Big towers feel like carbon sponges that stretch project timelines. They can leak heat in winter and swell bills in summer. Teams face slow lifts and high carbon output. You want tall, green towers without the wait.
In 2021, the code let builders use mass timber for towers up to 18 stories. Timber panels, like cross-laminated timber, store carbon and cut greenhouse gas emissions. This guide shows Benefits Of Mass Timber For Sustainable US Skyscrapers.
You will learn how mass timber speeds builds, cuts bills, and greens our skylines. Read on.
Key Takeaways
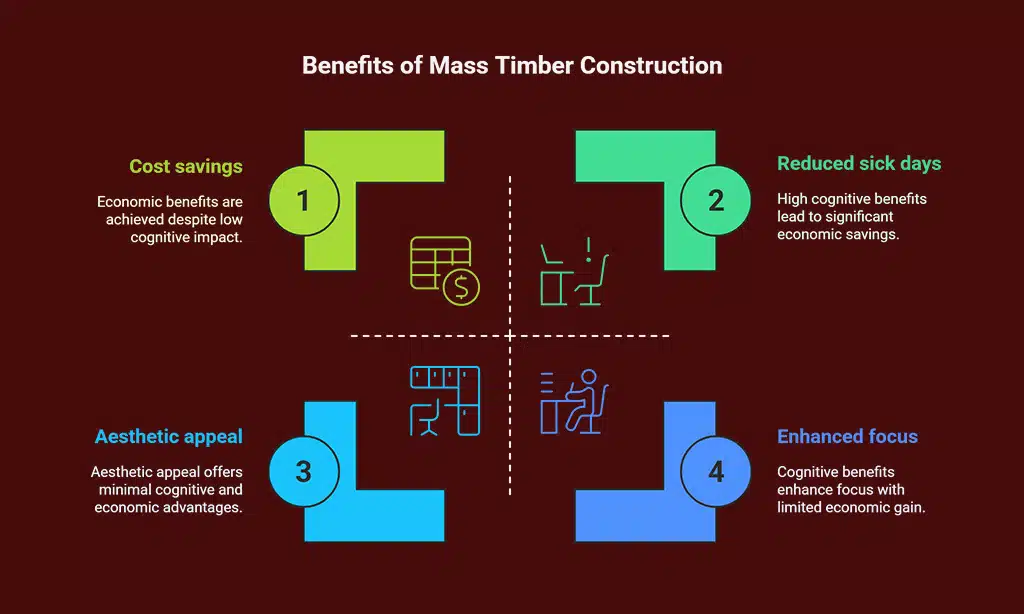
- Mass timber cuts carbon. In 2021, the US code let builders use it up to 18 stories. Mass timber towers emit about 19% less greenhouse gas than steel frames. Brock Commons in B.C. saved 2,432 metric tons of CO₂. Experts say North American timber can store 9.9–16.5 million tons of CO₂ each year by 2070.
- Builders speed work with prefab panels. They cut on-site time by 20–40% and need 50% fewer workers. The Community Foundation HQ, built with 99% mass timber, rose in under two years.
- Timber walls and floors boost energy savings. They trim HVAC run time by 20%. Offices feel warm and quiet. Biophilic design can save about $2,000 per person each year by cutting stress and sick days.
- Mass timber spurs local jobs and meets fire rules. By June 2023, the US saw 1,860 mass timber projects and over 1,700 tall timber buildings. Engineered wood forms a char layer that slows fire spread. Georgia now supplies enough wood for a 19-story tower every 16 minutes.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Mass timber locks carbon inside wooden beams. Engineered wood, such as cross-laminated timber, traps CO2 for years. Concrete and steel production cause almost 15 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions.
These buildings generate 19 percent fewer emissions than steel frames. Brock Commons in British Columbia cut 2,432 metric tons of CO2.
Experts say North American mass timber construction can store more carbon than it emits by 2034. Industry models show 9.9 to 16.5 million tons of CO2 storage each year from 2020 to 2070.
Sustainable forestry and careful timber sourcing support this carbon sequestration. Timber beams, from glue-laminated to nail-laminated, team with mass timber to shrink carbon footprints.
Renewable and Sustainable Material Source
Grown trees like Douglas fir, pine, spruce build a strong base. Cross-laminated timber (CLT), glue-laminated timber (glulam), nail-laminated timber (NLT), and structural composite lumber (SCL) flow from well-managed forests.
Georgia yields enough wood for a towering project such as 619 Ponce every 16 minutes. Forest management keeps logging at healthy rates and protects habitats. This cycle stores carbon through sequestration, lowers a project’s carbon footprint, and helps slow climate change.
Engineers cut panels to size in a factory, which cuts waste and speeds up work. Builders repurpose leftover parts into walls, floors, and even furniture for local mills. All materials break down after use since they remain fully biodegradable.
Lightweight Structure Reduces Foundation Requirements
Mass timber walls and floors weigh less than steel frames or cast concrete. They slash the number of truck trips needed for footing work. This cuts site traffic, and trims diesel fumes.
Engineers then specify smaller footings under International Building Code rules.
