Portugal has become a top choice for expatriates, investors, and retirees, offering an enviable lifestyle and financial advantages. Central to its appeal is Portugal’s Non-Habitual Residency 2.0, a tax regime introduced in 2025.
This revamped program builds on the success of the original NHR program, aligning it with international tax standards and focusing on economic growth. In this guide, we’ll explore what Portugal’s Non-Habitual Residency 2.0 offers, who qualifies, and how it can benefit you.
What is the Portugal Non-Habitual Residency (NHR) 2.0 Program?
The original NHR program was launched in 2009 to attract global professionals, retirees, and investors. It provided substantial tax exemptions on foreign income and reduced tax rates for qualifying domestic income. By 2025, however, global fiscal policies and economic demands prompted Portugal to introduce a more targeted program: Portugal’s Non-Habitual Residency 2.0.
This updated version focuses on attracting talent in strategic sectors like technology, scientific research, and sustainability. While some benefits, such as foreign pension tax relief, were removed, the program continues to offer significant advantages to those who qualify.
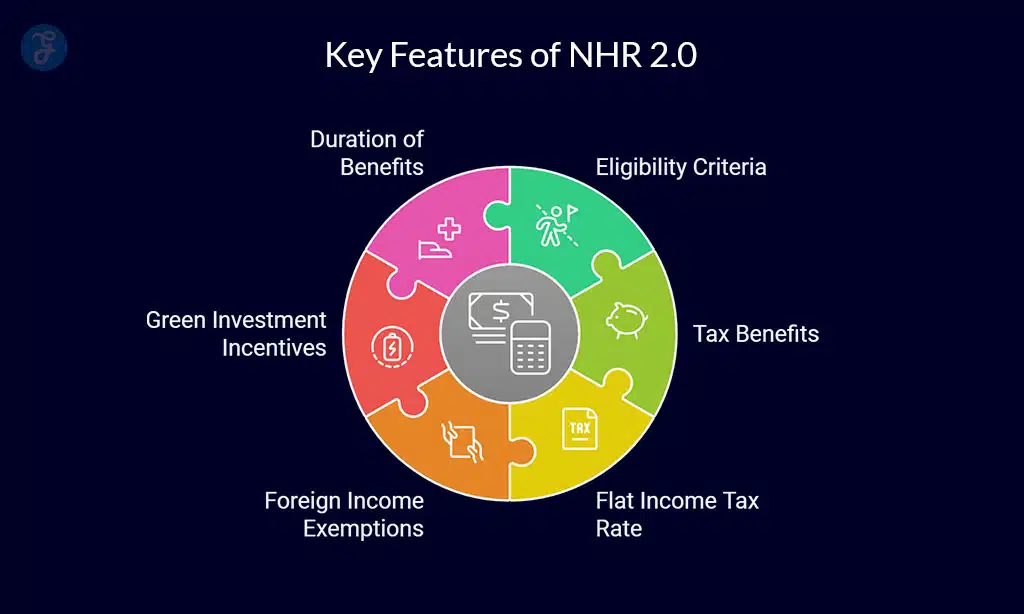
Key Features of NHR 2.0
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for NHR 2.0, applicants must meet the following criteria:
| Criteria | Details |
| Residency | Must reside in Portugal for 183 days annually or maintain a habitual residence in the country. |
