New Zealand’s sheep industry has been integral to the nation’s economy, cultural heritage, and global trade reputation for generations. Renowned worldwide for its premium quality wool, lamb, and mutton exports, the industry significantly contributes to New Zealand’s GDP, employing thousands of rural and urban workers across farming, processing, and exporting sectors.
Over the years, the sector has adapted successfully to market fluctuations and evolving consumer demands. However, as we move into 2025, the sheep industry faces unprecedented challenges that threaten its long-term sustainability and growth.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the 5 Challenges Facing New Zealand’s Sheep Industry in 2025, highlighting key issues, presenting real-world case studies, and proposing comprehensive, actionable solutions aimed at fortifying the industry’s resilience and securing its global competitiveness.
Challenge 1: Climate Change Impact on Sheep Farming
Climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing concerns for New Zealand’s sheep industry, influencing nearly every aspect of farm operations. Farmers are experiencing unpredictable weather conditions, longer dry seasons, and sudden, intense storms, making it difficult to plan and manage livestock efficiently.
These disruptions impact not only pasture growth and water availability but also increase the frequency of disease outbreaks and heat stress in sheep. With climate patterns expected to continue shifting unpredictably, long-term solutions are essential for ensuring the sustainability and productivity of the industry.
How Climate Change Affects New Zealand’s Sheep Industry
Climate change significantly threatens the resilience and productivity of sheep farming, posing both immediate and long-term risks. The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as prolonged droughts, devastating floods, and erratic temperature fluctuations, deeply disrupt farming operations. Extended drought conditions severely limit pasture growth, pushing farmers toward expensive supplementary feeding options that drastically elevate production costs.
Floods not only cause direct livestock losses but also lead to substantial infrastructural damage, necessitating costly repairs and disrupting farm management practices. Additionally, temperature irregularities can compromise sheep health and reduce wool quality, further affecting profitability. Collectively, these climate-related factors necessitate immediate, adaptive strategies to ensure the industry’s sustainability and growth.
Real-World Example:
In 2023, severe drought in Hawke’s Bay resulted in pasture shortages, leading farmers to spend significantly more on supplementary feed, causing widespread economic strain across the region.
Strategies for Adaptation
- Plant drought-resistant pasture and forage species.
- Implement predictive analytics to forecast weather-related risks.
- Invest in efficient water harvesting and management systems.
Quick Reference Table
| Climate Issue | Impact | Adaptation Strategies |
| Drought | Reduced pasture availability | Drought-resistant pastures, supplementary feeding |
| Flooding | Livestock loss, infrastructure damage | Flood barriers, elevated infrastructure |
| Temperature fluctuations | Health issues, reduced wool quality | Climate-controlled shelters, genetic adaptation |
Challenge 2: Increasing Production Costs
The rising costs of production have become a pressing concern for sheep farmers across New Zealand. With inflationary pressures, fluctuating global commodity prices, and the increasing cost of essential farm inputs, many farmers are struggling to maintain profitability. Feed prices continue to surge due to supply chain disruptions and climate-related reductions in pasture availability.
Fuel prices, driven by global economic instability and geopolitical tensions, further strain farm operations by increasing transportation and machinery costs. Additionally, labor shortages have led to higher wages, making skilled farm workers more expensive and harder to retain.
Environmental compliance and sustainability initiatives, while necessary for long-term resilience, require significant financial investments, adding another layer of cost pressure. If not addressed effectively, these rising expenses could threaten the long-term viability of sheep farming in New Zealand.
Factors Driving Up Costs
Rising production costs pose significant risks to New Zealand’s sheep industry, driven primarily by substantial increases in critical inputs such as feed, fuel, and labor wages, coupled with escalating expenses related to regulatory compliance. Feed prices have surged due to reduced pasture availability, increased global demand, and transportation complexities, directly inflating farm operating costs.
Fuel expenses have similarly increased with global market fluctuations, directly impacting transportation and machinery operation. Additionally, higher labor wages, propelled by workforce shortages and increasing competition from other industries, further pressure farm profitability.
Lastly, stringent environmental and safety regulations, although beneficial for sustainability, require substantial financial investment, placing additional strain on farmers’ economic stability. Collectively, these factors not only threaten individual farm profitability but also challenge the overall sustainability and competitive advantage of New Zealand’s sheep industry.
Real-World Example:
Recent data indicates feed costs rose by approximately 15% between 2022 and 2024, severely impacting farm budgets across Canterbury.
Cost-Management Solutions
- Embrace precision agriculture technologies for resource optimization.
