In today’s digital landscape, securing user data is more critical than ever. Web applications process and store vast amounts of sensitive information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
Failure to implement proper security measures can lead to data breaches, legal penalties, and loss of user trust. Companies like Facebook, Equifax, and Marriott have suffered massive breaches, affecting millions of users and costing billions in damages.
To help you safeguard sensitive information, we have compiled the 10 Best Practices for Securely Storing User Data in Web Apps. These strategies will ensure your web application remains secure, compliant, and resilient against threats.
Why Secure Data Storage is Crucial for Web Apps
With cyber threats evolving rapidly, web applications are at constant risk of breaches. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities to steal sensitive user information such as login credentials, financial details, and personal data. The 2024 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report states that the average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million, making security investments crucial for business sustainability.
| Threat Type | Impact on Web Apps |
| Phishing Attacks | Compromised login credentials, unauthorized access |
| Ransomware | Data encryption for ransom, business downtime |
| SQL Injection | Database manipulation, theft of user data |
| Insider Threats | Unauthorized access by employees or contractors |
Legal and Compliance Requirements
Data security is not just a best practice—it is a legal obligation. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation [GDPR], California Consumer Privacy Act [CCPA], and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act [HIPAA] require businesses to protect user data. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
| Regulation | Key Requirement |
| GDPR | Requires explicit user consent and secure data storage |
| CCPA | Grants users control over their personal data |
| HIPAA | Mandates strict patient data protection in healthcare |
User Trust and Reputation Impact
Users expect their data to be handled securely. A single security breach can erode trust and cause significant reputational harm. According to a 2023 PwC report, 87% of consumers will take their business elsewhere if they don’t trust a company’s security practices. Implementing best practices for securely storing user data in web apps builds confidence and strengthens your brand.
10 Best Practices for Securely Storing User Data in Web Apps
Ensuring the security of user data in web applications is a top priority for businesses operating in the digital space. With cyber threats evolving rapidly, developers and organizations must adopt robust security measures to protect sensitive information. The following best practices will help web applications minimize vulnerabilities, comply with regulations, and build user trust by implementing secure storage mechanisms.
1. Implement Strong Encryption Techniques
Encryption is the cornerstone of data security, acting as a fundamental defense mechanism for web applications. It ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties, preserving confidentiality and integrity. Modern encryption techniques help businesses prevent unauthorized access, mitigate cyber threats, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Without encryption, hackers can easily extract and misuse data, leading to financial fraud, identity theft, and severe reputational damage for companies handling sensitive information.
Key Encryption Methods:
| Encryption Type | Recommended Standard | Use Case |
| Data at Rest | AES-256 | Securely storing data in databases |
| Data in Transit | TLS 1.3 | Encrypting communication between clients and servers |
| Password Hashing | Argon2, bcrypt | Protecting stored passwords from breaches |
2. Use Secure Authentication and Access Controls
Strong authentication mechanisms prevent unauthorized access to user data by adding multiple layers of security. Traditional username-password authentication is no longer sufficient, as passwords can be easily stolen, guessed, or compromised through phishing attacks.
Implementing multi-layered security ensures that even if a password is compromised, unauthorized access is blocked through additional verification methods such as biometrics, OTPs, or authentication apps. Companies that prioritize secure authentication significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, ultimately protecting both their users and business reputation.
Best Authentication Practices:
| Security Measure | Benefit |
| Multi-Factor Authentication [MFA] | Adds extra security beyond just passwords |
| Role-Based Access Control [RBAC] | Limits access based on user roles |
| Least Privilege Principle | Ensures users have only necessary access |
3. Store Only Necessary User Data
Minimizing stored data reduces the impact of potential breaches by limiting the amount of sensitive information that could be exposed in an attack. Companies should avoid collecting and storing excessive user information unless required for operational purposes.
Storing unnecessary data increases the risk of misuse, compliance violations, and operational inefficiencies. By adopting data minimization strategies, businesses can improve security, streamline storage management, and enhance user privacy while reducing potential liability in case of a breach.
Data Minimization Strategies:
| Practice | Benefit |
| Collect only essential data | Reduces risk exposure |
| Anonymize or pseudonymize data | Protects user privacy |
| Regularly delete unnecessary data | Minimizes breach impact |
4. Regularly Update Security Protocols and Software
Outdated software and security protocols are common attack vectors that hackers exploit to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Cybercriminals often target known vulnerabilities in outdated applications, making regular updates a critical defense mechanism.
