Are you trying to make your building green? Do you want it to save energy and be comfy? It can be hard to know where to start.
Passive House and Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) both want buildings to be better. This piece shines a light on the Best Ways Passive House Design Aligns With LEED And Green Building Standards.
This article will show you how to make your project more eco-friendly and conserve energy. Ready to learn practical steps?
Key Takeaways
- Passive House and LEED help buildings be green and save energy.
- Airtight buildings cut drafts and save on energy bills.
- Good windows and insulation keep buildings comfy all year.
- Using green materials lowers the building’s impact on Earth.
- Combining Passive House and LEED makes efficient buildings.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency Standards
Passive houses focus on limiting energy use. It’s based on the building size. Passive house design aims for top energy efficiency. This helps with green buildings.
LEED certification has points for energy. It also covers the atmosphere. Energy savings matter a lot. Combining passive house and LEED leads to very efficient buildings. Passive house certification needs careful energy model work.
This predicts energy use. It forecasts operating costs.
Focus on Airtight Construction
A focus on airtightness is key for Passive House certification. It greatly boosts energy efficiency. Air sealing stops unwanted drafts. It keeps heat inside during winter. It also keeps heat out during summer.
The building envelope is critical. Proper sealing improves indoor air quality. Poorly sealed buildings allow pollutants to enter. Good air sealing helps control moisture, too. This prevents mold and damage.
Sealing can also cut down on space heating and cooling needs. This leads to big savings.
Airtight buildings have many perks. This means less energy consumption. Lower energy bills can occur. Superior insulation techniques can help. Also, air sealing can help. High-performance windows are also useful.
All of these boost worker comfort. Tools like blower door tests are important. Performance testing verifies the airtightness. Passive House design enforces strict checks to meet efficiency standards.
Integration of Superior Insulation Techniques
Superior insulation is vital. Passive House design uses super-insulation. Insulation helps keep buildings warm in winter. It also helps keep them cool in summer. Good insulation cuts down energy consumption.
It also lowers heating and cooling systems costs. This boosts energy savings.
Proper insulation is a key part of green buildings. Insulation helps lower the environmental footprint. It means less need for air conditioning systems. Insulation offers worker comfort, too.
Also, good insulation can help with thermal comfort, reducing energy consumption. Buildings get a tighter building envelope, aiding in energy conservation.
Emphasis on High-Performance Windows
High-performance windows play a big role. Passive House design utilizes these windows. These windows help save energy. They also let in natural light. Good windows keep heat inside during winter.
They keep heat out during summer. Windows are important for energy efficiency. Think of windows as a key part of the building envelope.
Great windows boost occupant comfort. They also cut energy consumption. Windows can impact indoor environmental quality. The right windows can help with LEED certification. They improve the environmental performance of buildings.
Using good windows lowers the environmental footprint.
Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
Heat recovery ventilation is key. It is a technique for a passive house. This system helps keep the air fresh inside. It also saves energy. Minimal energy needs mean lower bills. Excellent indoor air quality is a big plus.
These systems recover heat. They reduce energy consumption. Tools can help. Use building information modelling for design. Good ventilation means worker comfort. Indoor environmental quality is improved.
You can breathe easier in a green home.
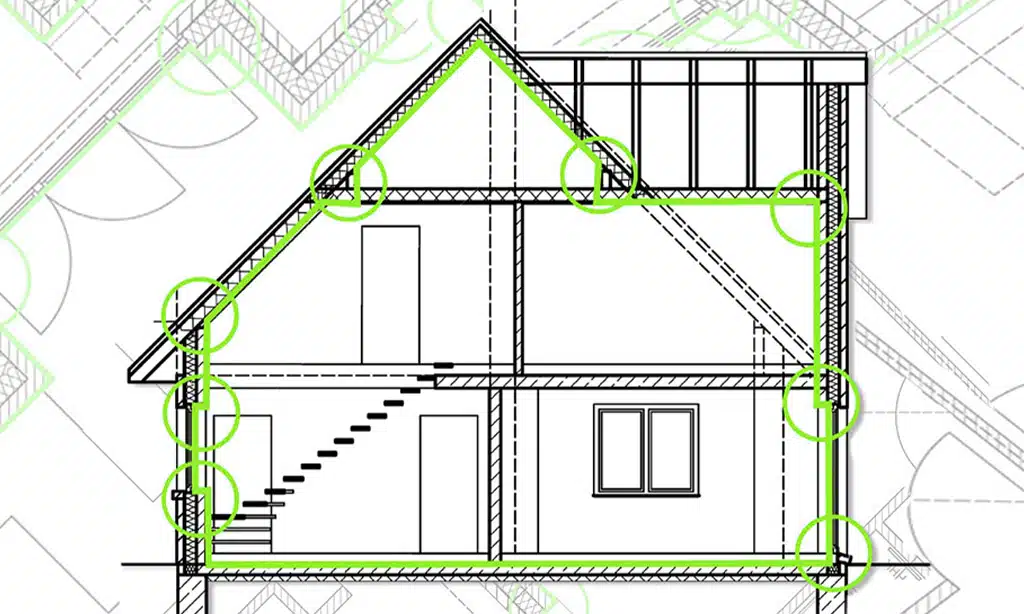
Promotion of Thermal Bridge-Free Design
Passive House design focuses on thermal bridging. Thermal bridges let heat escape. This wastes energy. Buildings need good insulation. Good insulation helps trim carbon footprint. Also, it lowers carbon emissions.
