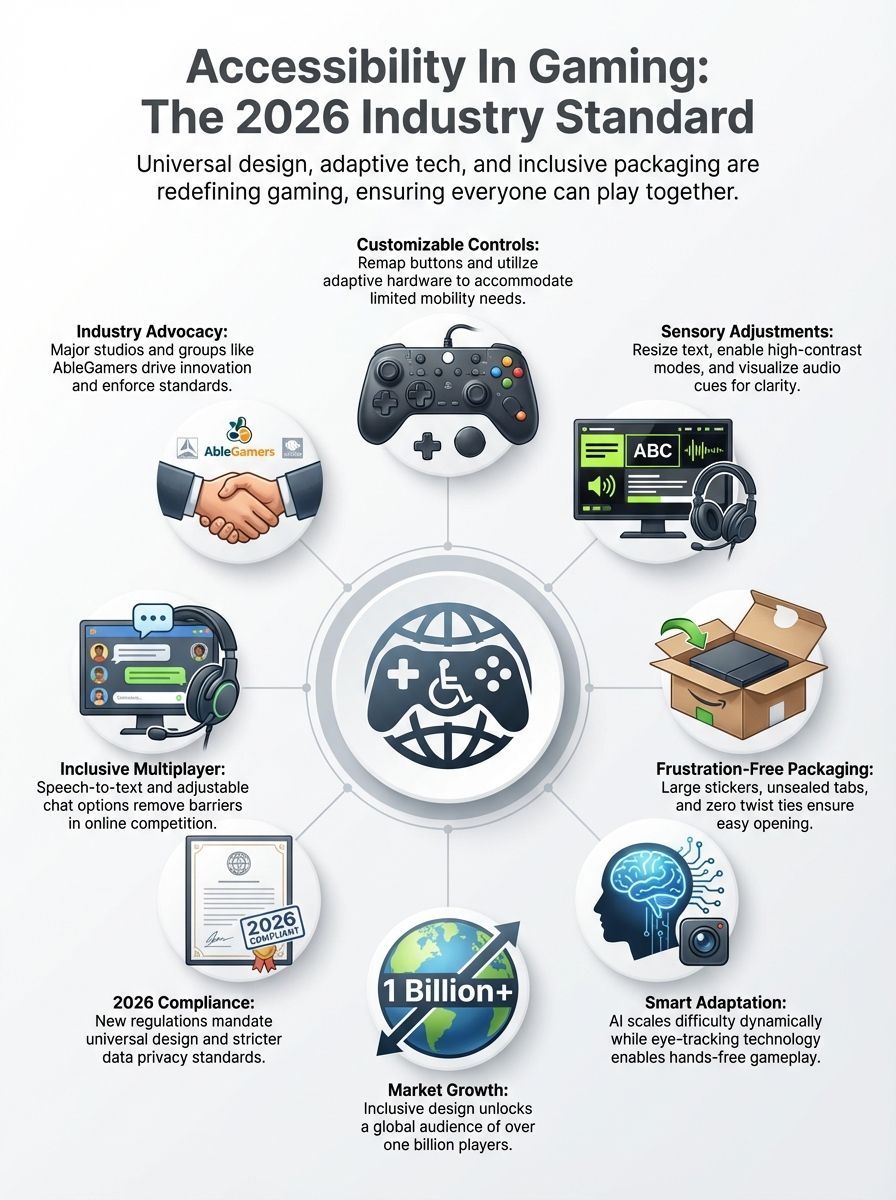
Accessibility in gaming means ensuring that video games are playable and enjoyable for everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. In my work analyzing lifestyle trends, I’ve seen a massive shift: inclusivity isn’t just a “nice-to-have” anymore; it’s a core requirement. We are moving past simple fixes like larger text and entering an era where entire control schemes and difficulty curves are built to be flexible from day one.
From what I’ve seen in the 2026 market, the defining trend is customization. It’s no longer about a single “accessible mode” but rather a suite of granular options that allow players to fine-tune their experience. A 2025 report from the Entertainment Software Association (ESA) found that 21% of adult gamers in the U.S. report having a disability. That is a massive segment of the 205 million Americans who play games.
