Is your house a steam room in hot, muggy summers? High bills, poor sleep, and trapped air can leave you wiped out. Passive cooling can cut your power costs by up to half. It taps into natural ventilation, the stack effect, and cool roofs.
This guide gives you 12 clear ways to cool your home. You’ll learn shading tricks, reflective rooftops, tighter insulation, plus water features and evaporative cooling. Each tip fits the sticky heat of the Southern USA.
Read on to beat the heat.
Key Takeaways
- Passive cooling can cut power bills by up to half. It uses 12 methods like orientation, shading, and cool roofs.
- Shade with wide eaves, awnings, and trees. This can cut heat gain by 30% and drop surfaces by 5–10°F.
- Light roofs and reflective coatings can reflect 95% of sunlight. They can lower roof temps by 20–30°F.
- Solid insulation and tight air sealing can cut cooling costs by 30–50%. They keep homes near 75°F.
- Cross breezes, solar chimneys, whole-house fans (5,000 ft³/min = 33,000 BTU/hr), and evaporative cooling (20–40 ACH) boost airflow. They cut AC time.
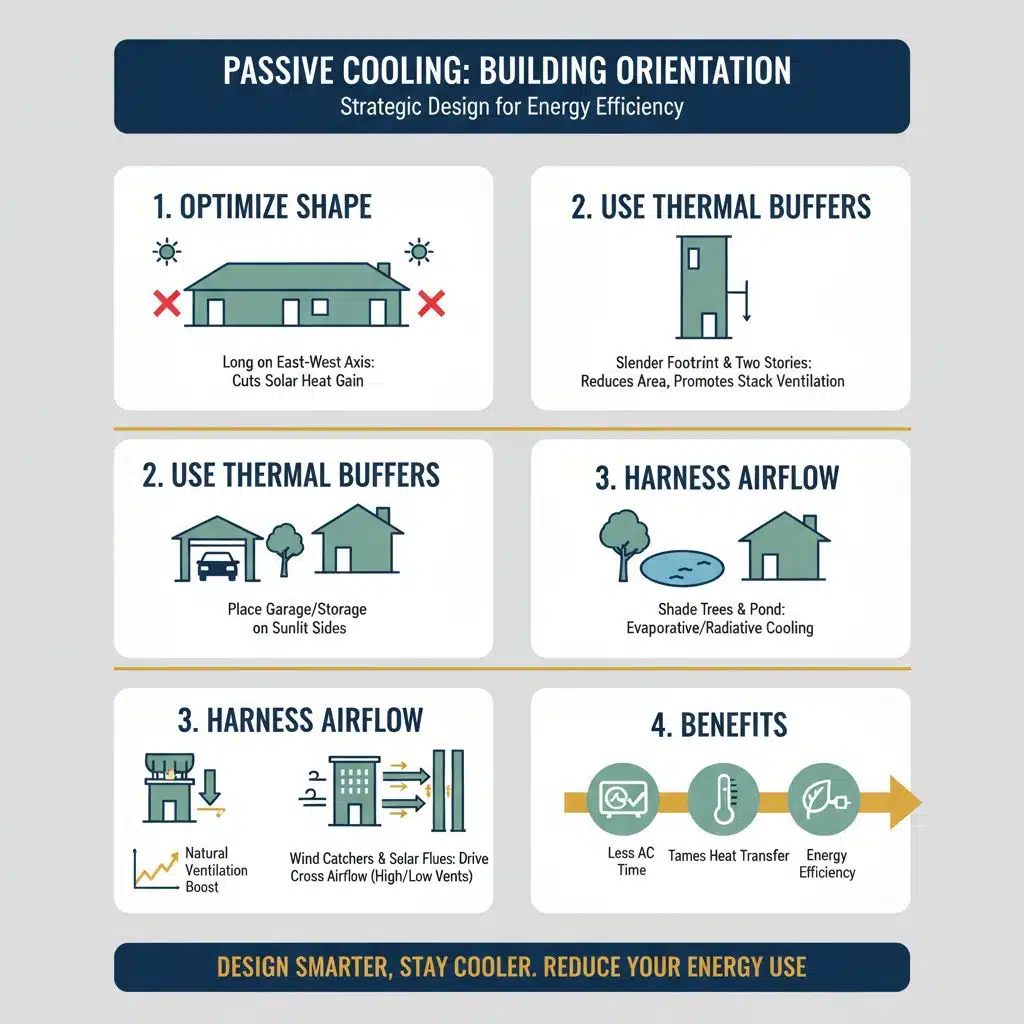
How can building orientation optimize passive cooling?
Orient your home long on the east–west axis to cut solar heat gain. East and west walls face about twice the solar radiation of north or south walls in summer, and roofs absorb three to four times more.
