Do you ever wake up, hit snooze three times, and still feel like a zombie? You drink your coffee, but the fog just won’t lift. If this sounds like your daily routine, I have some good news: you are not alone. In fact, recent data suggests that nearly one in three adults in the U.S. doesn’t get enough sleep. That is a lot of tired people.
Many of us wonder why we can spend eight hours in bed and still feel wiped out by lunch. The answer often isn’t just about “how much” you sleep, but what is happening inside your brain while you do.
Here is one eye-opener: while you sleep, your brain works hard to clear away toxins that build up during the day. If you do not get enough good sleep or move through the right sleep cycles, your brain just cannot keep things tidy.
In this guide, I’m going to walk you through exactly what happens when you close your eyes. We will look at why fatigue lingers, the science of sleep of your “inner clock,” and the tiny changes that can boost your energy for good.
So, grab a cup of coffee (while you still can today!), and let’s get started.
Understanding Sleep: What Happens When You Sleep
Your body works hard while you sleep. It clears waste, repairs cells, and stores memories. Each night brings a mix of deep rest and wild brain activity. It is far more than just “shutting down” for the night.
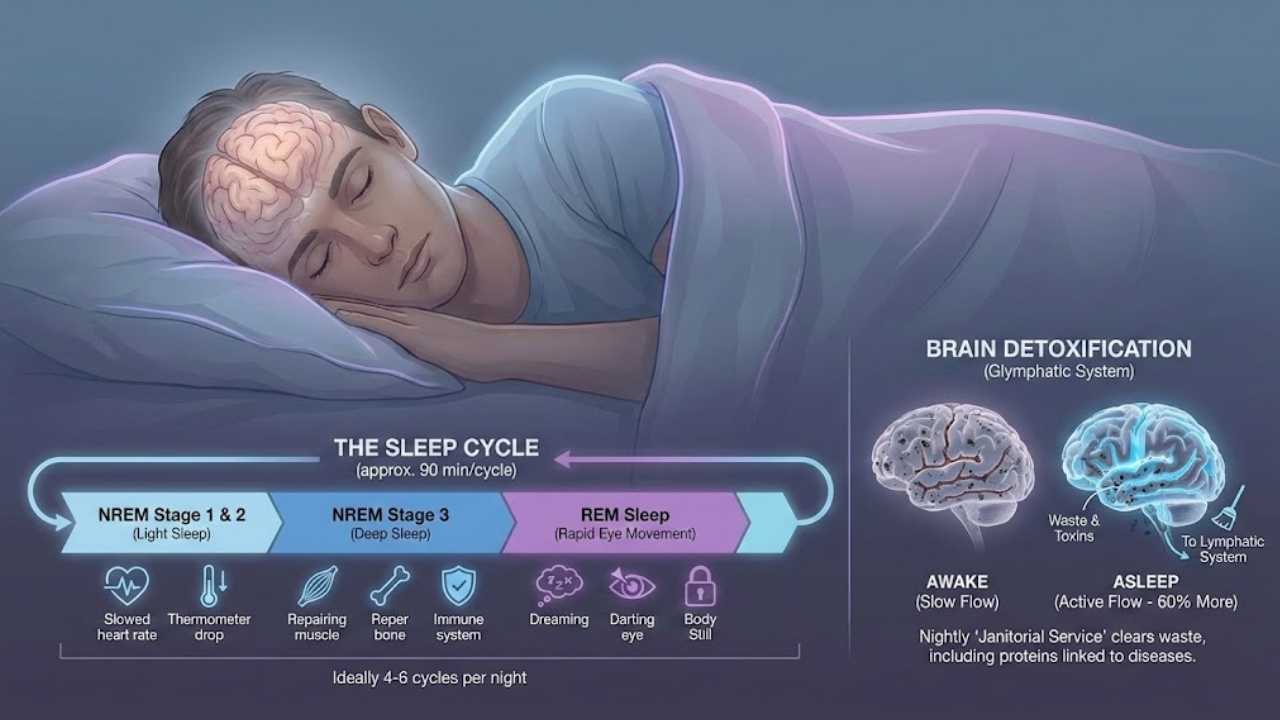
The sleep cycle: REM and non-REM sleep
Sleep moves in cycles, like a train chugging through different stops. In each cycle, the brain shifts between REM sleep and non-REM sleep. A full cycle takes about 90 minutes, and you ideally want to get through four to six of them every night.