In this guide, we will break down the specific features defining this new standard, look at the hardware making it possible, and explore the real-world impact on players and developers alike.
What is Accessibility in Gaming
We see that accessibility in gaming shapes how many people play and enjoy games. This means everyone, no matter their ability, can join and have fun together.
Key concepts and definitions
Accessibility in gaming creates an environment where barriers to entry are removed. In 2026, this concept has expanded beyond basic subtitles to include “Universal Design,” a philosophy where features are built to be useful to the widest possible audience from the start.
- Universal Design: This approach ensures features like button remapping help a player with limited mobility just as much as they help a pro gamer optimize their layout.
- Advanced Communications Services (ACS): Under updated FCC interpretations and the CVAA, in-game chat and UI must be accessible, pushing developers to include speech-to-text and text-to-speech as standard.
- Standardized Tags: In 2025, the Accessible Games Initiative (AGI) introduced 24 standardized tags. This common language helps players instantly know if a game supports “No Button Mashing” or “High Contrast UI” before they buy.
Simple features like large stickers on game boxes with unsealed tabs help those who have trouble gripping packages. Removing twist ties from packaging does the same. These physical changes mirror the digital ones, creating a holistic experience where the “game” is accessible from the moment you pick up the box.
Why accessibility matters in gaming
Every player should have the chance to enjoy games, regardless of their abilities. Making gaming accessible helps people with disabilities join in, connect, and have fun just like everyone else.
Financially, the data is clear. The market for accessible game platforms and software is projected to reach approximately $2.3 billion by the end of 2026. This growth is driven by the fact that accessible games simply sell better; they reach a wider audience and keep players engaged longer.
Socially, the impact is even greater. With over one billion people worldwide living with some form of disability, excluding this demographic cuts off a massive source of community and connection. When developers add features such as customizable controls, visual and audio options, and easier difficulty settings, they create an environment where all users feel included and valued.
“According to the 2025 ESA Essential Facts report, 56% of players with disabilities now rate video games as ‘very accessible,’ a number that has risen steadily due to these industry-wide efforts.”
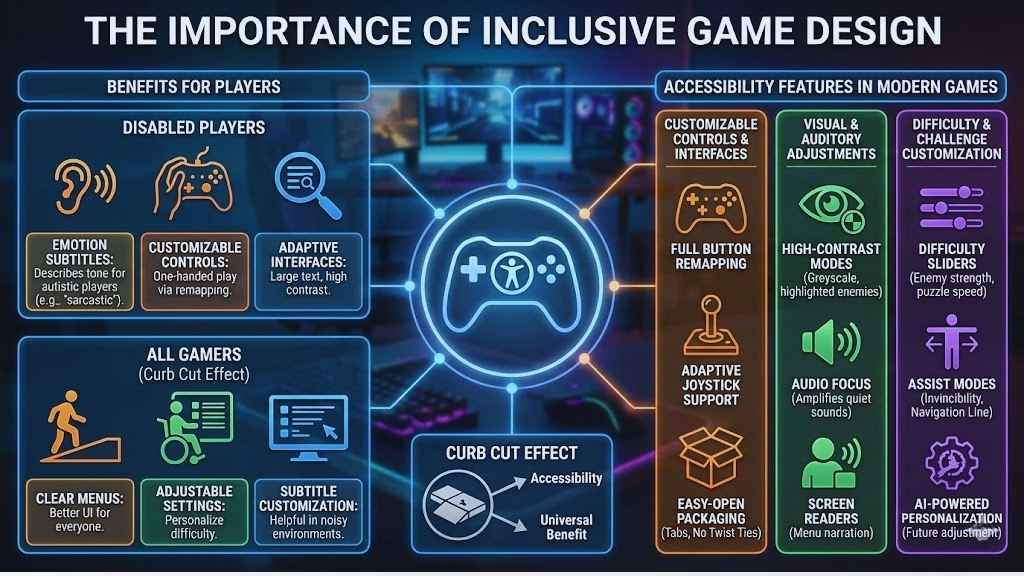
The Importance of Inclusive Game Design
Inclusive game design puts every player at the center, making sure no one feels left out. When we focus on accessibility, everyone can enjoy games in a way that fits their needs and skills, building a better experience for all.