Builders dig shallower trenches, and use less concrete. Crane operators lift cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glue-laminated timber (glulam) parts in fewer moves. This light load speeds up framing.
Next we explore how mass timber cuts construction timelines.
Faster and More Efficient Construction Timelines
Crews cut most panels off-site, then truck them to urban high-rise jobs. Prefabricated timber components trim construction timelines by 20 to 40 percent; they slash on-site work time.
A crane lifts panels of cross-laminated timber and engineered wood beams fast; crews bolt them with simple connectors.
Sites need half the usual labor, cutting worker counts by 50 percent. Projects like the Community Foundation headquarters, made with 99 percent mass timber, rose in under two years.
Prefab methods pair well with a simple 3D model and a construction schedule, so no delays stall the job.
Improved Energy Efficiency in Buildings
To build on that speed, mass timber also cuts energy bills. Layered spruce panels act like thick blankets. They lock heat in cold months and block it on hot days. Architects use energy modeling tools such as EnergyPlus and OpenStudio to set panel sizes and positions.
Wood’s natural strength and insulation improve thermal comfort and ease stress. Towers can lower HVAC hours by 20 percent.
Engineers pair engineered wood beams with high R-value insulation. They seal joints with stacked plank columns. Advanced framing cuts air leaks. Buildings earn LEED certification and other efficiency badges.
Staff members enjoy calm, quiet rooms with soft wood tones. Biophilic features can raise focus and save two thousand dollars per person annually.
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal and Warm Interiors
Following improved energy efficiency with cross-laminated timber walls, interior spaces glow with natural warmth. Light bounces off glulam beams, sparking a cozy mood in high-rise lobbies.
Studies show natural wood boosts mood, cognitive function, and trims stress. Design teams mix nail-laminated timber (NLT) panels and mass timber ceilings to evoke a hotel-like feel in office floors.
These wood surfaces lock in carbon, cut CO2 emissions, and support sustainable construction goals.
Biophilic Design Promotes Well-Being and Productivity
Natural wood panels in mass timber buildings boost mood, and cut stress, thanks to biophilic design ideas. Exposure to engineered wood finishes raises focus and memory. Cross-laminated timber walls soften noise too.
Experts link wooden surroundings to better cognitive function.
Employees log fewer sick days in towers with sustainable design, saving up to $2,000 per employee annually. Firms tap mass timber construction to blend style with wellness. This approach uses laminated beams and CLT panels to bring green spaces inside.
Teams work faster, and offices feel alive.
Greater Fire Resistance with Engineered Wood
Engineered wood products like cross-laminated timber and glue-laminated timber add fire resistance. They form a thick char layer during high heat. This char layer slows fire spread and cuts heat transfer inside beams.
It also links to sustainable construction goals.
Recent updates to the International Building Code let designers build up to 18 stories with mass timber. The Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat reports safe high-rise projects using CLT and glulam.
This rule shift boosts greener skyscrapers across US skylines.
Economic Growth Through Local Timber Industries
Timber mills spring to life in towns from Maine to Oregon. Mass timber buildings create jobs in logging, harvesting, and factory work. 1,860 mass timber projects were active or complete in the U.S. by June 2023, while the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat lists over 1,700 tall timber structures nationwide.
Georgia lifted wood height bans past three stories, sparking new glulam, cross-laminated timber work.
Developers earn carbon credits for wood carbon sequestration in beams. Its carbon registry turns low emissions into cash. Builders follow the International Building Code on engineered wood and post their environmental impact statement under the national environmental policy act.
Local firms grow, and small towns hum with new mills.
Takeaways
US firms pair layered wood boards and pressed wood beams in solid wood structures. They cut steel use and shrink the carbon footprint. These tall builds store carbon through carbon sequestration.
Builders speed work, they lower heating and cooling costs. Regulators clear paths with environmental impact statements, they approve plans fast. Cities gain warm spaces and natural light.
Modern minds and the planet both get a win.
FAQs
1. What is mass timber in sustainable construction?
Mass timber is a building material made of thick wood panels. It uses cross-laminated timber, nail-laminated timber, and glue-laminated timber. It stores carbon, cutting the carbon footprint. It blends strength with eco-friendly design.
2. How does mass timber boost fire resistance?
In a fire, cross-laminated timber chars on the outside, so the center stays strong. That gives real fire resistance and meets tough building code rules. Firefighters face less heat, and buildings stand firm.
3. How does mass timber fight climate change?
Mass timber soaks up carbon like a sponge. It cuts greenhouse gas emissions and locks in carbon storage. It helps decarbonize skyscrapers and shows real action on climate change.
4. Can tall mass timber buildings stand up in quakes?
Yes, engineered wood panels flex and bend under stress. They add seismic resilience to tall mass timber structures, so they absorb shocks like a tree in a stiff breeze.
5. Does mass timber speed up construction timelines?
Prefab wood panels arrive ready to fit. That slashes building time and cuts expenses. You can tackle a housing shortage fast, and still follow environmental assessment rules.
6. Are mass timber buildings energy-efficient?
They use tight joints and good insulation materials to stop heat loss. That shrinks energy bills and boosts overall environmental benefits.