- Non-REM Stage 1 & 2: This is light sleep. Your heart rate slows, and your body temperature drops.
- Non-REM Stage 3 (Deep Sleep): This is the most critical stage for physical recovery. Your body fixes tissues, grows muscles, and strengthens your immune system.
- REM Sleep (Rapid Eye Movement): This is where dreams take center stage. Your eyes dart behind closed lids, but your body stays still as a statue. This stage is vital for emotional processing and memory.
If you wake up feeling groggy, you might have interrupted one of these deep cycles. Research shows that missing out on either deep sleep or REM sleep can leave you feeling foggy, no matter how many hours you stayed in bed.
The role of sleep in brain detoxification
Here is a fascinating fact that scientists only discovered recently. In 2012, researchers identified something called the glymphatic system. Think of it as your brain’s nightly janitorial service.
While you sleep, this system flushes out waste and toxins that gather during the day, including proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Amazingly, this system is about 60% more active when you are asleep than when you are awake.
If you cut your sleep short, the janitors don’t have time to finish the job. The result? You wake up with a “dirty” brain, which feels like foggy thinking, slow reactions, and heaviness.
Why Do You Feel Tired All the Time?
You might wonder why your eyelids feel heavy before noon. There are many sneaky reasons your energy tanks so fast, and some may surprise you.
Lack of quality sleep
It is not just about hours; it is about quality. You can be in bed for nine hours, but if you toss and turn, you won’t get the restorative benefits. A common culprit here is something experts call “social jetlag.”
This happens when you stay up late on weekends and sleep in, then try to switch back to an early schedule on Monday. This yo-yo effect confuses your biology just as much as flying across the country does.
Sleep disorders
Sleep disorders can steal good rest right from under your nose. Conditions like insomnia or restless legs syndrome are common, but sleep apnea is a major, often hidden issue.
The American Medical Association notes that around 30 million people in the U.S. have sleep apnea, and many don’t even know it. This condition causes you to stop breathing briefly hundreds of times a night, preventing you from ever reaching deep, restorative sleep.
If you snore loudly or wake up gasping, it is worth asking a doctor. Treating this single issue can be a life-changer for your energy levels.
Chronic health conditions
Sometimes, the fatigue comes from your body fighting a battle you can’t see. Thyroid disorders and adrenal fatigue often slow you down, making even small tasks feel heavy.
Nutrient deficiencies play a massive role here too. For example, did you know that nearly 50% of Americans consume less than the estimated average requirement of magnesium? This mineral is crucial for relaxation and muscle function. Without it, your body struggles to wind down.
Low Vitamin D and B12 are also common energy thieves. A simple blood test can tell you if you are running on empty.
Stress and mental health factors
Stress acts like a thief. It steals your sleep at night and leaves you groggy the next day. Anxiety can keep your mind racing, making it tough to relax enough for restorative sleep.
There is also a phenomenon called “revenge bedtime procrastination.” This is when you stay up late scrolling on your phone just to reclaim some personal time after a busy day. It feels good in the moment, but it guarantees you will be tired tomorrow.
The Science Behind Sleep and Fatigue
Your body runs on a clock. If that clock gets out of sync, tiredness can hit you like a ton of bricks. Let’s look at the chemical gears turning behind the scenes.