- Create collective buying groups for negotiating better pricing.
- Transition to renewable energy and energy-efficient machinery.
Cost Breakdown Table
| Cost Factor | Recent Increase [%] | Management Solutions |
| Feed costs | 15% | Group purchasing, precision feeding |
| Fuel expenses | 10% | Renewable energy sources |
| Labor costs | 8% | Automation and mechanization |
Challenge 3: Global Market Competition
New Zealand’s sheep industry operates in an increasingly competitive global market where various forces are shaping demand and influencing profitability. As traditional markets shift and new players emerge, sheep farmers and exporters must navigate evolving challenges to maintain their foothold. Consumers are becoming more conscious about sustainability, animal welfare, and ethical sourcing, demanding higher transparency in farming practices.
Additionally, technological advancements in meat substitutes and plant-based proteins are creating alternatives that compete with traditional lamb and wool products. To remain relevant, the industry must explore new strategies, innovate, and differentiate itself from competitors.
Emerging Competitors and Market Trends
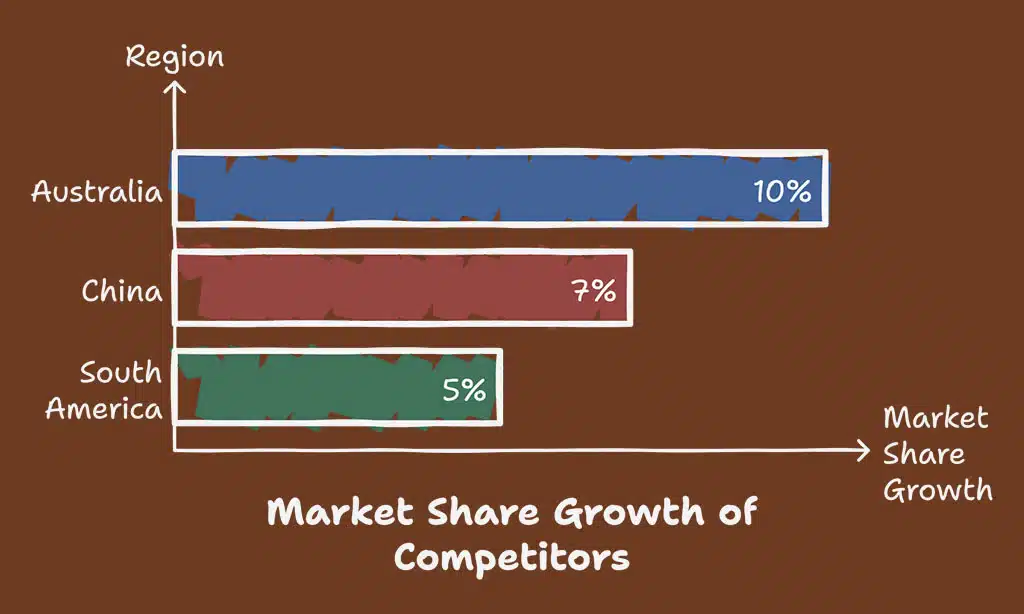
Competition from international producers such as Australia, China, and South America, alongside the rapid advancement and adoption of synthetic alternatives, poses a substantial threat to New Zealand’s traditional market dominance. Australian sheep producers have aggressively expanded their market share through targeted marketing and technological innovation, while South American countries offer competitive pricing due to lower operational costs.
Concurrently, China’s sheep industry continues to scale significantly, driven by domestic demand and improved production methods. Additionally, synthetic and plant-based alternatives, increasingly favored by environmentally conscious consumers, further erode the traditional wool and meat market segments.
These shifting consumer preferences towards sustainable and ethical products highlight an urgent need for New Zealand’s sheep industry to adapt by leveraging its strong environmental and quality-focused reputation.
Real-World Example:
Australian lamb exports grew 10% from 2020-2024, capturing significant market share previously dominated by New Zealand producers.
Ways to Strengthen Market Position
- Enhance branding of New Zealand lamb emphasizing sustainability.
- Obtain global certifications for ethical farming.
- Target growth in emerging premium consumer markets.
Market Competitiveness Table
| Competitor | Market Share Growth [%] | Strategic Response |
| Australia | 10% | Branding differentiation, quality assurance |
| China | 7% | Strengthened trade relations, niche marketing |
| South America | 5% | Premium positioning, sustainable certifications |
Challenge 4: Workforce Shortages and Skills Gap
Workforce shortages and a widening skills gap represent significant barriers to the sustainability and growth of New Zealand’s sheep industry. The evolving demographic profile, characterized by an aging workforce nearing retirement, exacerbates these challenges. Young individuals frequently perceive agriculture as less appealing due to its physically demanding nature, remote working locations, and perceived limited career advancement opportunities.