A slender footprint trims sun exposure, and a two-story shape shrinks roof area, letting warm air climb in stack ventilation. Sun path charts and wind rose maps guide the layout, boosting natural ventilation and thermal comfort.
Place the garage or storage bay on sunlit sides to act as a thermal buffer for living spaces. Shade trees or a small pond boost evaporative cooling and radiative cooling when dusk arrives.
Wind catchers and solar flues draw breezes up to 60 degrees off prevailing winds, spurring cross airflow through high and low vents. This cuts air conditioning time, tames heat transfer, and feeds energy efficiency.
Effective shading techniques for passive house cooling
Wide eaves and canopy shades block harsh sun, they cut heat gain on south walls. Living roofs and lattice pergolas add green cover, they boost cross ventilation and soften glare.
How do overhangs and awnings reduce heat gain?
Overhangs and awnings block direct solar radiation. They attach to east or west windows. They cut summer heat. Proper sizing lets in daylight. Homeowners cut electric lighting use by 30 percent.
Many local codes, like IECC and ENERGY STAR, list them as solar control measures. Roof gardens, phase change materials, or interior shades can work too.
Materials with a high Solar Reflectance Index reflect more rays. Adjustable awnings adapt to seasonal sun paths. They deliver passive cooling and improve the building envelope. Designers pair them with solar chimneys or wind towers for cross ventilation.
Homeowners see cooler rooms and lower HVAC bills.
What types of vegetation provide natural shading?
Mature canopy trees like live oak and southern magnolia cast broad shade on east and west walls. Smaller shrubs such as azalea and camellia cluster near foundations to slow heat gain.
Permeable ground cover, like grass or creeping thyme, cuts solar heat absorption on yards. Planting these greenery layers beside a solar chimney or wind tower boosts cross ventilation and natural ventilation.
Green roofs and roof gardens shield roof surfaces, cutting heat gain by up to 30 percent. Vertical gardens add extra thermal mass on walls. Pair trees with water features, such as small ponds or fountains, to boost evaporative cooling around patios.
This mix of plants, landscape design, and passive design measures trims a/c loads and tames the urban heat island effect.
Benefits of cool roofs in hot and humid climates
Bright, UV-reflective membranes bounce scorching rays away, cutting heat gain and trimming air-conditioning bills. Home crews use a non-contact infrared thermometer to spot hot spots fast, locking in steady thermal comfort all day.
How do reflective roof coatings help keep homes cool?
Sunlight beats down on a roof all day, and indoor temps spike. Reflective roof coatings boost the Solar Reflectance Index, so roofs stay cooler. Roofs take three to four times more summer solar radiation than north or south walls.
This level of sun drives serious heat gain and boosts indoor temps. A reflective layer can cut surface temps by dozens of degrees and trim cooling loads.
You can coat metal, tile, or asphalt shingles, without a full tear-off. This step helps homes meet U.S. DOE Zero-Energy Ready Home (ZERH) standards. Coatings even tie into federal energy-efficiency program compliance.
Pairing a cool roof with extra insulation yields top thermal performance.
Why choose light-colored roofing materials?
Light-colored roofing ranks high in passive cooling. These materials reflect solar energy and cut heat gain. Reflective coatings boost solar reflectance and cut indoor temps during peak summer.
Homeowners trim cooling loads without extra hvac use.
Cool roofs curb the urban heat island effect and earn credits in green building certification programs for energy efficiency. They work like a sunscreen for your house, bouncing heat back skyward.
Owners enjoy lower indoor temps, smaller hvac bills and sustainable design. This passive solution needs no electricity and can last decades.
How does improved insulation and air sealing enhance cooling?
Solid insulation in walls and roofs acts like a barrier to outside heat. It slows down heat gain that otherwise sneaks through studs and rafters. Closed-cell foam or dense-packed batt fills voids and cuts thermal bridging too.
A high-performance envelope, built to U.S. DOE Zero-Energy Ready Home specs, can trim cooling costs by 30 to 50 percent. State energy codes, such as the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code, guide the right insulation levels and sealing details.
Tightly sealed facades stop hot air from slipping indoors. Homes keep a steady 75°F without constant air conditioner bursts.
Air sealing finishes the job. Caulk and foam plug small cracks around windows, doors, and duct boots. These fixes reduce infiltration of steamy outdoor air. You shrink internal heat loads and boost thermal comfort.
Climate control systems and geothermal units work in a tighter box. They run fewer cycles and sip less electricity. Power outages still leave a cool interior for hours. Passive elements like a solar chimney or ground-coupled duct deliver extra airflow without power.
Sealed and insulated envelopes also fight mold growth in humid climates.