Benefits for players with disabilities
Game accessibility lets more people with disabilities enjoy video games. Features like large stickers on boxes with easy-grip tabs and fewer twist ties in packaging help many players open new games without frustration.
Specific innovations have reshaped the landscape. For example, the “Emotion Subtitles” introduced in titles like Assassin’s Creed Shadows (2025) describe the tone of the speaker—such as “sarcastic” or “tearful”—which is critical for autistic players or those who cannot hear vocal inflections. Customizable controls allow a player with one hand to map all essential actions to a single side of the controller, turning an “unplayable” title into a favorite pastime.
Advantages for all gamers
Accessibility features help everyone play games more easily. This is often called the “Curb Cut Effect”—changes made for disability access end up benefiting everyone. For instance, clear menus and adjustable settings mean we can change the user interface to fit what feels best, which leads to a better player experience.
| Feature | Benefit for Disabled Players | Benefit for All Players |
|---|---|---|
| Subtitle Customization | Essential for deaf/hard-of-hearing players. | Helps when playing with volume down or in noisy rooms. |
| Button Remapping | Allows play with limited motor function. | Lets competitive players optimize reaction times. |
| Visual High Contrast | Vital for low-vision users to see enemies. | Helps anyone spot items quickly in dark/cluttered levels. |
Being able to adjust visuals or sound, lessen packaging with hard-to-open twist ties, or set our own difficulty helps people of any age or skill level join in. Big developers are setting new standards by making inclusivity part of their game design process.
Accessibility Features in Modern Games
We see new games giving players more ways to play, learn, and enjoy at their own pace. These changes make games easier for everyone, no matter what challenges they face.
Customizable controls and interfaces
Customizable controls and interfaces are changing how we play games. These features help more people enjoy gaming, no matter their needs or abilities.
- Many new games now let us remap every button on a controller or keyboard, making it easier for people with limited movement to play comfortably.
- The Xbox Adaptive Joystick, released in early 2025, serves as a wired companion to the Adaptive Controller, allowing for one-handed play with 3D-printable thumbstick toppers.
- In 2026, hardware makers add large stickers with unsealed edge tabs to game boxes, so anyone can open them without trouble.
- Developers remove twist ties inside packaging, reducing frustration for players who have less hand strength or dexterity.
- Companies like SpecialEffect and AbleGamers push the industry forward by working with studios to create universal design standards that focus on usability and inclusivity.
- Customizable settings let users change sensitivity for thumbsticks, swap colors for higher contrast, and turn off flickering lights, which helps those affected by epilepsy or color blindness.
- Game studios now include presets for control layouts designed specifically for adaptive controllers, making accessible technology part of mainstream game development.
- Some online games allow players to set their own interface display size and adjust chat options for easier reading and participation in fast-paced multiplayer matches.
- The rise of flexible user interface systems lets everyone balance challenge and comfort; this creates a better player experience while boosting community engagement among diverse groups.
- The gaming market research predicts that customizable accessibility features will be expected as standard features in major releases starting in 2026 due to both moral responsibility and proven business benefits.
Visual and auditory adjustments
We see how visual and auditory adjustments help open up gaming for many players. These changes make games easier to use, more fun, and fair to everyone.
For audio, the PlayStation Access Controller received a significant update in April 2025 adding “Audio Focus.” This feature amplifies quiet sounds and adjusts frequencies, allowing players with partial hearing loss to detect footsteps or environmental cues they would otherwise miss. Similarly, games like F1 2025 adopted “Blind Driving Assists,” providing audio cues for turns and braking points, allowing visually impaired players to race competitively.
Visual tweaks have also become standard:
- High-Contrast Modes: Games now offer “High Contrast” settings that turn the world greyscale while highlighting enemies in bright red and allies in blue.
- Text Scaling: The ESA reports that 50% of disabled players rate adjustable text size as their most important feature, driving studios to offer massive font options.
- Screen Readers: Menu narration is now expected in 2026, reading out UI elements and inventory descriptions automatically.
Difficulty and challenge customization
Games today are more fun when we can match the challenge to what we need. Flexible options help us all get the best play, no matter our skill, disability, or style.