| Tax Residency History | Cannot have been a tax resident in Portugal during the last five years. |
| Visa Requirements | Non-EU/EEA/Swiss citizens must hold a valid residency visa, such as the D7 Visa (passive income visa) or the Golden Visa for investors. |
Tax Benefits
NHR 2.0 offers several tax incentives that make Portugal an attractive option for professionals and investors:
| Benefit | Details |
| Flat Income Tax Rate | A 20% flat tax rate applies to income earned from high-value-added activities in Portugal. |
| Foreign Income Exemptions | Dividends, interest, royalties, and other qualifying foreign-sourced income may be exempt from Portuguese taxation if a double taxation agreement exists. |
| Green Investment Incentives | Up to 5% tax credits are offered for investments in renewable energy and sustainable projects. |
| Duration of Benefits | These benefits apply for a period of 10 consecutive years. |
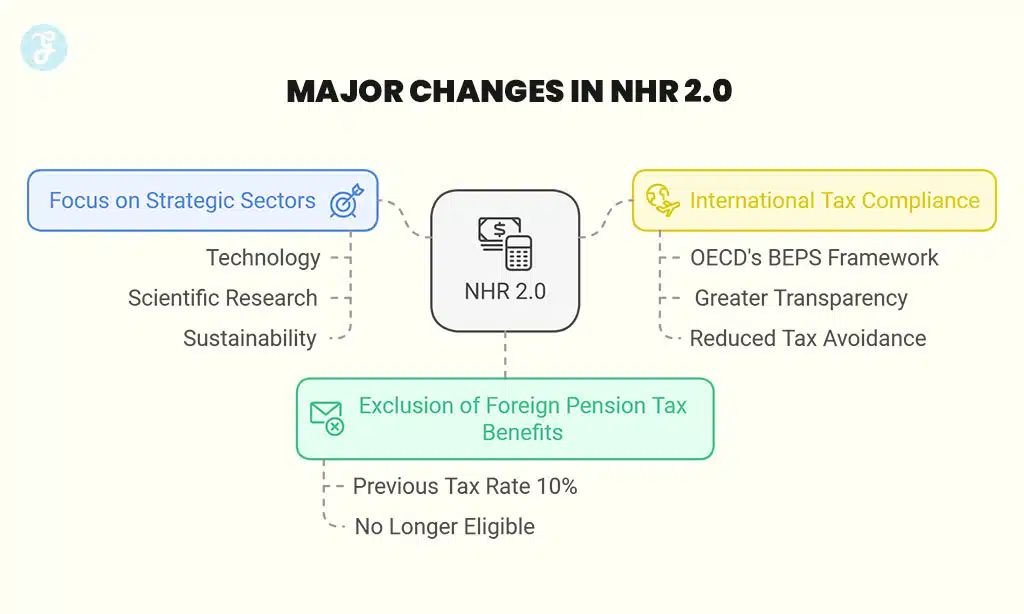
Major Changes in NHR 2.0
- Exclusion of Foreign Pension Tax Benefits: Previously taxed at a reduced 10%, foreign pensions are no longer eligible for special tax treatment under NHR 2.0.
- Focus on Strategic Sectors: The updated program targets high-value activities such as technology, scientific research, and sustainability-related professions.
- International Tax Compliance: Adheres to the OECD’s Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) framework, ensuring greater transparency and reducing the risk of tax avoidance.