How to maximize natural ventilation in your home?
Let your house breathe by placing windows on opposite walls for cross airflow, adding wall scoops, fitting a hot shaft, and running cool air through ground pipes—read on to learn more.
Where should windows be placed for better airflow?
Place windows on the upwind and downwind walls to boost natural ventilation, letting airflows sweep through rooms. Opposite windows on two walls drive strong cross ventilation, moving cool air in and warm air out.
If you link a window to a wind tower or wind scoop, lake breezes or yard winds flow straight inside.
Place higher windows near the ceiling of upper floors to exhaust hot air, much like a solar chimney does. Wide horizontal windows on multiple sides offer flexible airflows as wind shifts.
Use operable vents, transoms, and undercut doors to balance air changes per hour and match the needed airflows for comfort.
How do operable vents improve indoor ventilation?
Operable vents act like lungs in a home, driving natural ventilation. Low inlet vents pull in cooler air and high outlet vents push out warm air, thanks to the stack effect. A solar chimney boosts this draft by heating a vent shaft.
Skylight and roof vents send hot air up and out of attics. Vents in kitchens and bathrooms grab steam and local heat, and shove it outside.
Homeowners can set vents manually or let sensors handle them. Automated openers tie into an energy recovery ventilation system or a heat pump. Properly sized vents match airflow needs and block unwanted drafts when closed.
Good design stops heat gain, cuts cooling loads, and lowers energy consumption. This simple tool works with passive cooling ideas, green roofs, or earth tubes for cooler air on hot days.
What are the advantages of installing whole-house fans?
Morning breezes whip through living rooms at 100 to 200 FPM, natural ventilation brings fresh air near windows. A 5,000 CFM fan cools like 33,000 BTU per hour if outside air sits at 72°F and inside heat climbs to 78°F.
That kind of cross ventilation drives passive cooling without cranking a compressor, it slashes electricity use. DOE data from 2012 shows major energy savings, your electric meter thanks you, the environment smiles.
Modern fans run quietly, nest between ceiling joists, they sport insulated dampers and efficient motors. You pick the right size, set multiple speeds, and mount fans in central spots for uniform airflow.
Sufficient attic vents and simple rain guards stop moisture and wind damage in roofs. Proper sealing around gas appliances keeps your home safe, air pressure stays balanced.
How do radiative cooling materials work for passive cooling?
Radiative cooling coatings reflect up to 95 percent of sunlight and emit heat to the sky through thermal radiation. They sit on roofs or exterior walls. They lower heat gain without power.
They use high emissivity to boost passive cooling.
Materials work best under clear skies at night. They show peak heat loss then. Designers add phase change materials (PCMs) to store coolness. They pair well with cross ventilation and green roofs.
They support thermal comfort. They cut energy use.
Using high-performance windows to reduce heat gain
High-performance windows use low-e coatings and thermal breaks to keep heat at bay, sealing cool air inside. Explore solar heat gain coefficient ratings, energy model tools, and window films to find the best fit.
What is low-emissivity (low-E) glass and how does it help?
Low-E glass has metal oxide layers on its face. These coatings lower the solar heat gain coefficient by up to 40%. They reflect infrared rays and let in daylight, while blocking unwanted heat.
Project teams use building information modeling to size and place these panes in a high-performance building envelope.
Builders install low-E glass in new builds and retrofits. This step meets code compliance and wins bonus points in federal energy efficiency programs. They boost passive cooling, trim cooling loads, and cut hvac equipment work.
Occupants report more comfort and cut energy use.
How do window films reduce indoor heat?
Plastic films attach to existing windows in a few hours. They curb up to 78 percent of infrared and ultraviolet radiation, cutting solar heat gain and easing pressure on an hvac system.
A tinted layer also cuts glare near screens and adds a privacy shield. You can choose film by its SHGC and visible light transmission ratings to balance daylight and heat control. This retrofit costs a fraction of replacing entire glazing and meets many local energy codes.
Installers prep the glass with a mild cleaner and smooth the film for a lasting hold. This method gives a quick upgrade for older homes that lack thermally insulated facades. It pairs with cross ventilation or a solar chimney to boost thermal comfort.
These films join other passive cooling tools like green roofs or wind towers in sustainable living plans.
How do evaporative cooling systems work in humid regions?
Direct evaporative coolers add moisture and drop temperatures, but they struggle above a 70°F wet bulb. Indirect evaporative coolers run air through a heat exchanger, so they avoid extra humidity.
Neither unit replaces dehumidification gear. Typical setups aim for 20 to 40 air changes per hour. That means a 2,000 sq ft home with 8 ft ceilings needs 5,000 to 10,000 CFM of airflow.
