Bees are an essential part of New Zealand’s agriculture, playing a crucial role in pollination, biodiversity, and food production. As one of the world’s leading agricultural nations, New Zealand relies heavily on bees to sustain its fruit, vegetable, and livestock feed industries.
Without bees, many of the country’s staple crops would face significant production declines, impacting both local food supply and export revenues.
The economic contribution of bees to New Zealand agriculture is immense. According to industry reports, bee pollination contributes approximately $5 billion annually to the agricultural sector.
Given their significance, the declining bee populations pose a major concern, making it imperative to understand their role and adopt conservation strategies. Furthermore, large-scale farmers and beekeepers must work together to ensure sustainable farming methods that support bee survival and optimal crop yields. The importance of bees in New Zealand agriculture cannot be overstated, as they play a crucial role in pollination, directly impacting food production and biodiversity.
The Global Perspective on Pollinators
Bees are not only critical to New Zealand but also to global agriculture. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that 75% of the world’s food crops depend at least partially on pollination. Countries with strong pollination programs, such as the Netherlands and the United States, have seen a direct link between bee conservation efforts and increased agricultural productivity.
New Zealand can learn from such nations by implementing better policies and expanding research on bee-friendly farming practices.
The Critical Role of Bees in Pollination
Pollination is a process where pollen is transferred from the male part of a flower to the female part, allowing fertilization and fruit or seed development. Bees are among the most efficient pollinators, ensuring successful reproduction for many crops.
In New Zealand, over 80% of flowering crops depend on bee pollination, including apples, kiwifruit, blueberries, and clover for pasture. Bees enhance crop yield, improve fruit size, and increase quality, directly impacting market value. Without their contribution, many crops would experience lower productivity and irregular growth patterns.
Benefits of Bee Pollination on Crop Quality
| Benefit | Impact on Crops |
| Increased Yield | Higher fruit production and quality |
| Better Fruit Size | More uniform shape and weight |
| Enhanced Shelf Life | Longer storage duration |
| Improved Taste | Better sugar content and texture |
| Disease Resistance | Stronger plant resilience |
| Pollination Stability | Ensures consistent crop cycles |
| Nutritional Value | Improves vitamin and mineral content |
Native vs. Introduced Bee Species in New Zealand
New Zealand hosts a variety of pollinators, including native bees and introduced honeybees.
- Native Bees: These solitary bees play a role in pollinating native flora but are less efficient for large-scale agricultural crops. They are excellent pollinators for plants that are adapted to local environmental conditions. They thrive in undisturbed natural habitats, making conservation efforts critical for their survival.
- Honeybees (Apis mellifera): Introduced from Europe, honeybees are the primary commercial pollinators in New Zealand. They are kept in managed hives and deployed in orchards and farms during blooming seasons. Managed honeybee colonies are essential for large-scale pollination, as they are adaptable and can be moved across different agricultural regions as needed.