Strategic Focus of NHR 2.0
The NHR 2.0 regime specifically targets sectors that contribute to Portugal’s economic development:
| Sector | Examples |
| Scientific Research | Positions in universities, research institutions, or labs focusing on advancing knowledge and technology. |
| Technology and Innovation | Roles in software development, IT services, and startups driving digital transformation. |
| Export-Oriented Businesses | Jobs in companies generating at least 50% revenue from exports, promoting international trade. |
| Sustainability Projects | Investments in renewable energy, conservation efforts, and green technologies aligning with Portugal’s goals. |
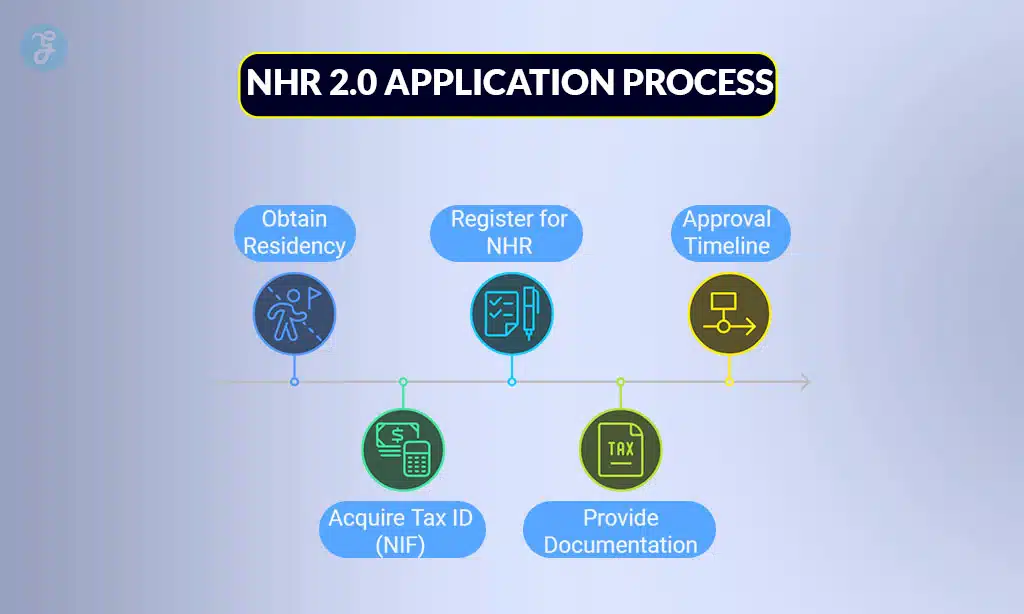
Application Process
Step-by-Step Process
- Obtain Residency:
- Reside in Portugal for over 183 days or own a habitual residence.
- Acquire a Portuguese Tax ID (NIF):
- This can be done through the Portuguese tax authorities or with legal assistance.
- Register for NHR:
- Submit your application online through the tax authority portal.
- Approval Timeline:
- Applications are typically processed within 3 to 6 months.
Applying for NHR 2.0 involves several steps:
| Step | Details |
| 1. Obtain Residency | Reside in Portugal for 183 days or establish habitual residency. |
| 2. Acquire a Tax ID (NIF) | Obtain a Portuguese Tax Identification Number (NIF), required for tax filings and legal matters. |
| 3. Register for NHR | Submit your application online via the Portuguese tax authority’s portal. |
| 4. Provide Documentation | Include proof of residency, NIF, and evidence of qualifying income or professional activity. |
| 5. Approval Timeline | Applications are typically processed within 3-6 months. |
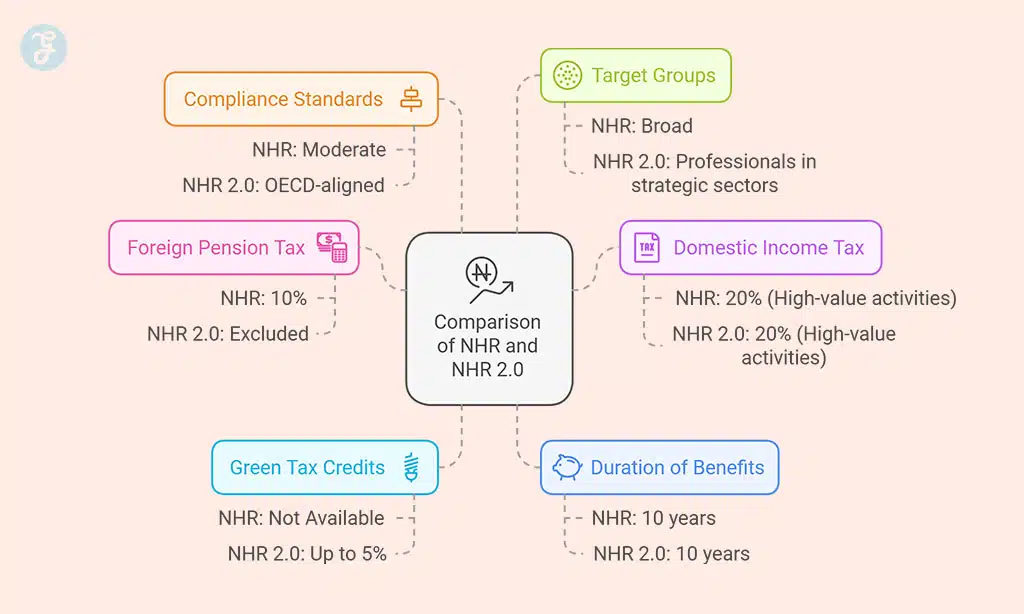
Comparison: NHR vs. NHR 2.0
| Feature | NHR (2009-2024) | NHR 2.0 (2025 Onwards) |
| Foreign Pension Tax | 10% | Excluded |
| Domestic Income Tax | 20% (High-value activities) | 20% (High-value activities) |
| Green Tax Credits | Not Available | Up to 5% |
| Duration of Benefits | 10 years | 10 years |
| Compliance Standards | Moderate | OECD-aligned |
| Target Groups | Broad | Professionals in strategic sectors |
Who Benefits Most from NHR 2.0?
1. High-Value Professionals
- Fields such as IT, healthcare, and scientific research enjoy reduced income tax rates.
- Opportunities in Portugal’s tech hubs like Lisbon and Porto.
2. Entrepreneurs and Investors
- Green investments receive tax credits, aligning with Portugal’s sustainability goals.
- Support for startup ventures through financial incentives and innovation hubs.