How circadian rhythms regulate sleep
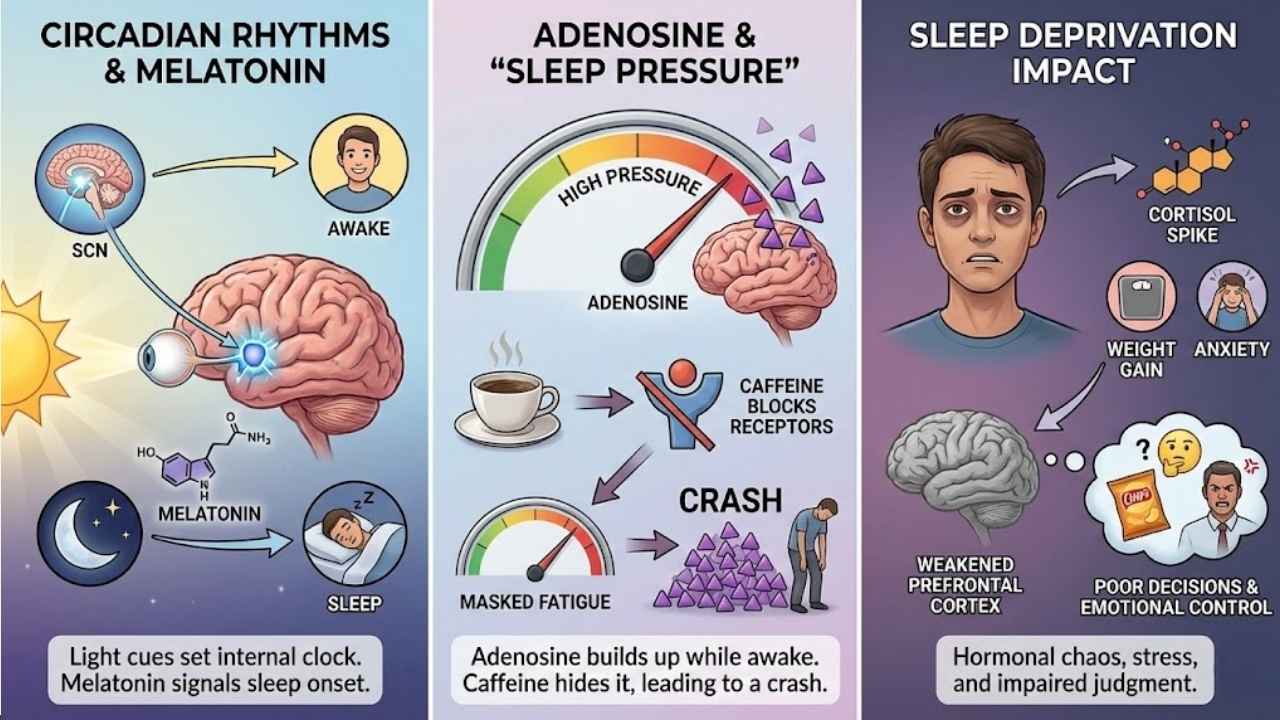
Your circadian rhythm is an internal clock controlled by a part of your brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). It uses light to set your schedule.
When light hits your eyes, it tells your brain to stay awake. When it gets dark, your brain releases melatonin, the hormone that signals it is time to sleep. This system is ancient and powerful. “Research shows that shifting your sleep schedule by even two hours can disrupt your metabolism and alertness for days.”
The role of adenosine and neurotransmitters
Why do you feel sleepier the longer you stay awake? You can thank a chemical called adenosine. Think of adenosine like “sleep currency.”
Every minute you are awake, you earn a little more adenosine. It builds up all day, creating “sleep pressure.” By bedtime, you should have enough to fall asleep easily. While you sleep, your brain “spends” this currency, clearing it out so you wake up fresh.
Here is the catch with coffee: Caffeine works by blocking adenosine receptors. It doesn’t get rid of the adenosine; it just hides it. Once the caffeine wears off (which takes about 5 hours on average), all that built-up sleepiness hits you at once.
The impact of sleep deprivation on the body and brain
Missing sleep messes with more than just your mood. It throws your hormones into chaos. Sleep deprivation spikes cortisol (the stress hormone), which can lead to weight gain and anxiety.