These designs use careful planning. Details stop heat from escaping through walls and roofs. Passive House certification needs strict testing. This testing checks for heat loss at thermal bridges.
Thermal bridges can affect energy consumption too. Reduced energy consumption helps the environment.
Use of Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
Green buildings use good materials. These are materials that are locally sourced. Recycled stuff or renewable materials work well. This lowers the environmental impact of buildings.
LEED also cares about materials. It rewards projects that use green options. Material sourcing matters a lot in green architecture.
Consider the construction industry. It can help the planet. Passive house design picks materials with care. This means less carbon emissions. LEED certified building looks at the big picture.
LEED addresses parts of sustainability passive houses miss. Think about material selection. Also, think about new ideas. For example, recycled resources play a vital role.
Alignment in Certifications and Performance Metrics
The push for sustainable building creates a synergy between Passive House and LEED. Both systems help you build efficiently.
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Certification Goals | LEED aims for varied green building aspects. This includes energy, water, waste, and indoor environmental quality. Passive House focuses primarily on energy use reduction. |
| Performance Benchmarks | LEED certification has levels like Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Each level corresponds to point totals from green categories. Passive House has strict energy performance criteria. This includes maximum space heating demand. |
| Complementary Strengths | Passive House excels in energy efficiency and comfort. LEED broadens the sustainability scope. It includes site selection, materials, and water management. |
| Points Overlap | Projects can earn LEED points by meeting Passive House standards. Meeting stringent energy performance standards, helps with this. Using sustainable materials also counts. |
| Streamlined Process | Builders who achieve Passive House certification may find LEED compliance easier. Principles like airtightness and insulation translate well. This aids LEED’s energy performance category. |
| Certification Bodies | Passive House certification comes from Passivhaus Institut (PHI) or Passive House Institute US (PHIUS). LEED comes from the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC). |
| Metrics of success | LEED employs a point-based system across eight categories. These range from Materials & Resources to Indoor Environmental Quality. Passive House uses quantifiable metrics. This includes annual heating and cooling demand. |
| Material Synergies | Both LEED and Passive House favor materials with low environmental impact. This includes recycled content and regional sourcing. They promote responsible forest management. |
| Design Integration | For best results, integrate Passive House and LEED goals early. This includes the design phase. Consider energy modeling and life cycle assessments. |
| Holistic Benefits | Combining Passive House and LEED yields buildings that are efficient, healthy, and sustainable. They have reduced environmental impact. Occupants also gain well-being. |
Takeaways
Passive House and LEED both help build better buildings. Going green reduces our impact on the earth. Consider Passive House design with LEED. It can boost energy savings. Think of tools like an energy model to make your next project shine and help the environment.
FAQs
1. What is a passive house?
It is a home built for big energy savings. It uses less energy than most homes. This helps the environment.
2. How does a passive house help the earth?
It cuts down on greenhouse gas emissions. This is good for combating climate change. Less energy use means a smaller carbon footprint.
3. What is LEED? LEED is a way to rate green buildings?
The US Green Building Council runs it. Getting LEED certification shows a building is good for the earth.
4. How do passive houses and LEED work together?
Passive house design helps buildings get LEED points. Both care about energy efficiency and indoor air quality. They both want to lower the environmental footprint.
5. What parts of a passive house help it meet green building standards?
High-performance windows and good material sourcing are key. Also, using solar energy and wind energy helps. These things boost energy savings.
6. Why should I care about passive houses and LEED?
They make buildings better for people and the planet. They improve worker comfort and occupant comfort. Plus, they promote a sustainable lifestyle. They also help with water efficiency.