Ensuring that all software, frameworks, and third-party libraries are up-to-date reduces the risk of security breaches. Regular updates also help maintain compliance with industry regulations and reinforce the overall security posture of web applications.
Key Measures:
| Update Strategy | Benefit |
| Automate security patches | Reduces human error |
| Regularly update dependencies | Ensures all components are secure |
| Use the latest encryption protocols | Protects against evolving threats |
5. Implement Database Security Best Practices
Databases are prime targets for attackers, making security measures essential. A poorly secured database can serve as an entry point for cybercriminals to access sensitive user data, leading to catastrophic breaches.
High-profile incidents, such as the Equifax breach, exposed the personal data of over 147 million users, largely due to unpatched vulnerabilities and weak access controls. Organizations must adopt robust database security strategies to prevent such attacks and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
By implementing best practices, businesses can mitigate risks, improve data integrity, and protect users from identity theft and financial fraud.
Database Security Techniques:
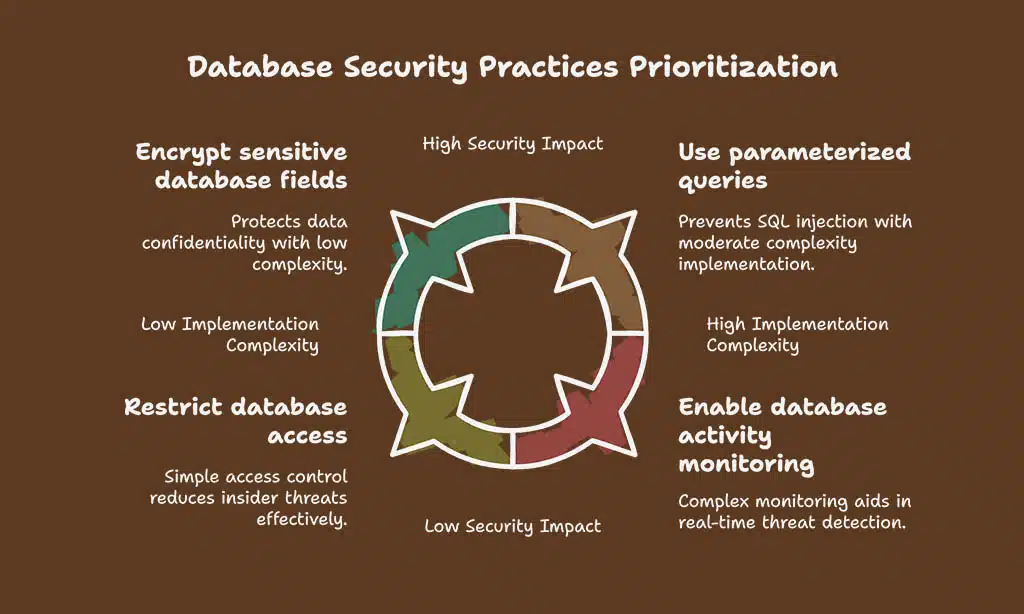
| Practice | Impact |
| Use parameterized queries | Prevents SQL injection attacks, a common exploit |
| Encrypt sensitive database fields | Ensures confidential data remains unreadable to attackers |
| Restrict database access | Limits unauthorized access, reducing insider threats |
| Enable database activity monitoring | Helps detect and respond to suspicious activities in real time |
| Regularly apply security patches | Fixes known vulnerabilities before they are exploited |
6. Monitor and Log Data Access Activities
Monitoring access logs helps detect suspicious activities early and enables proactive threat mitigation before any real damage occurs. By continuously tracking system interactions, businesses can identify unusual access patterns, unauthorized login attempts, and potential security breaches in real time.
Companies that fail to implement comprehensive logging and monitoring often detect breaches too late, resulting in significant financial and reputational losses. Incorporating AI-driven monitoring tools and automated alerts can further enhance the effectiveness of security log analysis.
Best Practices for Logging:
| Monitoring Method | Benefit |
| Real-time logging | Detects issues instantly |
| Intrusion detection systems [IDS] | Flags unusual behavior |
| Regular log analysis | Identifies attack patterns |
7. Backup Data Securely and Regularly
A robust backup strategy ensures data recovery in case of breaches, hardware failures, or cyberattacks such as ransomware. Many companies suffer data loss because they fail to implement a proper backup system, leaving them vulnerable to irreversible damage.
