People around the world are talking about how America acts on its own first. They wonder what this means for everyone else. One key fact stands out: President Trump made “America First” his main goal.
This changed a lot in how America deals with other countries.
Our blog will look at “The Global Impact of Trump’s ‘America First’ Policies in 2025”. We’ll see how these policies change trade, money matters, and relationships between countries.
You’ll learn what this all could mean for the future.
Get ready to understand more.
Resurgence of ‘America First’ Policies in 2025
On January 20, 2025, President Trump made a big move. He announced the “America First Trade Policy” through an Executive Order (EO). This EO told everyone that American interests come first in trade and tax dealings.
The important parts like the Treasury Department, Commerce Department, and U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) got tasks right away. They had to look into taxes from other countries that were not fair to U.S businesses.
Trump didn’t stop there. He also said no to the global tax deal by the OECD. That happened with another EO. Now, by April 1, 2025, these departments have to finish a report about these unfair taxes from other places.
This step shows Trump is serious about keeping jobs and money inside America first.
Impact on Global Trade and Tariffs
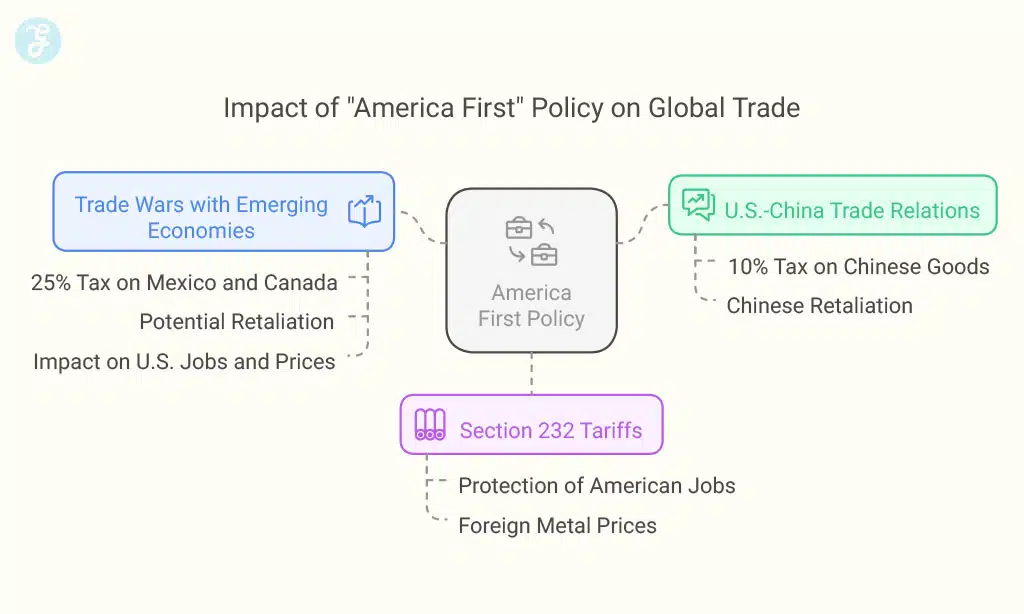
The “America First” policy in 2025 changes how the U.S. trades with other countries. It brings new fees on goods coming from places like China and Europe, making global buying and selling harder.
Changes to U.S.-China Trade Relations
President Trump signed a memorandum on January 31, 2025. It added a 10% tax on goods from China. This move made the trade situation between the United States and China tense. Both countries had been trading without such high taxes before.
The new tariffs are part of Section 301 investigations. These are checks into whether other countries’ trade actions hurt U.S. businesses. With the higher tariffs, prices for Chinese imports could go up in America.
This means Americans might pay more for things they buy from China.
China might react by putting its own taxes on American goods. This could make American products costlier in China, affecting U.S. sellers who send their products there.
The Reintroduction of Section 232 Tariffs on Steel and Aluminum
The U.S. brought back Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum. These taxes make foreign metal more expensive. It aims to protect American jobs in the steel and aluminum industries.
This move has a big impact on trade.
