Owning digital content can feel tricky. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are shaking up how digital rights work. They help creators protect and control their digital assets, like art or music.
Stick around to learn how NFTs are changing the game for creators and users alike!
What Are NFTs and How Do They Work?
NFTs stand for Non-Fungible Tokens. These are records stored on blockchains like Ethereum, using standards such as ERC-721. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, NFTs can’t be exchanged equally because each one is distinct.
Think of them as digital collectibles or deeds that prove ownership over a digital asset like art, music, or even virtual real estate.
Smart contracts power NFTs. They automatically enforce rules, such as ensuring creators earn royalties with every secondary sale. To create an NFT, artists mint it by adding their work to the blockchain—this process often requires paying gas fees.
By mid-2021, NFTs took off in popularity; even Beeple sold a piece for $69 million at Christie’s auction house!
The Role of NFTs in Digital Rights Management
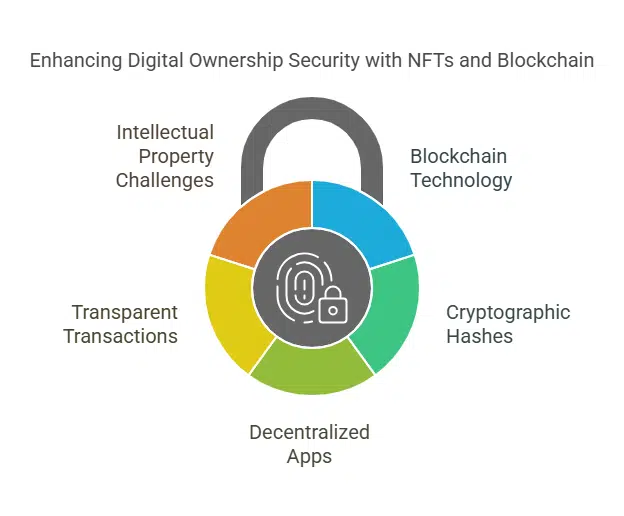
NFTs are shaking up how digital assets get managed and protected. They use blockchain technology to create clear ownership records, changing the way creators control their work.
Verifying Ownership of Digital Assets
Blockchain technology keeps a clear record of digital ownership. Every non-fungible token (NFT) has metadata that shows its creation, authenticity, and history. Such information prevents fakes and makes tracking easier for high-value items like digital art or virtual real estate.
Smart contracts handle transfers automatically during sales in NFT marketplaces. These automated processes ensure buyers receive true ownership without tampering. In 2022 alone, NFT trading hit over $5 billion globally, proving their rising use in securing assets across industries like luxury goods and crypto-art.
Preventing Unauthorized Distribution
NFTs make digital ownership safer by using blockchain technology. Every digital asset gets a cryptographic hash, acting like a fingerprint. This technique makes it tough to copy or fake. Creators can track where their digital goods go through decentralized apps and APIs.
Unauthorized sharing becomes harder since NFTs link to the buyer’s crypto wallet. Transparent transactions in NFT marketplaces help spot piracy quickly. Still, enforcing intellectual property rights may face challenges due to anonymity on these platforms.
7 Ways NFTs Are Changing Digital Rights Management
NFTs are shaking up how digital content gets managed, traded, and protected. They’re paving new paths for creators to take charge of their work while blocking misuse.
Securing Royalties for Creators
Creators earn royalties by using smart contracts in blockchain technology. These contracts automate payments on secondary sales of digital goods like digital art or virtual real estate.
Unlike traditional systems, artists no longer rely solely on first-time sales for income. Royalties, often set between 5% and 10%, provide a steady revenue stream.
NFT marketplaces built with ERC-721 or ERC-1155 standards make this system possible. By August 2022, global NFT trades hit over $5 billion, showing the rising value of these non-fungible assets.
Automated payouts ensure creators benefit financially every time their work is resold in virtual worlds or online markets.
Enabling Transparent Licensing Agreements
Smart contracts tied to NFTs simplify licensing. These agreements live on blockchain technology, making terms clear and unchangeable. Automation enforces them without middlemen, cutting costs while reducing disputes.
For example, musicians or digital artists can attach usage rights directly to their digital art or collectibles. This approach ensures compliance with rules like royalty payments during secondary sales.
