Agriculture is the backbone of India’s economy, employing over 50% of the country’s workforce and contributing around 18% to its GDP.
Despite its significance, the agricultural sector is fraught with challenges, including unpredictable weather patterns, fluctuating market prices, and increasing incidences of natural disasters.
To mitigate these risks and ensure farmers’ livelihoods, crop insurance has emerged as a vital tool.
Crop Insurance in India plays a dual role: it safeguards farmers against financial losses due to crop failures and contributes to the nation’s agricultural growth by fostering resilience.
By understanding the nuances and opportunities in crop insurance, stakeholders can unlock its full potential.
This article delves deep into the impact of crop insurance, explores the latest trends shaping the sector in 2025, and provides actionable insights for improving its effectiveness.
Overview of India’s Agricultural Sector
Agriculture has long been a cornerstone of India’s socio-economic framework. Beyond its economic contributions, it ensures food security for over 1.4 billion people.
The sector also supports ancillary industries like agro-processing and exports, further bolstering the economy.
However, it remains highly vulnerable due to its dependency on monsoons, which account for 80% of the country’s annual rainfall, making it susceptible to climatic uncertainties.
Challenges Faced by Indian Farmers
Farmers in India face a myriad of challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Increasingly erratic rainfall, floods, and droughts.
- Market Risks: Fluctuating commodity prices due to domestic and international factors.
- Limited Access to Technology: Small and marginal farmers often lack access to modern farming techniques.
- Rising Costs: Input costs like seeds, fertilizers, and labor have escalated, reducing profit margins.
These vulnerabilities underscore the critical role of Crop Insurance in India in stabilizing farmers’ incomes and encouraging sustainable farming practices.
| Key Agricultural Statistics | Value |
| Contribution to GDP | 18% |
| Workforce Employed | 50% |
| Monsoon Dependency | 80% of annual rainfall |
| Smallholder Farmers | 86% of total farmers |
What Is Crop Insurance?
Crop insurance is a risk management tool that provides financial compensation to farmers in the event of crop failures caused by natural calamities, pests, or diseases.
The primary goal is to protect farmers’ incomes, enabling them to recover and reinvest in farming.
By offering a safety net, crop insurance reduces the risk of indebtedness and encourages long-term planning.
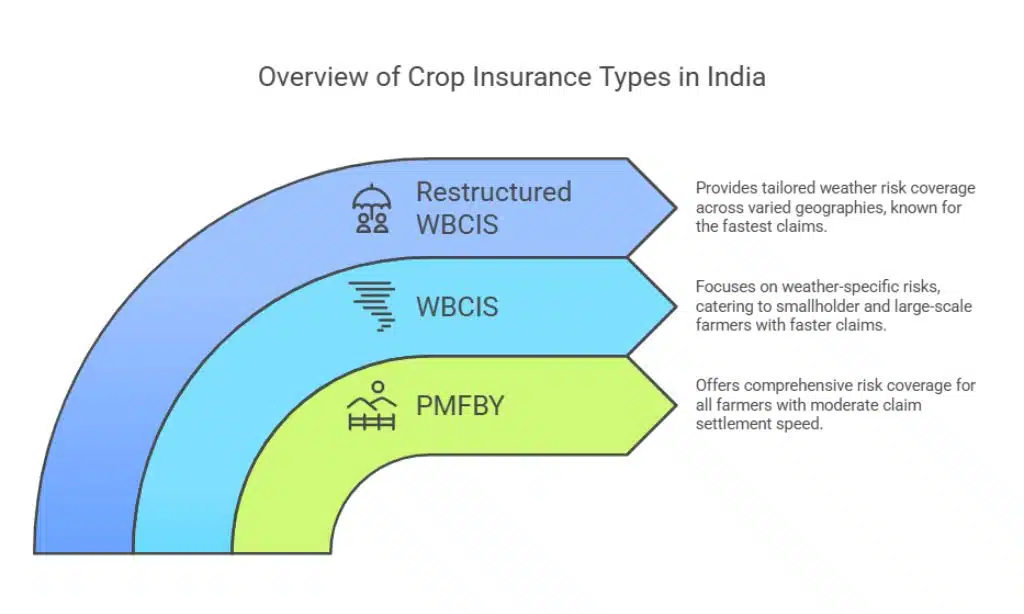
Types of Crop Insurance Available in India
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Covers risks such as droughts, floods, and pest attacks. It is a flagship scheme with extensive reach and government subsidies.
- Weather-Based Crop Insurance Scheme (WBCIS): Provides coverage based on weather parameters like temperature, rainfall, and humidity, ensuring quicker claim settlements.
- Restructured Weather-Based Insurance: Targets specific weather risks and is designed to cater to localized climatic conditions.
| Type of Insurance | Coverage | Eligibility | Claim Settlement Speed |
| PMFBY | Comprehensive risk coverage | All farmers | Moderate |
| WBCIS | Weather-specific risks | Smallholder and large-scale farmers | Faster |
| Restructured WBCIS | Tailored weather risk coverage | Farmers across varied geographies | Fastest |
The Impact of Crop Insurance on India’s Agricultural Growth
Protection Against Natural Disasters
Natural calamities like floods, droughts, and cyclones have a devastating impact on crops, often pushing farmers into debt.
Crop insurance provides a financial safety net, enabling farmers to recover losses and sustain their livelihoods.
For instance, in Odisha, farmers affected by Cyclone Fani in 2019 received timely compensation through PMFBY, highlighting its role in disaster resilience.
Safeguarding Farmers from Market Volatility
Market fluctuations are another significant challenge. By compensating for losses, crop insurance reduces the economic impact of unpredictable market conditions.