Secure backups provide a reliable safety net, ensuring that user data can be restored quickly in case of emergencies. Businesses must follow best practices such as encryption, offsite storage, and automation to maximize the effectiveness of their backup strategy.
Secure Backup Strategies:
| Backup Type | Benefit |
| Encrypted backups | Ensures data remains unreadable in case of theft |
| Offsite/cloud backups | Protects against physical damage or on-premises attacks |
| Automated backups | Reduces human error and ensures timely data recovery |
| Incremental backups | Saves storage space and speeds up recovery time |
| Disaster recovery plan | Provides a structured approach for data restoration |
8. Apply Secure API Practices for Data Handling
APIs facilitate data exchanges between web applications and third-party services, allowing seamless integration and functionality. However, if not secured properly, APIs can become a major vulnerability, exposing sensitive data and making applications susceptible to cyber threats such as unauthorized access, data leaks, and injection attacks.
Implementing strong API security measures helps protect user information, maintain compliance, and prevent malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities.
API Security Guidelines:
| Security Measure | Benefit |
| Use OAuth/JWT | Ensures secure authentication and tokenized access |
| Implement rate limiting | Prevents abuse, bot attacks, and DDoS attempts |
| Enforce HTTPS | Encrypts data transmissions to protect confidentiality |
| Validate API requests | Prevents injection attacks and unauthorized access |
| Use API gateways | Adds an additional security layer for request filtering |
| Monitor API activity | Helps detect suspicious behavior and potential breaches |
9. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security assessments are essential for identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by cybercriminals. Conducting frequent security audits ensures that security controls are effective, while penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to assess system resilience.
Key Steps in Security Audits and Penetration Testing:
- Perform Vulnerability Scanning: Use automated tools to detect weaknesses in applications, networks, and databases.
- Conduct Manual Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers simulate cyberattacks to uncover security flaws that automated tools may miss.
- Review Access Controls: Ensure proper user access management to prevent unauthorized data exposure.
- Assess Third-Party Security: Evaluate the security posture of vendors and partners to mitigate supply chain risks.
- Analyze Security Logs and Incident Reports: Identify patterns of suspicious activity and potential breaches.
- Ensure Compliance with Security Standards: Align security practices with industry regulations such as GDPR, ISO 27001, and NIST frameworks.
- Remediate Identified Issues: Prioritize and fix vulnerabilities based on severity and risk assessment.
By implementing regular security audits and penetration testing, organizations can proactively strengthen their cybersecurity defenses and reduce the risk of data breaches.
10. Educate Developers and Employees on Security Best Practices
Human error remains one of the most significant contributors to security breaches. Continuous security education ensures that both developers and employees are aware of potential threats and best practices, fostering a security-first culture within the organization.
Key Training Topics and Their Impact:
| Training Topic | Impact |
| Phishing Awareness | Prevents employees from falling victim to social engineering and email-based attacks. |
| Secure Coding | Helps developers write robust, secure code to minimize software vulnerabilities. |
| Password Management | Encourages strong password policies and the use of multi-factor authentication [MFA]. |
| Incident Response | Ensures employees know how to report and handle security incidents effectively. |
| Device and Data Security | Promotes the safe handling of sensitive information and secure device usage. |
| Security Culture | Encourages proactive security behaviors across the organization. |
Methods for Delivering Security Training:
- Regular Security Awareness Workshops: Conduct hands-on training sessions to keep employees updated on the latest security threats.
- Simulated Phishing Campaigns: Test employees’ ability to recognize phishing attempts and reinforce learning through real-world scenarios.
- Online Security Training Modules: Offer interactive e-learning courses on cybersecurity best practices.
- Code Reviews and Peer Training for Developers: Foster a security-conscious development environment through code audits and team-based learning.
- Security Newsletters and Alerts: Share regular updates on emerging threats, attack trends, and security tips.
By prioritizing security education, organizations can significantly reduce human-related security risks and cultivate a workforce that actively contributes to cybersecurity resilience.
Takeaways
Securing user data in web applications is a continuous process that requires proactive measures. By implementing these 10 Best Practices for Securely Storing User Data in Web Apps, businesses can safeguard sensitive information, comply with regulations, and enhance user trust.
Companies that prioritize security not only protect their users but also gain a competitive advantage in today’s digital world.