Managing taxes can be a daunting task for self-employed professionals. Unlike salaried employees, who typically have taxes withheld automatically, self-employed individuals must actively track income, calculate deductions, and ensure compliance with Australian tax laws.
Understanding these obligations is essential to avoid penalties and maximize your savings. This guide offers 12 essential tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia, ensuring you stay on top of your finances while reducing stress.
By implementing these tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia, you can secure your financial future and optimize your tax strategy.
Understanding the Basics of Taxation for Self-Employed Professionals
Being self-employed in Australia encompasses a variety of roles, including freelancers, consultants, sole traders, and small business owners.
Self-employed individuals enjoy the flexibility of setting their schedules and determining their workload.
However, this independence comes with the responsibility of managing all aspects of their business, including taxes.
Key characteristics of self-employment include:
- Generating income directly from clients or customers rather than being on a payroll.
- Responsibility for managing your own taxes, including income tax and GST.
- The need to register for an Australian Business Number (ABN) to operate legally.
Having an ABN is vital for invoicing and claiming GST credits, allowing smooth interactions with the Australian Taxation Office (ATO).
Additionally, self-employed individuals must manage their own superannuation contributions and maintain detailed financial records for compliance.
These foundational elements are critical for applying tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia effectively.
Overview of Tax Obligations in Australia
Self-employed professionals must fulfill several tax obligations, including:
- Income Tax: Based on your taxable income after allowable deductions, which must be declared annually.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Required for businesses earning over $75,000 annually, with mandatory quarterly reporting.
- Medicare Levy: A 2% levy on your taxable income to fund healthcare.
Failing to comply with these obligations can result in penalties, interest charges, or legal consequences.
Setting up proper systems for tracking income, expenses, and deadlines will help you manage your taxes efficiently and reduce stress.
These steps form the foundation for utilizing tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia effectively.
12 Essential Tax Tips for Self-Employed Professionals
1. Separate Personal and Business Finances
Separating your personal and business finances is critical for maintaining clear records and minimizing confusion during tax filing.
By keeping them distinct, you can easily identify deductible expenses and ensure accurate reporting.
Here’s how to start:
- Open a dedicated business bank account to handle all income and expenses.
- Use a business credit card for purchases related to your operations.
- Regularly reconcile your accounts to monitor your financial health and detect any discrepancies early.
Benefits of Separating Personal and Business Finances
| Benefit | Description |
| Simplified Tax Filing | Clear distinction between personal and business expenses. |
| Better Cash Flow Tracking | Accurate insights into business profitability and expenses. |
| Enhanced Professionalism | Builds trust with clients and financial institutions. |
Extra Tip:
Many banks offer business-specific accounts with features tailored to small business owners, such as automated reporting and integration with accounting software.
Research and choose the best option for your needs to implement this key tax tip for self-employed professionals in Australia.
2. Keep Accurate Records Year-Round
Accurate record-keeping is the cornerstone of effective tax management.
Self-employed individuals must maintain meticulous records to comply with ATO requirements and ensure all potential deductions are captured.
Essential practices include:
- Retaining invoices, receipts, and payment records for at least five years.
- Utilizing tools like Xero, MYOB, or QuickBooks for automated bookkeeping.
- Backing up digital records regularly to protect against data loss.
Practical Example:
Sarah, a freelance graphic designer, uses QuickBooks to track all her invoices and expenses.
By categorizing her expenses and syncing them with her bank account, she ensures accurate records and reduces her tax filing time by 50%.
This method highlights the importance of implementing tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
Recommended Accounting Tools
| Tool | Features | Price Range |
| Xero | Cloud-based, invoicing, expense tracking | $25 – $60/month |
| MYOB | Payroll integration, BAS reporting | $27 – $120/month |
| QuickBooks | User-friendly, multi-device support | $25 – $50/month |
3. Understand GST and When to Register
If your annual turnover exceeds $75,000, you must register for GST. Managing GST obligations requires proactive planning and consistent record-keeping.
Key steps include:
- Register for GST through the ATO’s online services to streamline compliance.
- Include GST in your invoices (10% of the total amount charged to clients).
- Lodge a Business Activity Statement (BAS) quarterly to report GST collected and claimed.
Key GST Information
| Aspect | Details |
| Registration Threshold | $75,000 annual turnover |
| GST Rate | 10% |
| Reporting Method | Quarterly BAS submission |
Extra Tip:
Keep a separate account for GST payments to avoid spending funds that must later be remitted to the ATO.
Automated reminders can also help you meet BAS submission deadlines. This approach is integral to mastering tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
4. Track and Maximize Business Deductions
Deductions are a powerful tool for reducing your taxable income, but they require careful tracking and substantiation.
