Blockchain technology is at the heart of Web3, revolutionizing industries by enabling decentralization, transparency, and security. Unlike traditional web infrastructure, Web3 leverages blockchain innovations to create a more user-centric and trustless ecosystem.
This article explores 10 key innovations in blockchain technology powering Web3, shedding light on their significance, use cases, and future potential.
From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), blockchain innovations are reshaping digital interactions and ownership.Smart contracts, interoperability solutions, and zero-knowledge proofs enhance efficiency and privacy in Web3 applications.
As blockchain adoption grows, these advancements are driving new business models and redefining online experiences. This article delves into these transformative technologies, providing insights into how they are shaping the future of the internet.
Web3 eliminates reliance on centralized authorities, granting users greater control over their data and digital assets. ‘
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are emerging as a new form of governance, empowering communities to make collective decisions.
Layer 2 scaling solutions improve blockchain efficiency by reducing congestion and lowering transaction costs.
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has emerged as one of the most transformative applications of blockchain technology. It eliminates intermediaries like banks and financial institutions, allowing users to access financial services through smart contracts. DeFi platforms provide lending, borrowing, staking, and yield farming opportunities, redefining the traditional financial system.
Key Features of DeFi:
| Feature | Description |
| Smart Contracts | Automates transactions and eliminates intermediaries |
| Yield Farming | Earn rewards by providing liquidity |
| Lending & Borrowing | Peer-to-peer financial transactions without banks |
| Stablecoins | Crypto assets pegged to fiat currencies |
Example: Uniswap, a decentralized exchange, allows users to swap tokens without intermediaries, demonstrating the power of DeFi.
2. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are blockchain-based digital assets that verify ownership and authenticity of unique items. Unlike cryptocurrencies, which are fungible and interchangeable, each NFT is distinct due to its embedded metadata.
This uniqueness has enabled transformative applications across various industries, including digital art, gaming, virtual real estate, and collectibles. By leveraging blockchain’s transparency and immutability, NFTs facilitate secure transactions, provenance tracking, and direct creator-to-consumer interactions, revolutionizing the digital ownership landscape.
Key Uses of NFTs:
| Use Case | Description |
| Digital Art | Ownership of rare digital artwork |
| Gaming Assets | Unique in-game collectibles and skins |
| Virtual Real Estate | Ownership of parcels in the Metaverse |
| Music & Media | Artists tokenize their work for direct sales- |
Example: The sale of Beeple’s digital artwork for $69 million highlights how NFTs are reshaping the art world.
3. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements encoded within blockchain technology, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks or legal entities. These contracts autonomously enforce and execute transactions once predefined conditions are met, reducing human intervention, enhancing efficiency, and minimizing the risk of fraud.
By leveraging blockchain’s transparency and immutability, smart contracts ensure secure, trustless agreements, making them invaluable for DeFi applications, supply chain management, and digital identity verification.
Their growing adoption is transforming industries by enabling automation, cost reduction, and seamless execution of complex agreements.
Advantages of Smart Contracts:
| Advantage | Description |
| Automation | Executes agreements without intermediaries |
| Security | Immutable and tamper-proof |
| Transparency | Open-source and auditable |
| Efficiency | Reduces transaction costs and time |
Example: Ethereum pioneered smart contracts, enabling dApps, DeFi, and tokenization of assets.
4. Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 solutions significantly enhance blockchain scalability by processing transactions off-chain while preserving the underlying network’s security and decentralization. These solutions address major challenges such as network congestion, high gas fees, and slow transaction speeds, making blockchain more efficient for widespread adoption. By leveraging technologies like rollups, state channels, and sidechains, Layer 2 solutions facilitate faster and cheaper transactions without compromising security.
Their growing adoption is crucial for supporting high-demand applications in DeFi, NFTs, and gaming, where seamless and cost-effective transactions are essential.
Popular Layer 2 Solutions:
| Solution | Description |
| Lightning Network | Speeds up Bitcoin transactions |
| Polygon | Enhances Ethereum’s scalability |
| Optimistic Rollups | Batches transactions to reduce congestion |
| zk-Rollups | Uses zero-knowledge proofs for security & speed |
Example: Polygon helps reduce Ethereum transaction fees while improving transaction speed.
5. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are self-governing entities powered by blockchain-based smart contracts, ensuring transparency, security, and fairness in decision-making.
Unlike traditional organizations, DAOs operate without centralized leadership, allowing token holders to propose, debate, and vote on key decisions collectively. This model fosters true decentralization, where governance is dictated by community consensus rather than hierarchical structures.
DAOs play a crucial role in Web3, revolutionizing industries such as finance, gaming, and social networks by enabling democratic participation in resource allocation and strategic planning.
Features of DAOs:
| Feature | Description |
| Transparency | Open-source governance and decision-making |
| Token-Based Voting | Users influence decisions via token holdings |
| Community Control | Eliminates centralized authority |
| Treasury Management | Funds managed collectively |
Example: MakerDAO governs the DAI stablecoin through decentralized voting mechanisms.
6. Web3 Identity & Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized Identity (DID) empowers individuals with complete control over their digital identities, eliminating the need for centralized intermediaries.
By leveraging blockchain technology, DID solutions ensure secure, verifiable, and self-sovereign identities that protect privacy, reduce the risk of identity theft, and enable seamless authentication across diverse digital ecosystems.