Comparison Between Native and Introduced Bees
| Feature | Native Bees | Honeybees |
| Pollination Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Commercial Use | No | Yes |
| Hive Formation | Solitary | Colonies |
| Preferred Plants | Native species | Agricultural crops |
| Resistance to Disease | High | Moderate |
| Contribution to Ecosystem | High | Essential for food crops |
| Population Stability | At risk due to habitat loss | Managed under beekeepers |
Key Agricultural Sectors Dependent on Bees
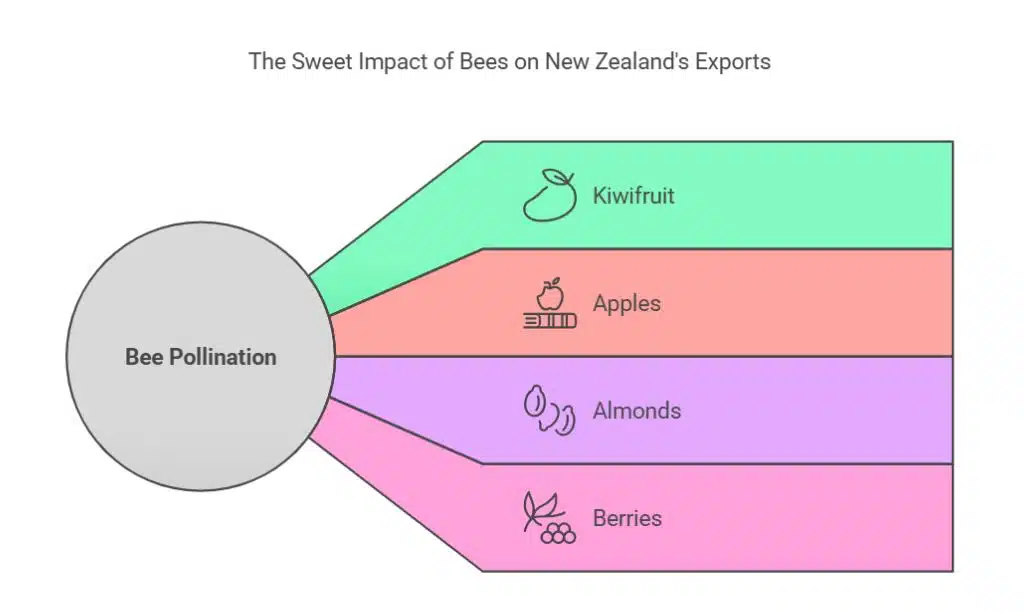
New Zealand’s fruit and nut industries rely heavily on bee pollination to produce high-quality, export-grade produce.
- Kiwifruit: One of the country’s largest export crops, requiring intensive bee pollination for optimal fruit development. A lack of adequate pollination leads to deformed fruit and reduced yields.
- Apples: Bees improve apple size, shape, and shelf life by ensuring even pollination. Well-pollinated apples are known to have better symmetry and higher market value.
- Almonds & Berries: These crops depend entirely on insect pollinators to set fruit and increase yield. Poor pollination in almond orchards can lead to nut drops and low production rates.
Impact of Bees on Fruit and Nut Production
| Crop | Pollination Dependency | Economic Impact |
| Kiwifruit | High | Major export revenue |
| Apples | High | Domestic & export markets |
| Blueberries | High | Growing industry |
| Almonds | Very High | Essential for production |
| Avocados | High | Essential for fruit set |
| Cherries | Medium | Enhances fruit size and quality |
| Strawberries | High | Improves sweetness and yield |
The Role of Bees in Dairy and Livestock Farming
Beyond crops, bees contribute indirectly to New Zealand’s dairy industry by pollinating clover, a vital component of pasturelands used to feed livestock.
- Clover fixes nitrogen: This natural fertilization process improves soil quality and reduces the need for artificial fertilizers. Fields rich in clover support higher milk production in dairy cows.
- Better Pasture Growth: Enhanced pollination results in richer, more nutritious pasture for dairy cows and sheep. High-quality pasture leads to better livestock health and increased dairy yields.
- Sustainable Feed Solutions: With growing concerns about synthetic fertilizers, bee-supported clover farming offers an eco-friendly alternative for sustaining livestock nutrition.
Contribution of Bees to Livestock Farming
| Aspect | Impact |
| Clover Pollination | Enhances pasture quality |
| Soil Fertility | Reduces dependency on synthetic fertilizers |
| Dairy Productivity | Improves milk yield and quality |
| Livestock Health | Supports nutrient-rich diets |
| Meat Production | Leads to higher quality beef and lamb |
| Climate Resilience | Promotes sustainable farming practices |
Takeaways
The importance of bees in New Zealand agriculture cannot be overstated. They support fruit and nut production, enhance dairy pasture quality, and contribute billions to the economy.
However, their survival is under threat due to habitat destruction, climate change, and pesticide use. By adopting sustainable agricultural practices and supporting conservation efforts, New Zealand can ensure a future where both bees and agriculture thrive.
Farmers, policymakers, and individuals all have a role to play in protecting bee populations. Investing in bee-friendly initiatives today will safeguard food security and biodiversity for future generations.
By making conscious efforts to protect bee populations, we can continue to enjoy the benefits of a healthy and thriving agricultural sector.