Countries that sell metal to the U.S. are not happy with these tariffs. They say it hurts their businesses. Some have started to put their own tariffs on American goods in response.
This situation can lead to trade wars, which might make products more expensive for everyone.
Escalating Trade Wars with Emerging Economies
Trade wars are growing with countries that are still developing. President Trump put a 25% tariff on goods from Mexico and Canada starting February 1, 2025. This might cause other countries to react strongly.
They could raise their tariffs on US products. This makes things more expensive for American companies and shoppers.
Countries like Brazil or India might join these trade fights. They could stop buying American stuff or make it harder for the US to sell there. These actions hurt jobs in the US and can lead to less choice and higher prices at home.
Trade agreements become tougher to make, affecting the global market deeply.
Economic Security Measures
In 2025, “America First” policies push the U.S. to boost its own factories and keep supply chains close to home. This move aims at making the nation less reliant on others for important goods and parts.
Find out how these changes could shape the future of global trade and investment.
Strengthening Domestic Manufacturing and Supply Chains
The U.S. government made plans to boost domestic manufacturing. They cut the corporate tax rate from 21% to 15% for firms that make goods in the U.S. This move aimed to encourage more companies to produce locally.
At the same time, tariffs hit those not manufacturing within the country.
These steps are big for America’s factories and workers. More businesses might start making products in the U.S. again. This could mean more jobs and stronger local economies. Also, having supply chains close to home helps keep things running smoothly, even when there are global problems.
Companies now think hard about where they build and make things because of these changes. They have good reasons to pick America for their manufacturing bases, thanks to lower taxes and a push against overseas production costs through tariffs.
Impact on Foreign Investment in the U.S.
Higher tariffs and more rules scare away people who want to put their money in the U.S. They see these as signs of a not-so-welcoming place for business from other countries. Big projects might find other homes where it’s easier and cheaper to start.
This means less money comes into the U.S.
Some companies benefit because they pay less tax, but others spend more because of the tariffs. Investors from outside look at this and worry. They think their money could be safer elsewhere.
So, they might decide not to invest in new jobs or factories in America. This can make things harder for cities that hoped for those investments.
Repercussions for International Tax Policies
Changing tax rules around the world could lead to big shifts in how companies do business. Find out more and see what this means for the global market.
Revisions to Cross-Border Taxation and Tariff Structures
On January 20, 2025, the Treasury Secretary began a review. This review was about how well foreign countries followed U.S. tax agreements. They looked at whether these countries were taxing American firms fairly according to deals made before.
The secretary had to report their findings and suggest changes within 60 days.
This move could lead to big shifts in cross-border taxation and tariffs that companies pay when they do business across countries. If the U.S finds some countries are not fair, taxes on goods from those countries might go up.
This means things could get more expensive for American buyers if tariffs increase.
These changes push us towards possible tension with global corporations who might face new taxes or higher ones in America.
Potential Tax Discrimination Against Global Corporations
After looking at changes in how countries charge taxes on goods and services coming from outside their borders, it’s clear there are worries about unfair treatment of worldwide companies.
Digital Services Taxes (DSTs) focus on U.S. technology businesses like software giants and internet firms. Laws in places such as Germany, the UK, and Australia have been pointed out for not treating these companies fairly.
Germany’s Section 49, the UK Diverted Profits Tax, and Australia’s law against big international companies avoiding tax show this trend. These rules aim to make sure these corporations pay more taxes where they do a lot of business online.
But many see this as an unfair strike at American tech leaders by making them follow special tax rules that don’t apply to everyone else. This situation puts pressure on global discussions about how to manage taxes for large, multinational enterprises better.
U. S. Withdrawal from Global Agreements
The U.S. stepping back from worldwide pacts could reshape global unity efforts—find out how by reading on.