- Many games now let us change the difficulty, making sure both new and skilled players enjoy them equally.
- Game developers like Xbox and PlayStation studios offer sliders for things like enemy strength or puzzle speed, which helps players with disabilities.
- Custom settings mean players can skip tough levels or make time limits longer, letting more people finish stories and take part in multiplayer modes.
- “Assist Modes” have evolved; titles like South of Midnight (2025) allow players to toggle invincibility or enable a “Navigation Line” with an audio beacon to guide them through complex maps.
- AI-powered personalization is on the rise for 2026, promising that future games will adjust to each person’s needs without much extra work from the player.
- Multiplayer action titles are getting new options for chaos levels and faster respawns so that everyone can jump back into the game quickly and stay included.
- Companies add game packaging changes too—such as large stickers and easy-to-open tabs—to make sure everyone starts playing with less hassle from boxes or setups.
- Games like “The Last of Us Part II” showed how user interface adjustments and adaptive technology make a big difference for many players worldwide.
- Less fiddly packaging inside boxes, such as fewer twist ties, shows how industry standards now look at every step of user experience—not just what happens once we turn on a console.
- These features boost participation and let us all enjoy design standards rooted in inclusivity, giving every gamer a fair shot at fun in 2026 and beyond.
Innovations Driving Accessibility in Gaming
New tools and smart solutions keep changing how we enjoy games. We now see fresh ways for everyone to play, no matter their needs… and the future looks bright.
Assistive technologies and peripherals
Games are now for everyone, including people with disabilities. To help all players, we use special tools and devices.
The hardware market has exploded with modular options. The Byowave Proteus Builder, released in late 2025, allows users to snap together small “cubes” to build a controller shape that fits their specific physical grip. This “LEGO-like” approach means a controller can be a flat board, a handheld stick, or a split device, depending on the day’s needs.
- Nintendo Switch 2 Features: The new console, launched in mid-2025, includes a USB-C port on top specifically to support the Hori Flex accessibility controller, along with uncensored voice-to-text chat.
- Haptic Suits: Wearable tech from companies like bHaptics provides vibration feedback on the body, giving deaf players physical cues for in-game events like explosions or damage.
- Eye-Tracking: Native support for eye-trackers in PC titles has become standard, allowing users to aim or select menu items simply by looking at them.
Dynamic game scaling and adaptive gameplay
We see more games using dynamic scaling and adaptive gameplay in 2026. These features change the game’s difficulty based on how players play. If we face tough challenges, the game can lower barriers or give extra hints.
Generative AI is playing a controversial but growing role here. According to the 2026 State of the Game Industry survey, while 52% of developers have concerns about AI’s impact on jobs, over half are using it. In accessibility, this tech is used to generate real-time sign language interpretation for dialogue or to dynamically adjust enemy aggression levels to match a player’s reaction speed, ensuring the game remains challenging but fair.
Industry Leaders and Pioneers in Accessibility
We see many groups and studios pushing new ideas for better access in games. Their work inspires more teams to make gaming open for all.
The role of AbleGamers and advocacy organizations
AbleGamers leads the way as an advocacy group for gamers with disabilities. They work to make games easier to play for people with different needs. Since its founding, AbleGamers has offered advice and support to game developers, showing them how design changes can help more people join in.
Their “Accessible Player Experiences” (APX) training has become a standard certification for many designers. Other groups like SpecialEffect in the UK have been instrumental in designing bespoke controller setups, like eye-gaze systems, that allow people with severe physical paralysis to play complex games like Minecraft.
Big-name developers making significant changes
Big-name developers like Microsoft and Sony are now setting new design standards for accessibility features. In 2026, clear packaging with easy-grip tabs and less use of twist ties in boxes have made games easier to open for everyone.
Microsoft’s Gaming for Everyone initiative continues to lead with hardware like the Adaptive Joystick. Meanwhile, Ubisoft has mandated that all their AAA titles, from Assassin’s Creed to Far Cry, must include text-to-speech and menu narration at launch. This top-down commitment ensures that accessibility is budgeted for early in development, rather than tacked on at the end.
