In today’s world, achieving a balance between cost and sustainability in real estate is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. The real estate sector significantly impacts the environment, contributing to global energy use, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion.
At the same time, developers, property owners, and investors are increasingly concerned about affordability and long-term financial viability.
By embracing sustainable practices, real estate professionals can address environmental concerns while cutting costs, increasing property value, and meeting market demand for eco-friendly homes.
This comprehensive guide explores 15 actionable strategies to balance cost and sustainability in real estate, providing insights into materials, technologies, and practices that promote affordability and environmental responsibility.
Why Balance Matters in Real Estate Development
Environmental Impact of Traditional Practices
Traditional real estate practices consume vast amounts of resources, from energy-intensive materials to inefficient construction processes. Buildings account for nearly 40% of global carbon emissions, making sustainable practices essential to mitigating climate change. By adopting eco-friendly measures, the industry can significantly reduce its carbon footprint while optimizing resource efficiency.
Rising Demand for Sustainable Housing
Modern buyers and renters prioritize sustainability. A property’s eco-friendly features often influence purchasing decisions, with energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints becoming top priorities. Striking a balance between cost and sustainability in real estate ensures accessibility without compromising ecological goals, catering to an environmentally conscious clientele.
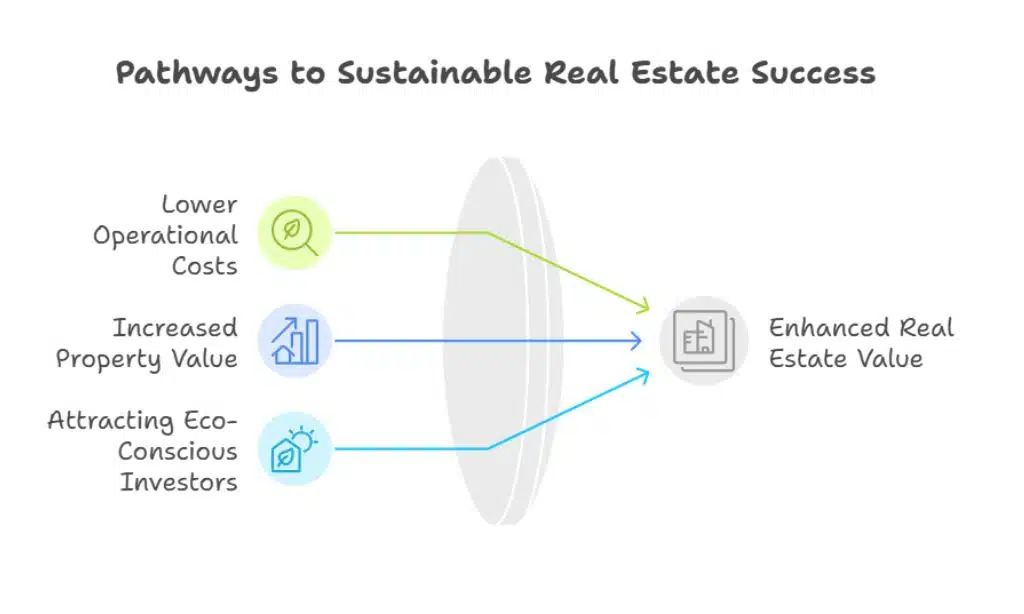
Benefits of Cost-Sustainable Real Estate Practices
- Lower Operational Costs: Energy-efficient materials and systems significantly reduce utility bills, benefiting both developers and occupants.
- Increased Property Value: Sustainable properties often command higher market prices and faster sales, offering better returns for investors.
- Attracting Eco-Conscious Investors: Environmentally friendly real estate projects align with investors’ growing emphasis on ethical and sustainable portfolios.
15 Practical Strategies to Balance Cost and Sustainability
1. Use Energy-Efficient Materials
Choosing energy-efficient materials is one of the most effective ways to balance cost and sustainability in real estate. Modern materials like recycled steel, bamboo, and precast concrete offer durability, affordability, and environmental benefits.
Affordable and Durable Options:
- Recycled Steel: Strong and recyclable, reducing demand for raw materials.
- Bamboo: A fast-growing alternative to traditional wood.
- Precast Concrete: Minimizes waste and enhances energy efficiency.
Comparison of Energy-Efficient Materials
| Material | Cost Efficiency | Durability | Environmental Impact |
| Recycled Steel | High | Very High | Low |
| Bamboo | Moderate | Moderate | Very Low |
| Precast Concrete | High | High | Low |
2. Incorporate Renewable Energy Solutions
Renewable energy systems are a cornerstone of sustainable real estate. Solar panels and wind turbines are increasingly affordable, offering long-term energy savings and reduced carbon footprints.
Key Benefits:
- Solar panels cut electricity costs by up to 70%.
- Wind turbines provide a reliable energy source in windy regions.
Renewable Energy Solutions Overview
| System | Initial Investment | ROI Timeline | Key Advantages |
| Solar Panels | $$$ | 5-7 years | Reduced utility bills |
| Wind Turbines | $$$$ | 7-10 years | Reliable in windy areas |
3. Opt for Green Building Certifications
Green certifications enhance a property’s market appeal while promoting sustainability. Programs like LEED, BREEAM, and Energy Star provide frameworks for eco-friendly construction.
Popular Certifications to Consider:
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design)
- BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method)
- Energy Star
Benefits of Green Building Certifications
| Certification | Focus Area | Benefits |
| LEED | Comprehensive | Higher property value, savings |
| BREEAM | Environmental Design | Improved performance metrics |
| Energy Star | Energy Efficiency | Lower utility costs |
4. Implement Smart Home Technology
Smart home systems improve energy efficiency while enhancing convenience. From programmable thermostats to motion-activated lighting, these technologies reduce waste and lower costs.