Environmental Agreements Affected by ‘America First’ Policies
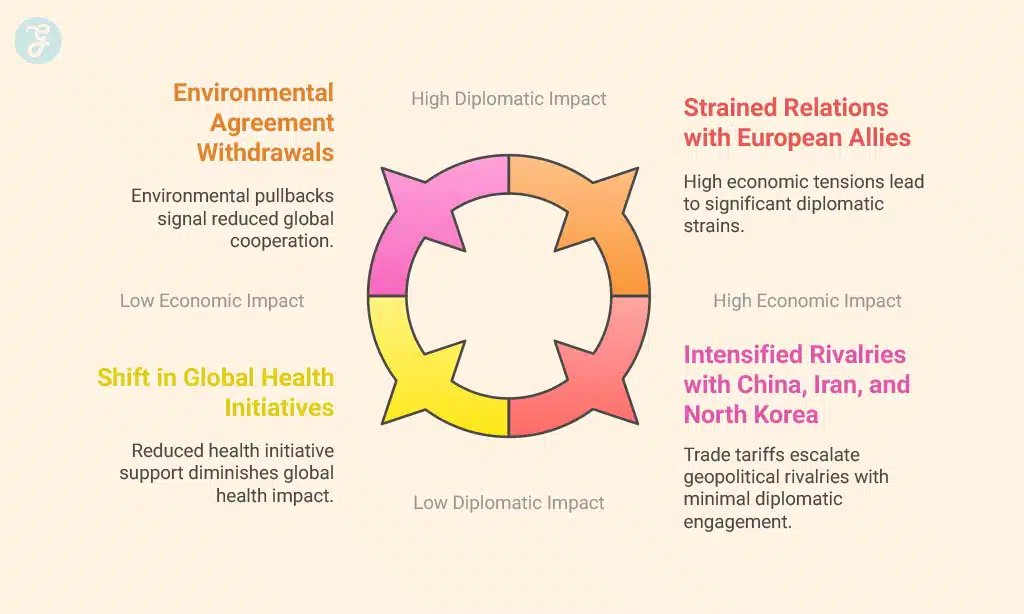
America First policies have made the U.S. rethink its part in global environmental deals. These rules say American economic goals come first, even if it means stepping back from agreements that help the planet.
For example, under these policies, the U.S. has stopped new spending on some green programs. This move shows a drop in support for international efforts against climate change.
These actions also led to questions about how serious the U.S. is in working with other countries on environmental issues. When America pulls back, it might lead other nations to do less too.
This is because they see a big player like the U.S. not doing its part. Also, focusing more on taxes and trade can distract from important work needed to keep our planet clean and safe for everyone.
Shift in U.S. Participation in Global Health Initiatives
The U.S. decided to leave the World Health Organization (WHO) on January 20, 2025. This move was complete by January 22, 2026. It marked a big change in how America takes part in global health efforts.
The WHO works worldwide to fight diseases and improve public health. Without the U.S., there could be less money and support for these tasks.
USAID also faced reviews that might stop or cut its programs. USAID helps countries deal with poverty, disease, and disaster aid. Its work includes giving vaccines and clean water.
With possible cuts, many people around the world might not get the help they need to stay healthy.
This shift shows a different path for America’s role in world health matters. Other countries may have to give more help or find new ways to fill gaps left by the U.S.’s actions.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The ‘America First’ stance in 2025 changes how the U.S. interacts with countries around the world—making friends question their trust and foes sharpen their strategies. This shift invites readers to explore further into the unfolding global narrative.
Strained Relations with European Allies
Relations with European countries got tense after Trump rejected the OECD Global Tax Deal on January 20, 2025. This move upset many countries in Europe that were following OECD Pillar Two rules.
They thought America was not playing fair in global economics.
Europe and the U.S. started to disagree more because of this decision. Trade talks became difficult, and working together on big problems was harder than before. Each side blamed the other for the issues they faced in trading and sharing money across borders.
Intensified Rivalries with China, Iran, and North Korea
Tensions with China, Iran, and North Korea grew because of Trump’s “America First” trade policy. The 10% tariff on China made things worse. This move led to more problems in trading with these countries.
It wasn’t just about selling goods anymore. Now, it was also a big part of national security talks.
These rivalries changed how the U.S. worked with other nations. They impacted everything from tariffs to who could invest in the U.S. Next up, we will see how developing economies reacted to these new trade policies.
The Effect on Developing Economies
The ‘America First’ policies have hit hard on developing countries, changing how they trade and grow. Learn more about their challenges and adjustments.
Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia’s Response to New Trade Policies
Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia are changing their trade ways. They want to deal better with America’s new rules. These areas are looking at how they send things to the U.S. This is because the U.S. might put extra costs on goods from these places.
Countries here rely on selling things to America.
They are also checking where their parts come from more closely, especially if from China. The reason is a big focus on keeping supply chains clean of Chinese parts by America’s rules.
Companies in these regions face hard tests in following these changing rules while the world’s economy goes up and down.
These areas might change what they sell and how they manage who makes what. Doing this could help them do well under America’s strict trade measures. Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia hope to keep doing business with the U.S., even with higher protections for American jobs and factories.
Latin American Countries and Repatriation Flight Disputes
Moving from Africa and Asia, Latin American nations face their own issues with the U.S. These countries are dealing with flight problems. On January 31, 2025, the U.S put a 25% tax on goods from Mexico and Canada.
This action made tensions high.
Latin American countries did not like the new flight rules about sending people back to their countries. They said these flights were unfair and caused too much strain between them and the U.S. In return, they warned they might take steps against the U.S policies that hurt their people and economies.
The Rise of ‘America First 2. 0’
The return of “America First 2.0” aims to boost the U.S. economy but may lead the world into more isolation. Explore how this shift affects everyone, from local businesses to global markets, in our detailed analysis.
Domestic Economic Growth vs. Global Economic Isolation
America First policies push for more jobs and factories in the U.S. This helps some U.S. companies by cutting their taxes. But, it also makes things cost more because of higher tariffs on goods from other countries.
These policies aim to make the U.S. economy strong by focusing on making more things in the country.
Yet, these actions can lead to less trade with other countries. When the U.S. puts high tariffs on imports or pulls out of global deals, other countries might do the same to American goods.
This can hurt global trade and make it hard for U.S. companies that sell things abroad or rely on parts from other places.
In trying to grow its economy alone, America faces challenges but also aims for independence in making and selling products. This approach has mixed results—good for some within America but causing tension with trading partners around the world.
Global Reactions to the Policies
Countries around the world responded to the policies. China and the European Union took steps against them.
Retaliatory Measures by China and the European Union
China and the European Union did not stand still after the U.S. put tariffs on their goods. They hit back with their own tariffs. On January 31, 2025, China added a 10-15% tariff on American products.
The EU followed by setting up new rules that made it harder for U.S. businesses to work there. These actions were in line with OECD Pillar Two rules, which aim to make sure companies pay a fair amount of tax wherever they do business.
These measures affect how much stuff costs and where companies decide to make or sell their products. With these higher costs, some American goods became more expensive in China and Europe.
This change made people in those places buy less from the U.S., hurting American sellers and makers.
Next, let’s look at how multinational organizations are trying to ease these policy impacts.
Efforts by Multinational Organizations to Mitigate U.S. Policy Impacts
Groups around the world are working hard to deal with America’s trade moves. They focus on talks and deals. Big groups like the OECD work on rules like UTPR, which lots of countries follow.
This effort helps make sure taxes are fair everywhere.
These organizations talk to each other to solve problems caused by America’s “America First” approach. They aim to keep trade smooth and stop conflicts over taxes and tariffs that hurt business worldwide.
Working together, they look for ways everyone can agree on, keeping global markets steady.
Takeaways
Trump’s “America First” stance reshaped global trade. It put U.S.-China relations on edge and brought back tariffs on metals. These moves sparked trade fights with many countries. The plan also pushed for stronger U.S. factories and less foreign money in American businesses.
This policy shift rattled international tax rules and made the U.S. step back from world agreements on the environment and health.
These changes strained ties with European friends and fueled rivalries, notably with China, Iran, and North Korea. Developing regions like Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia had to adjust their trade tactics as well.
At home, this approach aimed to boost economic growth by focusing inward but risked isolating the U.S. in global markets.
Countries around the world didn’t sit still—they fought back against these policies.
Think about these shifts: How might they affect you or your community? The choice now lies in understanding these impacts—and deciding what steps we can all take next.