Challenges and Opportunities in Accessibility
We face many hurdles, yet new doors continue to open for players and developers. Progress relies on teamwork and fresh ideas, shaping the games of tomorrow.
Overcoming current barriers
Making gaming accessible still meets a few hurdles. One significant challenge is the “Engine Gap”—older game engines often lack the built-in tools to support features like screen readers, requiring expensive custom coding to implement.
Legal issues also play a role. The European Accessibility Act (EAA), which became fully enforceable for digital products in June 2025, has forced global changes. Companies that want to sell games in Europe must now meet strict accessibility criteria, effectively making these the global baseline. While this is a positive pressure, it creates a scramble for smaller indie studios that may lack the resources to fully comply without external support.
The future of inclusive game design
We see inclusive game design shaping the industry as a new standard by 2026. Big changes are happening fast, thanks to AI personalization, adaptive technology, and updates in laws that protect data privacy and player safety.
We are moving toward “Accessibility by Default.” Instead of burying options in deep sub-menus, games like Doom: The Dark Ages now present an accessibility wizard upon the very first boot, asking players to set their text size, colorblind modes, and control preferences before the opening cinematic even plays. This ensures no player is blocked from the very first moment of the experience.
Case Studies of Accessible Games
We often find the best ideas in games that have listened to real player needs. These stories show what’s possible when developers put people first, sparking new ways to play for everyone.
Success stories of player-centric design
Game developers are helping more people play through player-centric design. Accessibility features in popular games are now shaping the whole industry.
- Doom: The Dark Ages (2025): Winner of the “Innovation in Accessibility” at The Game Awards, this title featured an industry-first “Parry Visualizer” that turned timing-based blocks into clear visual cues for deaf players.
- Forza Motorsport: Its “Blind Driving Assist” technology set a new bar, using stereo audio panning to let blind players know exactly where they are on the track, a feature later adopted by F1 2025.
- Assassin’s Creed Shadows: Introduced “Emotion Subtitles” and full audio description for cutscenes, ensuring that the narrative was accessible to players with cognitive and sensory disabilities.
- The Last of Us Part II Remastered rolled out over 60 accessibility options, setting the gold standard for third-person action games.
- Xbox added Adaptive Controllers in 2018, and in 2025 expanded the ecosystem with the wireless Adaptive Joystick, boosting community engagement.
- Street Fighter 6 revolutionized fighting games with “Dynamic Controls” and audio cues for distance, allowing blind players to compete at high levels in tournaments like EVO.
- AbleGamers partnered with big studios to help test adaptive technology, including gamepads with large buttons and easier-to-grip packaging like large stickers with unsealed tabs.
- Nintendo made strides by using simpler user interfaces in Animal Crossing: New Horizons, proving that accessible design can improve user experience for all ages and abilities.
- Accessible multiplayer games such as Rocket League now use visual cues, colorblind modes, and voice chat adjustments so everyone can compete at their own level of challenge.
- AI-powered personalization is expanding fast in game-based learning apps; these programs adjust content based on each player’s needs, supporting better participation for children who face cognitive or physical challenges.
Lessons learned from pioneering games
Many leading games have made big changes in accessibility features. We can use their work as a guide for future inclusive game design.
- Early Involvement is Key: Studios that consulted with disabled gamers during the concept phase, rather than beta testing, avoided costly redesigns later.
- Options, Not Easy Modes: Players want to overcome challenges, not skip them. Celeste proved that “Assist Mode” lets players tweak the difficulty (like slowing down game speed) without removing the sense of accomplishment.
- Standardization Works: The adoption of the AGI’s standardized tags has reduced confusion, proving that the industry benefits when everyone uses the same terminology for features like “Subtitle Sizing” or “Input Remapping.”
Final Thoughts
We have seen how accessibility in gaming is changing the way we design and play. From the “Blind Driving Assists” in racing simulators to the “Emotion Subtitles” in massive RPGs, the industry has proven that inclusion drives innovation.
In 2026, accessibility is no longer a niche feature; it is the foundation of modern game design. By embracing universal standards and listening to the 21% of gamers with disabilities, developers are building a richer, more vibrant ecosystem for us all. Let’s keep building a future where all can play together and enjoy the adventure equally; after all, anyone should get to press start on their own story.