Keeping your home warm in freezing winters can feel like a never-ending struggle. High heating bills, cold drafts, and poor indoor air quality—all of these add up to discomfort. Many homes waste energy with heat loss, leaving homeowners frustrated every season.
Passive house design offers a smart solution for cold climates like the northern USA. These homes are energy-efficient, keeping you cozy without racking up big utility costs. By using techniques like airtight construction and proper insulation, passive houses reduce heat transfer and improve thermal comfort year-round.
This guide will help you design or improve your home simply and effectively. From building orientation to high-performance windows, we’ll walk through steps that work for cold weather living.
Ready to stay warm while saving money? Read on!
Understanding Passive House Design
Passive houses focus on cutting energy use while keeping spaces cozy. They rely on smart planning to trap heat and block cold, making them perfect for chilly climates.
What is a Passive House?
A passive house is an energy-efficient building. It stays warm in winter and cool in summer with little or no active heating or cooling. This design relies on things like super-insulation, airtight construction, and high-performance windows to reduce heat loss.
Solar gains play a huge role too, as the home captures sunlight for natural warmth.
Passive homes prove that comfort doesn’t have to cost the Earth!
These houses focus on creating a balanced indoor climate year-round. They use heat recovery ventilation systems to provide fresh air while keeping energy use low. Builders aim for nearly zero-energy consumption while improving thermal comfort and cutting down on utility bills in cold climates.
Benefits of Passive House Design in Cold Climates
Passive house design cuts energy use. These homes stay warm without traditional heating systems. Thick thermal insulation and airtight seals keep the heat in. This reduces drafts, lowers bills, and improves comfort during icy winters.
Triple-pane windows allow in natural light while stopping heat loss. Solar gain from proper building orientation provides extra warmth for free.
Fresh air stays constant with mechanical ventilation systems like an energy recovery ventilator [ERV]. These systems save heat while filtering outdoor air. High-performance materials also prevent thermal bridges that leak warmth through walls or floors.
The result? A healthier indoor environment with fewer problems like mold growth and cold spots, even on freezing days!
Building Orientation and Site Selection
The way your house faces can make or break its warmth. Clever planning saves energy and keeps cold winds at bay.
Maximizing Solar Gains
Face your home toward the sun. In cold climates like the Northern USA, this boosts passive solar heating. Large south-facing windows capture sunlight and provide natural warmth during winter.
The sun is free heat—why not use it?
Plant deciduous trees nearby for summer shading while letting in winter light after leaves fall. A well-angled roof can also support solar panels for extra energy savings year-round.
Keep walls insulated to trap this gained heat longer indoors, reducing dependence on heating systems!
Minimizing Wind Exposure
Place the building where natural barriers, like hills or trees, block strong winds. Deciduous trees can protect in winter while letting sunlight through. Thick shrubs work well as windbreaks too.
Shape the house to cut down on wind hitting it directly. A compact design holds onto heat better and reduces drafts. Use materials that withstand cold climates for extra durability against harsh winds.
Super-Insulated Building Envelope
A super-insulated building envelope keeps the cold out and the warmth in. Thick insulation acts like a cozy coat for your home, cutting heat loss to save energy.
Importance of High-Performance Insulation
Thick insulation keeps warm air inside during cold winters. It reduces heat loss, saving energy and lowering heating costs. In passive house design, high-performance insulation is a must for thermal comfort.
A well-insulated building envelope stops drafts and keeps indoor spaces cozy.
In cold climates like the Northern USA, proper insulation can cut energy use by up to 60%. It works with airtight construction to trap heat. Walls, roofs, and floors need strong thermal barriers to prevent heat leaks even in freezing conditions.
This also helps avoid frozen pipes or chilly spots indoors!
Airtight Construction
Keep drafts out and heat in with airtight construction—it’s like wrapping your home snugly in a winter coat.
Reducing Heat Loss and Drafts
Seal gaps in walls, windows, and doors. Even tiny cracks let cold air sneak inside. Use caulk or weatherstripping to block these leaks. Air sealing keeps warmth indoors and reduces heating costs.
Airtight construction is key for passive houses. This stops drafts from creeping through the building envelope. Pair it with high-performance insulation to trap heat effectively during harsh winters in cold climates.
High-Performance Windows and Shading
Good windows trap warmth and keep cold out, even during icy winters. Add smart shading to let sunlight in when you need it, but block it when you don’t.
Selecting Triple-Glazed Windows
Triple-glazed windows trap heat better than double-glazed ones. Their three layers of glass create extra insulation, cutting down energy loss. Homes in cold climates benefit the most since they hold warmth during freezing months.
These windows also block outside noise, keeping interiors quiet and cozy.
Look for models with low-emissivity coatings and gas-filled gaps like argon or krypton between panes. This combo boosts efficiency without making spaces feel stuffy. Though pricier upfront, triple glazing slashes heating costs over time, saving money in the long run.
Opt for sturdy frames made of wood, fiberglass, or insulated vinyl to seal out drafts effectively.
Using Shading for Seasonal Efficiency
Shading helps control heat gain and loss. In summer, use shading to block intense sunlight. Install overhangs or exterior shutters for this purpose. Deciduous trees can also provide natural shade during hot months.
In winter, remove or adjust shading to allow more sun inside. Sunlight adds passive heating, reducing the need for extra energy use. Properly planned shades save money and improve comfort all year long.