Common deductions for self-employed professionals include:
- Home Office Expenses: Rent, utilities, and internet costs proportional to your workspace usage.
- Travel Costs: Flights, accommodation, and meals for business-related trips.
- Equipment: Purchases such as laptops, phones, and software directly used for your work.
Common Tax Deductions and Tips
| Expense Category | Example | Tips |
| Home Office Utilities | Electricity, Internet | Calculate business-use percentage accurately. |
| Travel Costs | Flights, Hotels | Keep receipts and travel logs for substantiation. |
| Professional Services | Legal, Accounting Fees | Use services exclusively related to your business. |
Example:
Tom, an independent software developer, uses a portion of his home for work.
By measuring the area of his workspace and calculating the percentage of his home’s total area, he accurately claims deductions for utilities and rent.
This method demonstrates the practical application of tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
5. Stay on Top of Quarterly BAS Reporting
For GST-registered businesses, quarterly BAS reporting is mandatory. Ensuring accurate and timely submissions prevents penalties and simplifies GST management.
Follow these tips:
- Set calendar reminders for BAS deadlines to avoid last-minute stress.
- Use accounting software to calculate GST automatically and prepare reports.
- Double-check entries for errors that could trigger audits.
BAS Deadlines
| Quarter | Deadline |
| January – March | April 28 |
| April – June | July 28 |
| July – September | October 28 |
| October – December | January 28 |
Extra Tip:
Consider outsourcing BAS preparation to a registered BAS agent if your reports are complex or time-consuming.
This investment can save you significant time and ensure compliance while applying tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
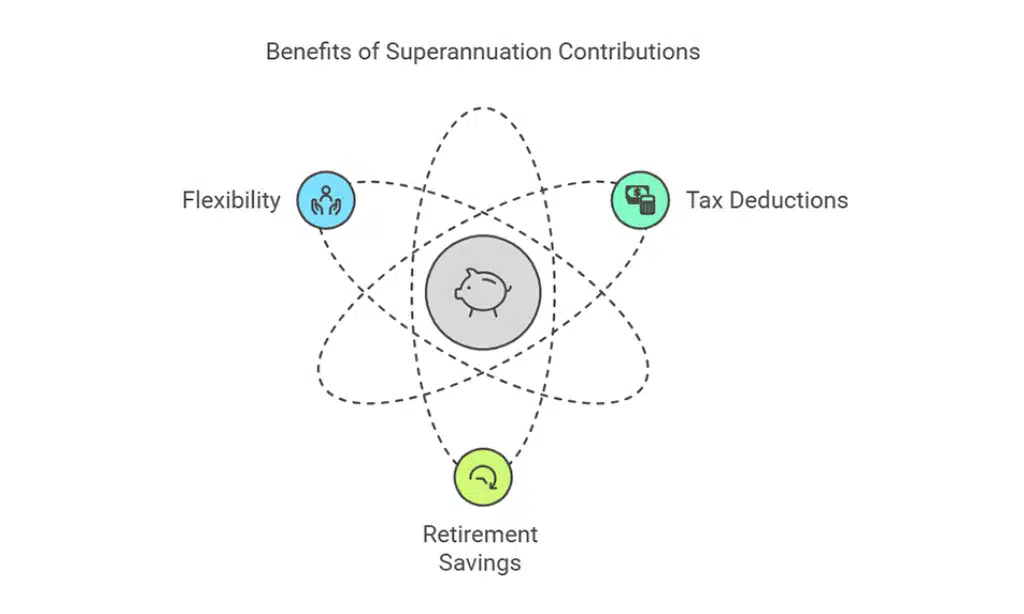
6. Consider Superannuation Contributions
Superannuation contributions are not mandatory for self-employed professionals in Australia, but they offer significant long-term benefits.
Planning for retirement while reducing taxable income is an effective strategy.
Here are the key points:
- Tax Deductions: Contributions to your super fund are tax-deductible, reducing your overall taxable income.
- Retirement Savings: Ensures financial security during retirement.
- Flexibility: Self-employed individuals can choose their contribution amount and frequency.
Super Contribution Limits (2025)
| Type of Contribution | Annual Limit |
| Pre-Tax (Concessional) | $27,500 |
| After-Tax (Non-Concessional) | $110,000 |
Extra Tip:
Emily, a freelance writer, contributes $15,000 annually to her superannuation fund.
By claiming this as a tax deduction, she saves on her tax bill and secures her retirement, demonstrating the value of implementing tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
7. Save for Tax Payments in Advance
Unlike salaried workers, self-employed professionals must set aside money for tax payments.