Benefits of Decentralized Identity:
| Benefit | Description |
| Self-Sovereignty | Users control their own identity |
| Privacy | Eliminates data leaks and surveillance |
| Security | Reduces identity theft risks |
| Interoperability | Works across multiple applications |
Example: Microsoft’s ION is a decentralized identity solution built on Bitcoin’s blockchain.
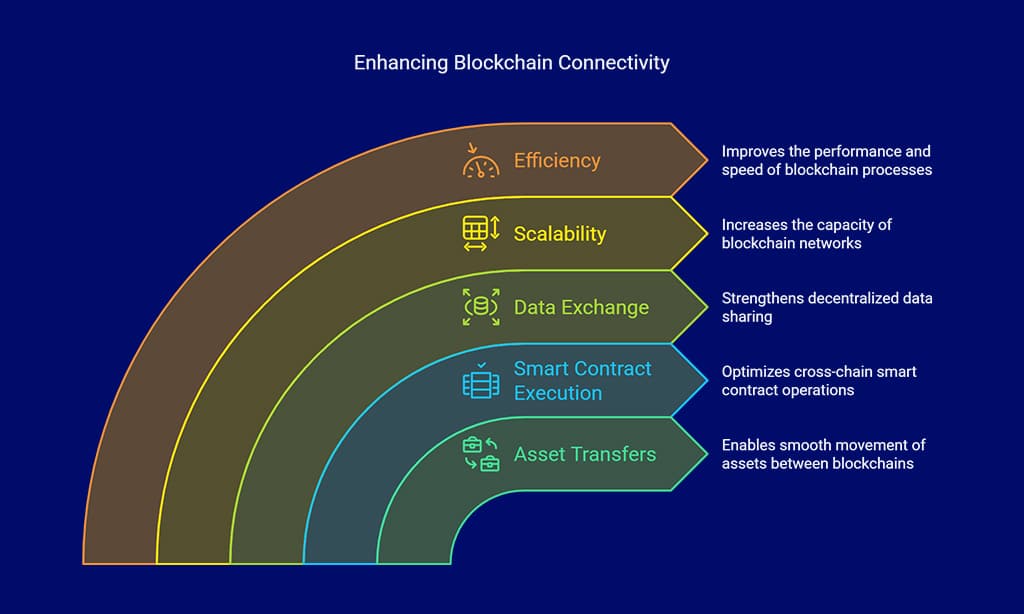
7. Cross-Chain Interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability facilitates seamless interaction between distinct blockchain networks, allowing frictionless asset transfers, optimized execution of cross-chain smart contracts, and fortified decentralized data exchange.
This integration enhances blockchain ecosystem scalability, efficiency, and adaptability, fostering a more interconnected and versatile digital landscape.
Key Interoperability Protocols:
| Protocol | Functionality |
| Polkadot | Connects multiple blockchains into one network |
| Cosmos | Facilitates blockchain communication |
| Chainlink | Provides oracles for cross-chain transactions |
| Wanchain | Connects isolated blockchains |
Example: Polkadot’s parachain architecture allows different blockchains to operate together.
8. Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Management
Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by providing an immutable and verifiable ledger, ensuring precise tracking of goods at every stage while bolstering security and trust.
It minimizes fraud, reduces delays, and enhances efficiency by enabling real-time data sharing among stakeholders.
Smart contracts automate transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and lowering costs. Companies can trace the origin of products, ensuring authenticity and compliance with regulations. This technology fosters a more resilient, accountable, and efficient supply chain ecosystem.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chains:
| Benefit | Description |
| Transparency | Tracks goods from origin to consumer |
| Fraud Prevention | Prevents counterfeit products |
| Efficiency | Reduces paperwork and verification delays |
| Cost Savings | Minimizes middlemen and transaction fees |
Example: IBM’s Food Trust blockchain enhances food traceability for safety and efficiency.
9. Privacy-Preserving Technologies
Privacy-focused blockchain innovations, such as Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) and Confidential Transactions, significantly enhance user security by ensuring transactional privacy and minimizing data exposure.
Privacy Technologies:
| Technology | Purpose |
| Zero-Knowledge Proofs | Verifies data without revealing content |
| Ring Signatures | Conceals transaction participants |
| Confidential Transactions | Hides transaction amounts |
Example: Zcash implements ZKPs to offer private cryptocurrency transactions.
10. Tokenization of Real-World Assets
Tokenization transforms real-world assets such as real estate, art, and commodities into blockchain-based digital tokens, facilitating fractional ownership, improved liquidity, and seamless global trading.
By leveraging smart contracts and blockchain security, tokenized assets enable investors to buy, sell, and trade portions of high-value assets in a transparent and efficient manner.
Tokenization Benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
| Fractional Ownership | Allows shared asset investment |
| Liquidity | Makes assets more tradable |
| Security | Reduces fraud and ensures transparency |
| Global Access | Enables cross-border investments |
Example: RealT tokenizes real estate properties, allowing investors to own fractions of real estate assets.
Final Words
The rapid advancements in blockchain technology are fueling the growth of Web3, driving innovation across multiple industries by enhancing decentralization, transparency, security, and user autonomy.
These 10 key innovations in blockchain technology powering Web3 are reshaping traditional finance, governance, privacy, and digital ownership while opening new avenues for trustless and efficient digital interactions.
As these groundbreaking technologies continue to evolve, they offer scalable solutions to long-standing issues such as high transaction costs, data privacy concerns, and centralized control. The future of Web3 promises a more inclusive and user-empowered digital ecosystem where individuals, businesses, and economies can operate with greater security, efficiency, and autonomy.