Moreover, rapid technological advancements in agriculture require workers to possess specialized skills in areas such as precision farming, automated machinery operation, and digital farm management systems.
Without effectively addressing these workforce challenges, the industry faces potential productivity declines and difficulty in maintaining global competitiveness.
Workforce Challenges in New Zealand’s Sheep Industry
The aging demographic of farm workers presents an urgent challenge, as the current generation approaches retirement age without adequate younger replacements. This demographic shift is compounded by limited recruitment among younger generations, who often seek employment opportunities perceived as more attractive or technologically oriented.
Furthermore, the industry faces critical skill mismatches due to rapid technological advancements in farming practices. Younger entrants often lack essential skills in precision agriculture, animal husbandry, and farm management technology, creating an operational gap.
Addressing these challenges requires strategic initiatives aimed at increasing youth participation, improving agricultural training and education, and promoting a modernized image of farming as an innovative and viable career choice.
Real-World Example:
A recent survey indicated the average farmer age has risen to 58 years, highlighting the urgent need to attract younger talent.
Initiatives to Bridge the Skills Gap
- Youth incentives, including scholarships and apprenticeships.
- Promoting specialized agricultural education programs.
- Highlighting technology-based farming careers.
Workforce Development Table
| Workforce Issue | Current Situation | Recommended Initiatives |
| Aging workforce | Average age 58 years | Apprenticeships, mentorship programs |
| Youth recruitment | Declining interest | Educational incentives, tech-focused career promotion |
| Skill mismatch | Technological skills gap | Vocational training, industry partnerships |
Challenge 5: Disease Management and Biosecurity Threats
Maintaining sheep health is crucial for sustaining productivity, profitability, and international trade confidence in New Zealand’s sheep industry.
Effective disease management involves addressing both prevalent conditions that consistently affect sheep welfare and productivity, and mitigating the risks posed by emergent diseases introduced through global trade and movement.
Failure to adequately manage these risks could result in severe economic impacts, substantial losses in livestock numbers, and diminished consumer confidence both domestically and internationally.
Potential Risks to Sheep Health
Biosecurity threats, such as foot-and-mouth disease and sheep scab, present severe risks to New Zealand’s sheep industry, with potentially devastating effects on productivity, economic stability, and international trade relations.
Foot-and-mouth disease, highly contagious among livestock, could lead to rapid, widespread outbreaks resulting in export bans, livestock culling, and significant economic losses. Sheep scab, while less catastrophic, substantially reduces wool quality and sheep welfare, affecting both domestic productivity and international market confidence.
With increasing globalization and trade, the risk of disease transmission intensifies, highlighting the crucial need for rigorous biosecurity measures, continuous monitoring, and immediate response protocols to protect the industry and maintain New Zealand’s status as a trusted international supplier.
Real-World Example:
The 2021 outbreak of sheep measles caused significant export disruptions, illustrating vulnerabilities in existing biosecurity systems.
Effective Disease Prevention Strategies
- Strengthened farm-level and national biosecurity measures.
- Advanced surveillance technologies for rapid disease detection.
- Routine vaccinations and veterinary health checks.
Biosecurity Measures Table
| Disease Risk | Potential Impact | Prevention Measures |
| Foot-and-mouth disease | Export ban, productivity loss | National surveillance, vaccination, biosecurity checkpoints |
| Sheep scab | Reduced wool quality | Regular vet inspections, targeted treatments |
| Sheep measles | Export disruptions | Effective worming, monitoring, and reporting systems |
Takeaways
Effectively addressing the 5 Challenges Facing New Zealand’s Sheep Industry in 2025 necessitates comprehensive, integrated, and proactive measures that focus on building climate resilience, managing escalating production costs efficiently, enhancing competitive branding strategies, addressing critical workforce shortages and skill gaps, and strengthening biosecurity measures against disease threats.
Success will depend significantly on the unified and collaborative efforts of farmers, industry associations, researchers, policymakers, and educational institutions.
To tackle climate change, the industry must invest in climate-resilient farming techniques, including advanced irrigation systems, drought-resistant pasture varieties, and sustainable grazing management. Managing rising production costs will require innovative cost-saving solutions such as cooperative purchasing agreements, renewable energy adoption, and automation in farming