen plasters improve indoor air quality and cut volatile organic compounds (VOCS).
Proper ratios matter for strong walls. Too much sand gives brittle plasters that crack under stress. Too little sand leads to shrinkage cracks as the mix dries. A standard ratio stays near 3 parts sand to 1 part clay, plus a pinch of fiber.
This mix cuts embodied energy and fits zero-energy buildings. It works in eco stucco and low carbon designs.
Fiber-Infused Plaster
Fiber-Infused plaster mixes carry natural fibers, binder, and sand. Crafts use clay plaster or lime plaster as the binding agent. Fiber strands grip the mix like a net. This design boosts durability and stops cracking.
These mixes support earthen plasters in sustainable homes.
This recipe fits the sustainable materials trend. Local straw or hemp adds organic strands to each blend. Builders tweak plastic limits with gypsum plaster or montmorillonite clay.
Resulting walls resist humidity swings and guard indoor air quality. Low embodied energy helps curb climate change impacts.
Unique Properties of Earthen Plasters
They breathe with your walls, they channel moisture through tiny pores and store heat in their mass. They adsorb indoor gases, much like a chromatography setup takes in a mobile phase, but they use swelling clay and linseed oil, not lab gear.
Breathability and vapor permeability
Contractors used cement stucco after WWII. That non‐porous mix traps water inside walls. It hurts mud walls and slows air flow. Earth plasters like clay plaster and lime plaster let walls breathe.
Earthen plasters adsorb and release moisture. Smectites in clay plaster swell in a mobile phase. Local plasters tame water content in walls. Builders mix soil with straw and natural fibers.
This mix cuts embodied energy in sustainable construction. Homes enjoy better indoor air quality and less mold.
Natural insulation capabilities
Clay plaster and lime plaster serve as natural plasters and insulation materials. These coatings trap warmth in winter and coolness in summer. They can cut HVAC energy use by up to 20 percent.
Each earthen mix adds thermal mass and boosts indoor air quality.
Local materials slash embodied energy and feed renewable resources. Gypsum plaster and plaster of paris lack the same heat storage. Earthen blends absorb heat by day and give it off at night.
You see steady comfort and lower bills.
Durability and longevity
Mainly earthen plasters resist wear and heat. Craftspeople use natural plasters for their fire-retardant traits. They suit sustainable construction goals. Calcium hydroxide plaster gains strength as it traps carbon dioxide, it may harden over a century.
This firmness helps indoor air quality by keeping mold at bay. Walls coated with gypsum plaster also resist cracks for years.
Builders add zorbax beads to boost abrasion resistance. They blend local soils, linseed oil and natural fibers to cut embodied energy. This mix stays non-porous yet breathes. Some artisans stir in cactus juice for better cohesion.
Homeowners find these surfaces last decades without major repair.
Aesthetic Advantages of Earthen Plasters
Say goodbye to plain gypsum plaster, and hello to clay swirls, cactus juice gleam, linseed oil shine, and natural pigments that make your walls pop—keep reading to learn more.
Diverse textures and finishes
Artisans mix earthen plaster with natural fibers, local materials and natural pigments to craft eight different finishes. Clients can pick hundreds of color and texture variations for walls and accents.
Some teams use clay plaster as a soft base. Others add lime plaster or gypsum plaster to boost strength. Mothers seal walls with linseed oil or cactus juice for water resistance. They tap renewable resources and low embodied energy.
Some surfaces display reliefs, sculptures or frescoes. Others use a Tadelakt effect for a glossy, marble-like sheen. Plaster lovers enjoy endless options. Walls can look like art and feel like craft.
Natural, earthy color palette
Terracotta, ochre, olive, slate and sand hues fill a room with calm. American Clay mixes natural clays, recycled aggregates and vibrant natural pigments to craft earthy tones in natural plasters.
Binders like cactus juice and linseed oil help pigments stick. Color blends spread easily with a trowel or paintbrush. Homes gain warmth and charm from this palette.
Earthen plaster surfaces like clay plaster and lime plaster hold those colors. Fiber-infused plaster layers use natural fibers that add fine ridges and soft texture. These colored plasters still breathe, boosting indoor air quality by balancing humidity.
Local renewable resources lower embodied energy and flag sustainable construction, making them top sustainable building materials. This palette pairs with gypsum plaster trim and lime wash.
Customizable for artistic designs
Artisans mix clay plaster with natural pigments and cactus juice for workability. They shape murals, frescoes, reliefs, and Tadelakt effects with a hand tool. This natural plaster uses sustainable building materials and local resources.
You can add gypsum plaster for crisp sculpting or blend in linseed oil for sheen. Patterns and sculptures pop from the wall, while the surface adsorbs moisture for better indoor air quality.
Each artistic idea finds life in earthen plaster’s creamy mix.
Environmental Impact of Earthen Plasters
Many builders use a Life Cycle Assessment tool to weigh embodied energy, and they spot big savings in earthen plasters over gypsum mixes. These earth coatings sip energy like a straw, using local hemp hurd and sunflower fibers to shrink a home’s carbon footprint.
Low carbon footprint materials
Clay plaster and lime plaster bring low carbon footprints. They need minimal heat to process, so kilns burn less fuel. They use wheat stalks and other natural fibers, which grow back each year.
This approach slashes embodied energy in life cycle assessments.
Builders grab clay and lime from nearby quarries, so trucks drive fewer miles. That step trims transport emissions and curbs greenhouse gases. Projects tap renewable resources such as wheat straw and other natural fibers.
