Washington and Beijing have moved closer to resolving one of the most contentious issues in their ongoing trade standoff — the future of TikTok’s U.S. operations. After several days of discussions in Madrid, U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent confirmed that the two countries had agreed on a framework deal that lays the groundwork for TikTok’s American ownership. The announcement marked a turning point in negotiations between the world’s two largest economies, as both sides are also seeking progress on broader trade issues such as tariffs, market access, and data governance.
The framework emerged just days before a looming deadline requiring ByteDance, TikTok’s parent company based in Beijing, to divest its U.S. operations or face a nationwide ban. The talks in Madrid brought together senior American and Chinese officials, with U.S. President Donald Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping expected to give their final approval later in the week. The outcome could shape not only TikTok’s presence in the U.S. but also the trajectory of U.S.-China economic relations.
The Deadline and Previous Extensions
The U.S. government had set September 17, 2025, as the latest deadline for ByteDance to finalize a sale. This followed multiple extensions after the law requiring divestiture was passed in 2024. Originally, ByteDance was given just a few months to comply, but the complexity of negotiations, legal challenges, and ongoing trade tensions led to repeated delays.
Earlier in 2025, TikTok even experienced a temporary blackout in the U.S. after the law technically came into effect. That shutdown lasted a day before the Trump administration issued a 75-day postponement, allowing ByteDance to continue operations while seeking buyers. These delays reflected the difficulty of balancing legal requirements, national security concerns, and the app’s immense popularity among American users, who now number around 170 million.
Oracle and Potential Buyers
As discussions intensified, several potential buyers emerged for TikTok’s U.S. operations. Reports from U.S. media outlets indicated that Oracle, already a long-time contender, was part of a consortium exploring ways to ensure TikTok could keep running under American control. Tech investors such as Oracle co-founder Larry Ellison, YouTube creator MrBeast, and billionaire Frank McCourt were also mentioned as potential backers of different proposals.
While details of the framework remain limited, Oracle’s role is seen as crucial because of its experience in data security and cloud storage, which are central to U.S. concerns. The framework deal suggests that American firms would oversee TikTok’s U.S. data storage, auditing, and possibly its recommendation system to ensure no influence or backdoor access by Beijing.
National Security Concerns Driving the Deal
At the heart of the standoff are U.S. national security concerns. Officials in Washington have argued that TikTok’s access to sensitive data from millions of American users could be exploited by China’s government. The U.S. Justice Department has repeatedly stressed that this risk is not theoretical but represents a significant threat to national security. Analysts fear that personal data, location tracking, and behavioral information collected by the app could be used to train artificial intelligence models, enhance China’s cyber capabilities, or even inform military intelligence.
ByteDance has strongly rejected these accusations, insisting that TikTok’s U.S. operations are independent and that American user data has never been shared with Chinese authorities. The company also argued that an outright ban would violate free speech rights and harm the platform’s huge American user base, which includes small businesses, creators, and influencers who rely on TikTok for income.