3. Retirees
- Retirees may still benefit from Portugal’s low living costs, healthcare system, and high quality of life, despite the removal of foreign pension tax benefits.
Why Was NHR Revamped?
The revamp was driven by international scrutiny, particularly from the EU and OECD, which raised concerns about potential tax abuses under the original regime. By introducing NHR 2.0, Portugal aims to maintain its competitiveness as a destination for skilled professionals while ensuring compliance with global tax norms. This update reflects a strategic shift towards a knowledge-based economy.
Economic Impact and Statistics
The NHR program has significantly contributed to Portugal’s economy:
| Metric | Details |
| Total Participants (2009-2024) | Over 30,000 individuals benefited from the original program. |
| Foreign Direct Investment | FDI grew by 18% in 2023, partly attributed to NHR. |
| Economic Contribution | Expats contribute an estimated €600 million annually. |
Challenges and Criticisms
- Housing Market Strain: Rising expatriate demand has inflated property prices in Lisbon and Porto.
- Reduced Retiree Benefits: Exclusion of foreign pension tax relief has discouraged some retirees.
- Perceived Exclusivity: Critics argue the program disproportionately benefits wealthy professionals.
Economic Impact and Statistics
- Since its launch, over 30,000 individuals have benefited from the NHR program.
- In 2023, foreign direct investment (FDI) in Portugal grew by 18%, with significant contributions from NHR participants.
- The program generates an estimated €600 million annually for the Portuguese economy.
Why Choose Portugal for Non-Habitual Residency?
Portugal offers more than financial incentives:
- Lifestyle: Mediterranean climate, rich cultural heritage, and scenic landscapes.
- Strategic Location: Easy access to Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
- Affordability: Lower living costs compared to other EU countries.
Takeaways
Portugal’s Non-Habitual Residency 2.0 cements Portugal’s status as a global hub for talent, innovation, and investment. While the updated program narrows its scope to focus on strategic sectors, it continues to offer substantial tax benefits for professionals and entrepreneurs.
Whether you’re a skilled professional, investor, or entrepreneur, Portugal’s Non-Habitual Residency 2.0 provides opportunities to enjoy financial advantages in one of the world’s most attractive destinations. By consulting a tax advisor, you can maximize the benefits of this program and begin your journey toward a better quality of life in Portugal.