It also weakens your prefrontal cortex, the part of your brain responsible for logical decisions. This is why you are more likely to snap at a coworker or eat a whole bag of chips when you are tired. Your brain simply loses its ability to hit the brakes.
Lifestyle Factors That Affect Sleep
The things you do each day can mess with your sleep, even if you don’t notice right away. Small changes in daily habits can mean the difference between dragging through the morning or waking up ready for anything.
Diet and caffeine consumption
We mentioned caffeine, but timing is everything. Since caffeine has a half-life of about 5 hours, a coffee at 4:00 PM means half of that caffeine is still in your system at 9:00 PM.
To fix this, try setting a “caffeine curfew” around 2:00 PM. Also, watch out for heavy meals right before bed. Your body cannot focus on deep sleep if it is busy digesting a steak dinner. Spicy foods can also cause heartburn, which wakes you up in the micro-moments between sleep cycles.
| Food & Drink to Avoid Before Bed | Sleep-Friendly Alternatives |
|---|---|
| Coffee, Energy Drinks, Soda (Caffeine) | Herbal Teas (Chamomile, Peppermint) |
| Alcohol (Disrupts REM sleep) | Tart Cherry Juice (Natural Melatonin) |
| Spicy or Acidic Foods | Small handful of Almonds or Banana |
Exercise and physical activity
People who move their bodies often fall asleep faster and sleep deeper. A short walk after dinner can help calm the mind and fight fatigue. Scientists say regular activity helps balance your circadian rhythm.
However, try to avoid high-intensity interval training (HIIT) within an hour of bed. The adrenaline spike can keep you wired. Gentle movement, like stretching or yoga, is perfect for the evening.
The use of technology before bed
This is the big one. Bright screens from phones emit blue light, specifically in the 460-480 nanometer range. This specific light spectrum tricks your brain into thinking it is noon.
When your eyes see this light, your brain halts melatonin production immediately. Scrolling through social media right before bed is physiologically the same as drinking an espresso.
Pro Tip: Most phones have a “Night Shift” or “Eye Comfort” mode that turns the screen orange. Turn this on automatically at sunset, but better yet, try to keep screens out of the bedroom entirely.
How to Improve Your Sleep Quality
Better rest is possible, and small changes can make a big difference. If you are ready to stop feeling like a zombie, here are the most effective, science-backed strategies to try tonight.
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule
Getting up and heading to bed at the same time each day is the single most effective way to reset your circadian rhythm. Yes, even on weekends.
If you sleep until noon on Sunday, you won’t be tired Sunday night, and Monday morning will be painful. Consistency trains your body to release hormones at the right time, making sleep automatic rather than a struggle.
Creating a sleep-friendly environment
Your bedroom should be a cave: dark, cool, and quiet. According to the National Sleep Foundation, the ideal sleeping temperature is between 60 and 67 degrees Fahrenheit.
If your room is too warm, your body cannot drop its core temperature, which is a signal it needs to initiate deep sleep. Blackout curtains are also a great investment. Even a little street light creeping in can disturb your sleep cycles.
Managing stress and relaxation techniques
You cannot go from 100 mph to zero in five minutes. You need a “wind-down” routine. Try the 4-7-8 breathing technique championed by Dr. Andrew Weil.
It is simple:
- Breathe in quietly through your nose for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 7 seconds.
- Exhale forcefully through your mouth for 8 seconds.
Repeat this four times. It acts like a natural tranquilizer for your nervous system. Other great options include reading a physical book (no screens!) or taking a warm bath to relax tense muscles.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you have tried all the tips above and sleep still slips through your fingers, it is time to ask for backup.