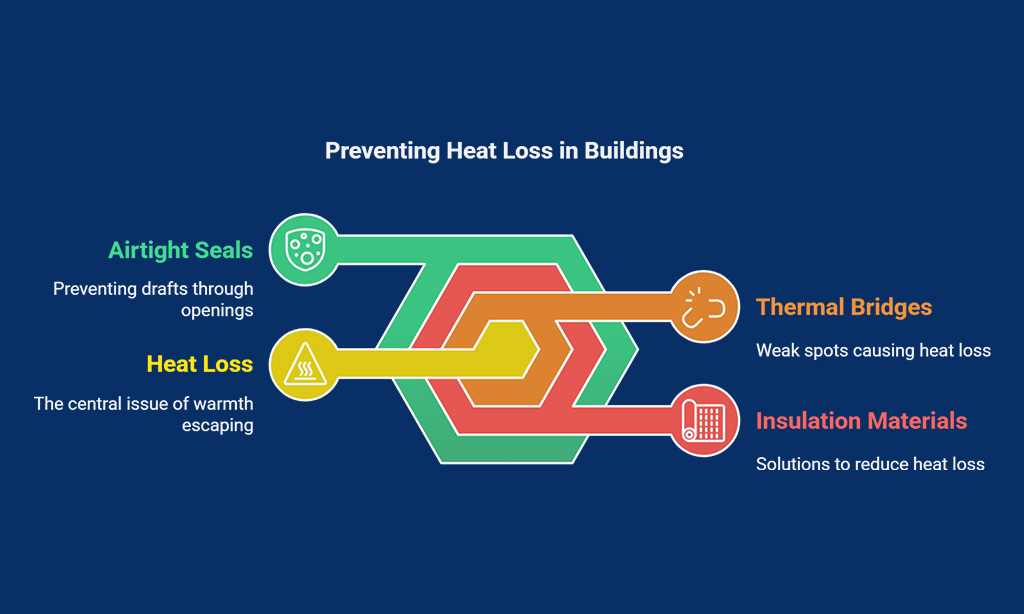
Thermal Bridge-Free Construction
Heat escapes through weak spots in walls, floors, and roofs—these are thermal bridges. Stop them cold with smarter designs and better materials.
Preventing Heat Loss Through Structural Elements
Gaps and weak spots in walls, floors, or roofs act like escape routes for heat. These areas, called thermal bridges, leak warmth fast. Insulating these parts is key to keeping cozy indoors during cold months.
Use materials with high thermal breaks to stop this problem. For example, foam boards or mineral wool work well in reducing heat loss at junctions. Ensure windows and door frames have airtight seals too.
Small cracks around them can let drafts sneak into your home unnoticed!
Mechanical Ventilation with Heat Recovery [MVHR]
Fresh air is a must in cold climates, but cracking open windows wastes heat. MVHR systems solve this by swapping indoor air with outdoor air while keeping the warmth inside.
Ensuring Fresh Air and Energy Efficiency
Heat recovery ventilation systems keep air fresh without wasting heat. They pull stale air out, bring clean air in, and use the outgoing heat to warm incoming air. This works well for cold climates, cutting energy waste while keeping homes comfortable.
High-performance HVAC systems like heat pumps also help with heating and cooling. These systems use less energy compared to older units. Pair them with good insulation and airtight construction for better results.
Good airflow boosts indoor comfort and reduces humidity problems during long winters.
Thermal Mass Integration
Thermal mass absorbs, stores, and releases heat slowly, keeping your home cozy in winter; learn the tricks to maximize its use.
Storing and Releasing Heat Effectively
Thick walls and floors made from concrete, brick, or stone absorb heat during the day. At night, they release it back into your home. This process keeps indoor environments cozy even in cold climates.
High thermal mass materials like these work best if paired with passive solar design.
A trombe wall is a good example of this technique. It uses sunlight to trap and store heat behind glass panels. Water tanks can also store warmth effectively due to water’s high capacity for holding energy.
Both systems boost thermal comfort while cutting down on space heating costs in winter months!
Takeaways
Passive house design in cold climates makes life cozy and efficient. Good insulation, airtight walls, and the right windows keep heat inside. Smart building orientation taps into sunlight for natural warmth.
Using thermal mass helps save energy while improving comfort. Start small, but make thoughtful changes—your wallet and the planet will thank you!
FAQs on Passive House Tips for Northern USA Climates
1. What is a passive house, and why is it good for cold climates?
A passive house is an energy-efficient building designed to minimize heating and cooling needs. It works well in cold climates because of features like thermal insulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilators.
2. How does building orientation impact energy efficiency in passive houses?
Building orientation maximizes solar gain by positioning the home to capture sunlight during winter. This reduces the need for conventional energy sources for space heating.
3. What role do thermal envelopes play in keeping homes warm?
Thermal envelopes help trap heat inside by reducing air leaks and preventing thermal bridging. They improve indoor air quality while cutting down on heating costs.
4. Can renewable energy be used with a passive house design?
Yes, renewable energy sources like solar panels or solar thermal systems pair perfectly with passive housing to achieve net-zero energy goals.
5. How can natural ventilation improve indoor comfort in a cold climate home?
Natural ventilation allows fresh air into the home without losing too much heat when paired with proper humidity control and vents.
6. Are specific materials better for creating sustainable buildings in northern areas?
Yes, using green building materials like double-glazed windows or trombe walls improves thermal mass while supporting long-term sustainability goals such as LEED certification or the Living Building Challenge.