Planning ahead avoids financial stress.
Here’s how to prepare:
- Set Aside Income: Allocate 25-30% of each payment to a tax savings account.
- Track Earnings: Use accounting software to monitor income fluctuations.
- Make Quarterly Payments: Submit voluntary payments to the ATO.
Tax Savings Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
| Open a Tax Savings Account | Separate account dedicated to taxes. |
| Automate Contributions | Automatically transfer a portion of income. |
| Estimate Quarterly Payments | Avoid surprises with regular estimates. |
Extra Tip:
Freelancer Ben sets up automatic transfers to a savings account for every payment he receives.
This ensures he’s always prepared for tax deadlines, an essential habit for mastering tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
8. Claim the Instant Asset Write-Off
The instant asset write-off allows immediate deductions for business purchases.
Key details include:
- Eligibility: Sole traders and businesses with annual turnover under $10 million.
- Deduction Limits: Updated annually; check ATO guidelines.
- Asset Types: Includes tools, equipment, and technology used for business.
Instant Asset Write-Off Details
| Criteria | Details |
| Business Turnover Limit | $10 million |
| Deduction Threshold | Refer to ATO updates |
| Eligible Purchases | Business equipment, vehicles, technology |
Extra Tip:
Laura, a self-employed architect, purchased a new computer for $3,000. She claimed the full amount using the instant asset write-off, reducing her taxable income significantly.
9. Leverage Small Business Tax Offsets
Small Business Income Tax Offsets help reduce tax payable for eligible businesses.
Key points:
- Eligibility: Applies to sole traders and small businesses earning less than $5 million annually.
- Maximum Offset: Up to $1,000.
- Automatic Application: Offset is applied when lodging your tax return.
Small Business Tax Offset Highlights
| Feature | Details |
| Eligibility | Sole traders, small business owners |
| Maximum Offset | $1,000 |
| Application Process | Automatic with tax return |
Extra Tip:
Anna, a sole trader earning $60,000 annually, received a $600 offset through the Small Business Tax Offset, demonstrating the value of exploring all available tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
10. Work with a Registered Tax Agent
Hiring a tax agent simplifies tax management and ensures compliance.
Benefits include:
- Expertise: Access to updated tax laws.
- Time-Saving: Focus on business while the agent handles taxes.
- Maximized Deductions: Discover additional claims you might miss.
Benefits of Hiring a Tax Agent
| Benefit | Description |
| Expertise | Understands complex tax laws |
| Accuracy | Reduces risk of errors or penalties |
| Efficiency | Saves time and ensures timely filing |
Extra Tip:
Hiring a registered tax agent saved freelance designer Mike countless hours and increased his deductions by 20%.
11. Regularly Review Your Income
Self-employment often involves fluctuating income.
Regular reviews help:
- Adjust Budgets: Adapt to seasonal variations.
- Track Growth: Identify income trends.
- Plan Tax Payments: Prepare for larger tax obligations during peak months.
Income Review Checklist
| Task | Purpose |
| Analyze Monthly Earnings | Understand trends and identify slow periods. |
| Set Financial Goals | Plan for growth and investments. |
| Adjust Budgets | Align expenses with income fluctuations. |
Extra Tip:
Regular income reviews enabled Alex, a consultant, to forecast cash flow and save for upcoming tax payments efficiently.
12. Stay Updated on Tax Law Changes
Tax laws frequently change. Staying informed ensures compliance and maximizes benefits.
Steps include:
- Monitor ATO Announcements: Check for updates regularly.
- Subscribe to Newsletters: Industry updates often highlight changes.
- Consult Experts: Tax agents can provide personalized guidance.
Resources for Tax Updates
| Source | Details |
| ATO Website | Official updates on Australian tax laws. |
| Professional Newsletters | Industry-specific tax tips and changes. |
| Tax Agent | Personalized advice on compliance and claims. |
Extra Tip:
In 2023, updates to small business offsets helped freelancer Katie save an additional $800.
Staying informed enabled her to effectively implement the latest tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia.
Takeaways
Navigating the complexities of taxation as a self-employed professional in Australia can be challenging, but implementing the right strategies can make a significant difference.
By adopting these tax tips for self-employed professionals in Australia, such as keeping accurate records, maximizing deductions, leveraging the instant asset write-off, and staying informed about tax law changes, you can streamline your tax management and secure your financial future.
Remember, proactive planning, disciplined financial habits, and regular reviews of your income and expenses are key to minimizing stress and maximizing savings.
For personalized advice, consult a registered tax agent who can tailor strategies to your unique circumstances.
With these tips, you’ll not only stay compliant with Australian tax laws but also optimize your business’s profitability and growth potential.