This assurance enables farmers to plan future cropping cycles more confidently.
Encouraging Investments in Modern Farming Techniques
With the assurance of financial protection, farmers are more likely to adopt advanced technologies like precision agriculture, drip irrigation, and high-yield seeds, resulting in increased productivity and efficiency.
Role in Poverty Alleviation
Crop insurance reduces the economic vulnerability of smallholder farmers, thereby contributing to poverty alleviation in rural India.
A World Bank report estimates that effective crop insurance schemes can reduce poverty levels among farmers by up to 15%.
| Impact Areas | Key Benefits |
| Disaster Resilience | Financial recovery from crop losses |
| Economic Stability | Steady incomes despite market risks |
| Technological Adoption | Investments in modern farming tools |
| Poverty Reduction | Improved livelihoods for small farmers |
2025 Trends in Crop Insurance
Use of AI and Big Data for Accurate Risk Assessment
Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics are being used to predict risks more accurately, ensuring fairer premiums and faster claims processing.
For example, satellite imagery combined with AI algorithms helps insurers assess crop damage in real-time, reducing delays.
Blockchain for Transparent Claims Processing
Blockchain technology is being explored to enhance transparency and reduce fraud in claims processing, benefiting both insurers and farmers.
By creating immutable records of policy details and claims, blockchain ensures accountability and builds trust.
| Technology | Application in Crop Insurance | Benefits |
| Artificial Intelligence | Risk assessment, damage prediction | Fair premiums, faster processing |
| Blockchain | Claims transparency, fraud reduction | Trust, accountability |
| Satellite Imagery | Real-time damage evaluation | Quick settlement, accuracy |
Updates to the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
In 2025, PMFBY is set to include enhanced digital platforms for policy enrollment and claims tracking, making it more accessible for farmers.
The government is also piloting parametric insurance models for faster payouts based on predefined triggers like rainfall levels.
Increased Subsidies and Farmer Awareness Programs
The government is increasing subsidies and launching awareness campaigns to ensure wider adoption of crop insurance.
In 2023, awareness drives in Rajasthan resulted in a 40% increase in PMFBY enrollment.
Growth of Microinsurance for Marginal Farmers
Private insurers are offering microinsurance products tailored to the needs of smallholder farmers.
These products focus on affordability and targeted risk coverage, bridging the gap for underserved communities.
Collaborations Between Insurers and Agri-Tech Startups
Collaborations between insurance providers and agri-tech startups are resulting in innovative insurance solutions and wider outreach.
For instance, a partnership between an insurer and a drone company in Tamil Nadu facilitated quicker damage assessments post-floods.
Benefits and Limitations of Crop Insurance
Advantages for Farmers
- Reduced Financial Stress During Crop Failures: Farmers receive timely compensation for losses, enabling quicker recovery.
- Promotion of Sustainable Farming Practices: Financial stability encourages the adoption of environmentally friendly practices.
- Access to Credit: Insured farmers are more likely to secure loans from financial institutions.
Common Challenges and Gaps
- Delayed Claim Settlements: Farmers often face delays in receiving compensation due to bureaucratic hurdles.
- Low Penetration Among Smallholder Farmers: Despite its benefits, crop insurance adoption remains low among marginal farmers due to lack of awareness and high premiums.
- Policy Mismanagement: Instances of underinsurance or improper risk assessment reduce the effectiveness of schemes.
| Challenges | Proposed Solutions |
| Delayed Claims | Digitized claim processes |
| Low Awareness | Extensive farmer education programs |
| High Premiums | Increased government subsidies |
How to Make Crop Insurance More Effective?
Simplifying Policy Terms for Better Understanding
Simplifying jargon-heavy policies can make crop insurance more accessible to farmers with limited literacy.
Visual aids like infographics and multilingual brochures can enhance understanding.
Leveraging Mobile Technology for Accessibility
Mobile apps offering real-time updates on policy terms, weather forecasts, and claims processing can significantly enhance accessibility.
For example, the eNAM platform integrates crop insurance details, streamlining the process for farmers.
Partnerships Between Government, Private Sector, and NGOs
Collaboration between stakeholders can ensure a more inclusive approach to crop insurance.
NGOs can play a critical role in spreading awareness and educating farmers in remote areas.
Increasing Farmer Education Programs
Educational initiatives can build awareness about the benefits of crop insurance and how to enroll.
Programs conducted by Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) have shown promising results in bridging the knowledge gap.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Positive Impact of Crop Insurance on Farmers in India
Farmers in Maharashtra reported a 30% reduction in financial losses after adopting PMFBY.
Similarly, in Andhra Pradesh, timely payouts under WBCIS enabled farmers to reinvest in the next cropping season without falling into debt.
Global Best Practices in Crop Insurance
Countries like Japan and the USA leverage advanced technologies and public-private partnerships, offering valuable lessons for India.
In the USA, parametric insurance models have reduced claims processing time by 50%.
| Country | Best Practices | Impact |
| Japan | Government-backed universal coverage | High farmer participation |
| USA | Parametric models, tech integration | Faster claims, increased adoption |
| Brazil | Community-driven insurance programs | Empowered local farmers |
Takeaways
Crop Insurance in India is a cornerstone of the country’s agricultural resilience. As we move into 2025, advancements in technology, supportive government policies, and active private-sector participation are set to revolutionize the sector.
By addressing existing gaps and promoting widespread adoption, Crop Insurance in India can play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable agricultural growth and improving the lives of millions of farmers.
The future of Indian agriculture hinges on the collective efforts of all stakeholders to make Crop Insurance in India more inclusive, efficient, and impactful.