The Role of Trade Negotiations
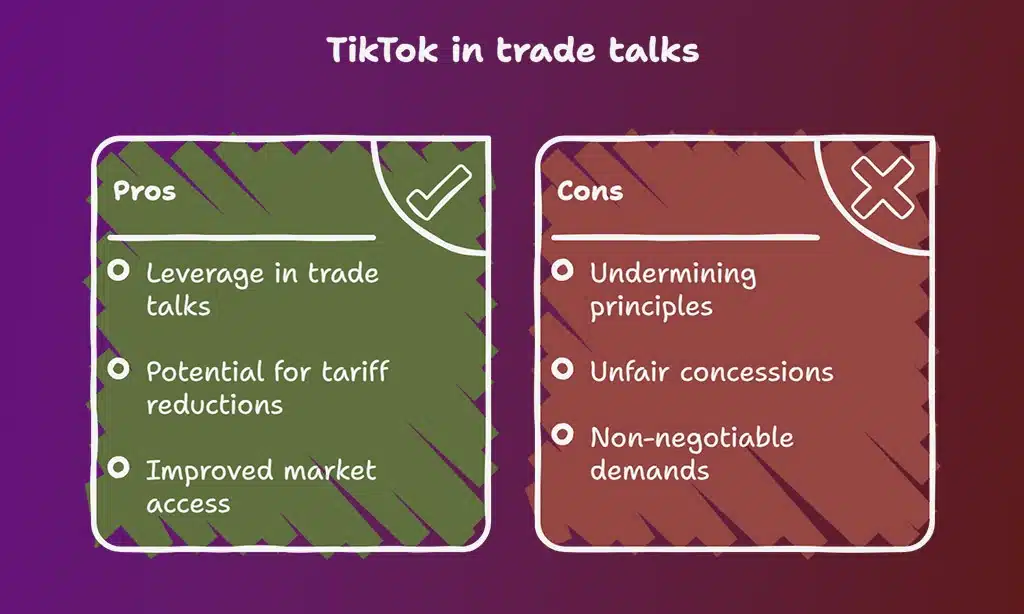
The TikTok issue has become deeply tied to the broader U.S.-China trade war. At its height, tariffs imposed by both countries reached 145% on certain goods, hurting businesses and consumers in both economies. By linking TikTok’s ownership structure to trade talks, negotiators hoped to use the popular app as leverage in discussions about tariff reductions, intellectual property protections, and access to each other’s markets.
For Beijing, agreeing to a U.S. framework deal on TikTok represents a delicate balance. Chinese officials emphasized that no deal would be signed if it undermined the country’s principles or forced Chinese companies into unfair concessions. For Washington, ensuring that TikTok’s algorithm, data storage, and operational independence fall under American oversight has become a non-negotiable demand.
Algorithm and Data Security Questions
Despite progress on ownership, many unresolved questions remain. Experts warn that transferring TikTok’s powerful recommendation algorithm may prove more complex than signing a sale agreement. The algorithm is widely regarded as TikTok’s most valuable asset, shaping the app’s global success by customizing content for each user.
National security analysts argue that unless the U.S. gains full control over the algorithm and can conduct independent audits, risks will persist. Questions also remain about whether TikTok’s American user data will be fully encrypted and stored on U.S. soil, and whether safeguards will be introduced to prevent covert access by Chinese authorities. These technical issues may determine whether the deal is seen as credible protection against foreign interference or merely a symbolic gesture.
Supreme Court Ruling and Legal Backdrop
The push to resolve TikTok’s ownership stems from legislation passed in April 2024, requiring ByteDance to divest its U.S. arm or face a ban. In January 2025, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the law, rejecting arguments that it violated free speech protections. The ruling gave Congress and the executive branch clear authority to enforce the sale on national security grounds.
This ruling set a legal precedent for how the U.S. might handle other foreign-owned technology companies deemed security risks. It also increased pressure on ByteDance by leaving little room for further legal appeals, forcing the company to engage in negotiations despite its reluctance.
Stakes for ByteDance and the U.S.
ByteDance is one of China’s most prominent technology companies and a global leader in artificial intelligence. Losing control over TikTok’s U.S. operations would represent a significant setback. Analysts say it could weaken ByteDance’s position in the international market and reduce its ability to monetize one of its most valuable platforms.
For the U.S., securing control of TikTok is about more than one app. It reflects broader concerns about Chinese influence in the digital economy and the need to set standards for data security. If the framework deal is finalized, it could serve as a model for future U.S. actions against foreign-owned digital platforms.
What Comes Next
The framework is not yet a final agreement. Both governments must still iron out technical details, legal compliance, and political acceptance. President Trump and President Xi are expected to meet at the end of the week to finalize terms. Until then, questions remain over how much ownership ByteDance may retain, whether U.S. investors can fully control TikTok’s algorithm, and how data security will be enforced.
If the deal succeeds, it could prevent TikTok from being banned in the U.S., safeguard American user data, and ease tensions in U.S.-China trade talks. However, if negotiations collapse, the U.S. government may move forward with enforcing the ban, potentially shutting out one of the world’s most popular apps from the American market.