Natural plaster from local materials beats gypsum plaster for low embodied energy.
Sustainable and renewable resources
Builders grab clay, straw and slaked lime, all from nearby quarries and farms, to craft sustainable building materials. Workers heat limestone to at least 900°C to yield quicklime, then rehydrate it, forming a binder with low embodied energy compared to gypsum plasters or cement.
Local soils burst with natural pigments for earthy hues.
Natural fibers like straw and clay keep indoor air quality high by adsorbing moisture and VOCs. Craftspeople turn to moisture meters and mixing trowels to apply these renewable resources, an eco tool kit that beats inputs from the cement industry.
Practical Considerations for Application
Use a paddle knife and mud pail to whip up the clay blend, then smooth it with a hawk on a dry, firm wall. Watch the water ratio and seal tiny cracks to curb slip-offs.
Preparing surfaces for earthen plasters
Bert stripped old paint and loose mortar off the wall. He grabbed a stiff brush, and swept away chalky dust. Next, he wiped wood studs and gypsum plaster board with a damp rag. He let them air dry until the moisture meter read below 12%.
That prep step stops clay plaster from powdering, and sets a firm base for earthen plasters.
Sara blended ingredients for her earthen plasters with cactus juice and linseed oil as binders. She spooned in chopped hemp for extra strength. Then she applied a thin key coat with a trowel, and leveled it with a spirit level.
She let that coat cure for seven days. The pause tames dusting in lime plaster and boosts indoor air quality.
Mixing and applying techniques
Mud plaster mixes combine binder, sand, and natural fibers in a bucket. You stir with a paddle mixer until the blend feels like cake batter. Clay plaster or lime plaster coat walls and improve indoor air quality.
This simple mix uses sustainable materials and local clay. Workers press each coat with a steel trowel, then smooth edges once dry. Homeowners can book remote support at $25 per hour to guide their project.
Maintenance and upkeep
Moisten a soft cloth with mild soap and water, then wipe the surface. Rinse the cloth with clear water and buff the area dry. A gentle sponge also works. This routine keeps walls free of dust and boosts indoor air quality.
Fix chips with a small trowel and a fresh mix of natural plaster. Press the earthen plaster patch into place, let it dry, then sand any ridges. Tiny scrapes fade into a warm patina over months.
Low embodied energy in these sustainable materials makes long-term care simple.
Real-Life Applications in US Homes
Homeowners coat walls with clay base plaster, then swirl in earth pigments and plant fibers for a breathable finish. They use simple monitors and test kits to watch humidity, carbon levels, or radon so families can breathe easy.
Interior wall finishes
I applied over 10,000 square yards of clay plaster across New Hampshire and Vermont during a decade in business. These earthen plasters work with other natural plasters to coat interior walls.
This clay based mix uses clay, sand and natural fibers to coat walls, it outdoes gypsum plaster in breathability. It absorbs indoor pollutants, boosts indoor air quality, limits mold, and regulates humidity.
Craftspeople spread lime plaster, clay plaster or fiber-infused plaster with a trowel, then texture with a hawk or float. Cactus juice and linseed oil boost adhesion and flexibility in some mixes.
They use local materials, cut embodied energy, and qualify as sustainable building materials in green design. They deliver smooth or textured finishes in earth tones, or allow artists to paint freeform murals.
The system resists cracking, cleans easily, and adds value to healthy US homes.
Decorative accents and designs
Earthen plasters suit bold patterns and quirky sculptures. You mix clay plaster with local materials, natural pigments, cactus juice, and linseed oil. Trowel or flexible spatula shapes bas-relief motifs, and palette knife etches swirling waves.
Fresco and trompe-lœil painting add vibrant color to walls.
These plaster works fight poor air quality, they trap CO2 and adsorbed moisture. Breathable lime plaster and clay coatings resist mold and mildew. They also lower embodied energy in sustainable building materials.
Owners love the organic feel and spa-like calm.
Takeaway
Clean walls can boost indoor air quality. They absorb carbon dioxide and tame moisture. Mud coat or chalk mortar means no mold. You pick earth dyes, linseed oil, and local sand. A trowel or mixing drill does the work.
Interiors Green trains you to apply them right.
FAQs on Earthen Plasters for Healthy US Indoor Air Quality
1. What are earthen plasters in sustainable construction?
They are natural plasters made from clay plaster, lime plaster, gypsum plaster, natural pigments and local materials. They blend in cactus juice, linseed oil, natural fibers or dung. They give walls a soft, breathing feel and they cut embodied energy.
2. How do these plasters boost indoor air quality?
They act like a sponge, they absorb moisture, trap homoki z. radon, then elute stale air. They keep rooms fresh, they cut dust and toxins, they help you breathe easier every day.
3. Can I swap painted walls for natural plaster?
Yes, you can. Natural plaster walls skip harsh chemicals. You pick colors with natural pigments. You get texture, charm, and a living surface instead of flat paint. Your room feels new, like after a spring rain.
4. Do earthen plasters work in every room?
Absolutely. Use them in living rooms, kitchens, baths or bedrooms. You can add a gypsum plaster mix or a lime coat. A bit of cactus juice or linseed oil makes them water-wise. They fit every corner of your home.
5. How do I choose the right earthen plaster?
Look for low embodied energy and local materials. Check that the mix has renewable resources and natural fibers. Talk to a builder who knows sustainable materials and sustainable building materials. Pick a blend of clay plaster or natural plaster that suits your style and budget.