Each 1,000 CFM calls for 1 to 2 sq ft of net free vent area.
Air quality events cut performance unless you add filtration. Homeowners must plan for reliable water supply and regular maintenance. Wind towers and cross ventilation paths boost airflow.
Integrating water features and shade trees increases passive cooling. This approach lowers energy use and keeps homes comfy in the Southern heat.
Landscaping strategies to cool your home naturally
Line your west wall with shade trees to block heat, plant a small pond to cool the breeze, drape a pergola in vines to boost airflow—read on to get more tips!
How can shaded outdoor areas lower temperatures?
Patios and decks stay cool under a thick canopy of trees. Vines treat a semi-open pergola to cut heat gain by blocking sun rays. Perforated roofs and jaali walls cast dappled shade over seating areas.
Homeowners map the sun path to align pergolas and screens for max cooling. These designs drive passive cooling and enhance thermal comfort outdoors. You might see surface temps drop by 5 to 10 degrees in shaded spots.
Shaded buffer zones reduce solar heat gain in walls and windows. That cuts indoor cooling loads and trims energy use. Wind scoops and natural ventilation pull air across shaded patios.
The steady air flows keep spots fresh and dry. You lower AC runtime and stretch energy savings with this simple trick.
What role do water features play in cooling?
Garden pools, reflecting basins, and other water features sit near windows. They boost evaporative cooling, spark passive cooling, like a mini oasis. Water jets at operable vents mimic cross ventilation.
Misters at air inlets add local chill with little water waste.
Recirculating systems pull rooftop heat into moving water. They lower ceiling temps and ease HVAC duty. Shaded basins work well with vegetation and thermal mass. They cut cooling load, trim energy consumption, and ease upkeep.
How to reduce internal heat gains effectively?
Cut indoor heat gain by sealing gaps around windows, adding thermal mass to walls, and using energy-efficient lighting—keep reading to find out how.
Which energy-efficient lighting and appliances help reduce heat?
LED bulbs cut heat gain. They use less power and send minimal waste heat into rooms. ENERGY STAR lights match passive cooling goals, they trim electric use and help reduce energy consumption.
Induction cooktops give off almost no ambient heat, they cook fast and cool down quickly. High-rated fridges and dishwashers push out little excess heat, they ease the load on cooling systems.
Energy-saving power strips stop phantom draws, you can unplug gadgets and block sneaky heat.
When is the best time to cook outdoors or indoors?
Barbecue pits shine under the midday sun, cutting heat gain inside. They use passive cooling by stopping ovens from boosting heating loads. Chefs switch to stovetops at dawn or after dusk.
Exhaust vents clear steam fast and aid cross ventilation.
Open doors and windows add natural ventilation to the kitchen. A solar chimney design pulls warm air out as you work. Open-air pergolas fit well over outdoor cookers, letting air flow freely.
Takeaways
Kick the AC habit and let your house breathe. Site layout, cross breeze, and a solar chimney pull in fresh air. Reflective coatings on light roofs block harsh rays before they hit your attic.
Shade trees, pergolas, and adjustable vents guard your living spaces. These 12 tactics slash bills, boost ease, and keep you cool as a cucumber.
FAQs on Passive House Cooling in Hot and Humid Regions
1. What is natural ventilation and how does it boost passive cooling?
Natural ventilation moves air flowing through a house; it uses cross ventilation and wind towers. Set building orientation to match the sun path. This cuts heat gain and boosts passive cooling.
2. How do cool roofs and green roofs lower heat gain?
Cool roofs reflect sun away to cut heat gain. Green roofs plant life on your ceiling, they insulate and add shade. Both boost sustainable architecture and aid passive cooling.
3. What role do water features and evaporative cooling play?
Water features cool air like a pond’s breeze, they add damp shade. Evaporative cooling sprinkles fine mist at vents; it takes heat away fast. Both freshen your home with no power surge.
4. How do thermal mass and thermally insulated facades help?
Thermal mass walls soak up heat by day and release it at night. Thermally insulated facades block sun, they insulate your walls. Building materials like stone or brick store cool and keep heat out. You win steady thermal comfort.
5. How can a solar chimney, perforated roofs, and semi-open pergolas aid cooling?
A solar chimney uses rising warm air to pull cool air in. Perforated roofs let light filter in but block harsh sun. Semi-open pergolas cast shade, they let air flow under slats. All three add layers of passive cooling.
6. How do window placement, wind towers, and basements fit in passive cooling?
Smart window placement grabs cool drafts and blocks sun. Wind towers catch breeze at high vents and push it down. Radiant cooling pipes in a cool basement pull heat from floors. You slash heating and cooling loads in energy-efficient buildings.