Examples of Smart Tech:
- Smart Thermostats: Optimize heating and cooling schedules.
- Energy-Saving Lighting Systems: Automatically adjust to natural light levels.
Smart Home Technology Benefits
| Technology | Functionality | Cost Savings |
| Smart Thermostats | Optimizes energy use | High |
| Motion-Activated Lights | Reduces energy waste | Moderate |
5. Focus on Water Conservation Techniques
Water-saving installations contribute to sustainability and cost-efficiency. Features like rainwater harvesting systems and low-flow fixtures minimize water waste.
Affordable Water-Saving Installations:
- Low-flow showerheads and faucets.
- Rainwater collection systems for irrigation.
Water Conservation Techniques
| Technique | Installation Cost | Water Savings |
| Low-Flow Fixtures | Low | Moderate to High |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Moderate | High |
6. Prioritize Passive Design Principles
Passive design leverages natural elements to optimize building performance. By carefully considering orientation, insulation, and ventilation, developers can minimize energy use without significant additional costs.
Key Principles:
- Maximize natural light.
- Utilize cross-ventilation to reduce cooling needs.
Passive Design Elements
| Element | Benefit | Cost Implication |
| Natural Lighting | Reduced electricity use | Low |
| Cross-Ventilation | Lower cooling costs | Low |
7. Reuse and Recycle Construction Waste
Recycling construction waste not only reduces landfill use but also cuts material costs. For example, reclaimed wood and bricks can be repurposed for new projects.
Practical Tips:
- Partner with recycling facilities.
- Use reclaimed wood for flooring or paneling.
Recycling Benefits
| Material Reused | Cost Savings | Environmental Benefit |
| Wood | Moderate | High |
| Bricks | Low | Moderate |
8. Design Multi-Functional Spaces
Space efficiency is a critical component of balancing cost and sustainability. Multi-functional spaces, like co-living areas or offices that double as guest rooms, maximize utility without increasing square footage.
Examples:
- Convertible furniture for dual-purpose rooms.
- Modular layouts that adapt to changing needs.
9. Opt for Locally Sourced Materials
Sourcing materials locally supports regional economies and reduces transportation emissions. Choosing locally available sustainable materials further enhances affordability.
10. Invest in Energy Modeling Tools
Energy modeling software helps developers predict a building’s energy use, identify inefficiencies, and calculate the ROI of sustainable features.
Top Tools:
- eQUEST
- OpenStudio
- EnergyPlus
Energy Modeling Tools Overview
| Tool | Key Features | Cost Efficiency |
| eQUEST | Detailed energy simulations | High |
| OpenStudio | Open-source and customizable | Moderate |
11. Explore Tax Incentives and Grants
Governments worldwide offer financial incentives for sustainable construction. Tax credits and subsidies make eco-friendly upgrades more accessible to developers and property owners.
Tax Incentives and Grants
| Region | Incentive Type | Key Benefits |
| USA | Green Tax Credits | Reduced installation costs |
| EU | Subsidies | Lower upfront investment |
12. Build with Low-Impact Foundations
Low-impact foundation techniques, such as floating foundations or minimized cement use, reduce construction costs and environmental impact.
13. Choose Eco-Friendly Paints and Finishes
Low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints and finishes improve indoor air quality while reducing environmental harm. These options are cost-effective and widely available.
14. Incorporate Green Roofs and Vertical Gardens
Green roofs and vertical gardens provide insulation, reduce urban heat islands, and enhance a building’s aesthetic appeal. While the upfront cost can be higher, these features pay off through energy savings and increased property value.
Case Study: In Chicago, the City Hall’s green roof reduces energy costs by 25% annually, proving its cost-effectiveness.
Green Roof Benefits
| Feature | Installation Cost | ROI Timeline | Key Advantages |
| Insulation | $$ | 3-5 years | Lower energy costs |
| Aesthetic Appeal | $$ | Immediate | Higher property value |
15. Focus on Community-Shared Resources
Shared resources, such as community solar farms and water recycling systems, distribute costs across multiple stakeholders, making sustainability more affordable for everyone involved.
Community Resource Sharing
| Resource Type | Cost Savings | Environmental Impact |
| Solar Farms | High | High |
| Water Recycling | Moderate | High |
Case Studies: Success Stories in Balancing Cost and Sustainability
Affordable Eco-Homes in Europe
Developers in Scandinavia have successfully implemented modular construction techniques to create affordable, energy-efficient homes.
Urban Green Projects in North America
Cities like Portland and Vancouver have pioneered sustainable urban development with green roofs, shared energy systems, and eco-friendly public spaces.
Lessons from Emerging Markets
Countries in Asia and Africa are leveraging traditional materials and techniques to create sustainable yet cost-effective housing solutions.
Interactive Tools to Make Sustainable Real Estate Decisions
Cost vs. ROI of Sustainable Real Estate Features
| Feature | Initial Cost | ROI Timeline | Key Benefits |
| Solar Panels | $$$ | 5–7 years | Energy savings, tax credits |
| Green Roofs | $$ | 3–5 years | Improved insulation |
| Low-Flow Water Fixtures | $ | 1–2 years | Water conservation |
Checklist: Steps for Developers to Get Started
- Identify key sustainability goals.
- Explore local incentives and grants.
- Evaluate sustainable materials and technologies.
- Consult with green building experts.
- Monitor and adjust strategies during construction.
Takeaways: The Future of Sustainable Real Estate
Balancing cost and sustainability in real estate is not just about meeting today’s market demands; it’s about building a better future. By integrating the strategies outlined in this guide, developers, investors, and homeowners can achieve financial and environmental harmony.
Now is the time to take actionable steps toward creating real estate that benefits everyone—economically and ecologically.