Recognizing signs of chronic sleep issues
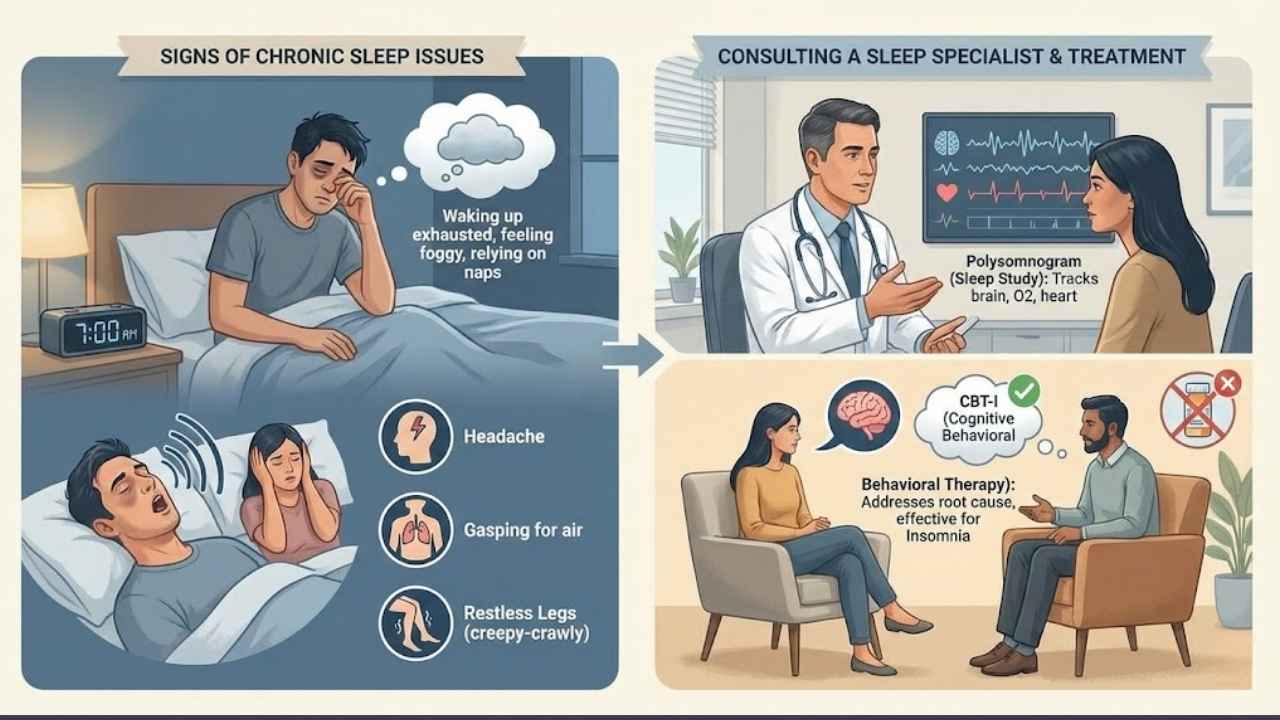
Waking up exhausted after a full night of sleep is a major red flag. If you feel foggy every day, rely on naps to function, or snore loudly enough to wake your partner, these are signs of an underlying disorder.
Other warning signs include waking up with headaches, gasping for air at night, or having creepy-crawly sensations in your legs (Restless Legs Syndrome).
Consulting a sleep specialist
Sleep specialists are doctors who can see what is happening while you are unconscious. They might recommend a polysomnogram, which is a sleep study that tracks your brain waves, oxygen levels, and heart rate overnight.
For insomnia, the gold standard treatment is CBT-I (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia). Studies show it is effective for 70-80% of patients, often working better than sleeping pills in the long run because it addresses the root cause of your sleeplessness.
Final Thoughts
Getting good sleep is like hitting the reset button for your mind and body. It is not just about laziness or luxury; it is a biological necessity for a happy, healthy life. Simple changes, like keeping a set bedtime, cooling down your room, and respecting your caffeine curfew, can make a world of difference. Why not try just one of these tips tonight?
Have you checked if stress or hidden health issues are stealing your energy? Taking small steps today could lead to brighter mornings and sharper thinking tomorrow. If tiredness weighs you down no matter what you try, speak with a doctor who can help untangle deeper problems. You deserve to wake up feeling great!