Trademark owners benefit too by using non-fungible tokens for branding deals. The U.S. Copyright Office recognizes NFTs as a strong tool in intellectual property protection. Clear licensing through these tools builds trust between creators and buyers across NFT marketplaces worldwide.
Enhancing Copyright Protection
NFTs help creators protect their digital assets. They act as proof of ownership on blockchain technology, which keeps data clear and secure. This prevents misuse or theft of intellectual property like digital art or music.
Creators no longer need to rely solely on legal battles to claim their rights.
Every NFT comes with unique metadata tied to the owner’s cryptocurrency wallet. The data makes it easy to track the asset’s origins and verify its authenticity. Fraud becomes harder, while artists maintain control over their work in NFT marketplaces and beyond.
Simplifying Content Monetization
Creators tokenize their digital goods with blockchain technology to earn more money. Musicians, for example, use non-fungible tokens (NFTs) to sell music royalties directly to fans.
The process removes middlemen and increases profits. Tokenized art or videos can also generate secondary sales on NFT marketplaces, providing extra income streams.
Smart contracts automate royalty payments. Artists no longer chase unpaid fees as transactions happen instantly through crypto wallets. Platforms like OpenSea make it easy for creators to manage rights and monitor revenue streams in real time without expensive database management systems (DBMS).
Reducing Piracy and Fraud
Blockchain technology fights piracy with strong encryption. It creates a secure digital record for every NFT (non-fungible token). This record proves ownership of digital assets like art, music, or videos.
By August 2022, NFT trading reached over $5 billion globally, showing how big this market has become. With proof of ownership stored on the blockchain, illegal downloads can be tracked easily.
Smart contracts play a key role in stopping fraud. They automate legal agreements and enforce rules without mistakes. For example, if someone tries to resell stolen digital collectibles on NFT marketplaces, the system detects it and blocks the sale.
This safeguards the intellectual property of creators and deters potential thieves.
Facilitating Global Access to Content
NFTs break barriers for creators and audiences worldwide. Digital assets like digital art or virtual goods become accessible to a broader audience, no matter their location. In 2021, NFTs surged in popularity, making headlines globally.
This growth opened doors for diverse content sharing through NFT marketplaces.
Smart contracts allow royalty systems to thrive across borders. Creators earn revenue from secondary sales without intermediaries cutting into profits. Digital tickets powered by NFTs also grant access to exclusive events or communities online.
By connecting people globally, these tokens revolutionize the way content spreads and reaches everyone efficiently.
Empowering Independent Creators
Non-fungible tokens give independent creators control over their digital assets. Artists like Mike Winkelmann, also known as Beeple, earned millions through NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea and Nifty Gateway.
Smart contracts on blockchain technology let creators set automatic royalty fees, guaranteeing earnings from secondary sales.
Play-to-earn games offer another way for creators to thrive in the virtual economy. Gamers can earn crypto or sell digital collectibles tied to intellectual property they create. This approach opens new revenue streams and boosts opportunities without relying heavily on big companies or traditional middlemen.
Challenges in Implementing NFTs for Digital Rights
Using NFTs for digital rights comes with hurdles that demand attention. Issues like energy usage and unclear laws create big roadblocks.
Scalability and Energy Consumption
NFT transactions often strain energy systems. Networks like those using proof of work (PoW) consume large amounts of electricity, causing high carbon emissions. By mid-2021, NFTs gained massive attention, pushing concerns about sustainability to the forefront.
Critics point out that NFT-related activities could add 4.56 million tons of CO₂ by 2030.
The shift to proof of stake (PoS) technology is a step toward solving this issue. This method uses far less energy per transaction compared to PoW systems. Some regions, such as New York, have even banned fossil-fuel-based cryptocurrency mining to fight environmental impact.
As NFT marketplaces expand, they must balance growth with lowered energy use for better scalability and eco-friendliness in digital commerce.
Legal and Regulatory Concerns
NFTs face legal hurdles due to unclear rules. The U.S. Congress now includes NFT businesses in anti-money laundering laws. This change means stricter monitoring and compliance for companies trading digital collectibles or digital goods.
NFTs may also fall under different labels, such as securities or intellectual property, depending on jurisdiction. Each classification carries separate governance challenges, making rules confusing for buyers and sellers alike.
Ownership does not always mean control over the original work tied to the token. This gap complicates intellectual property rights for creators and collectors of digital assets like virtual real estate or online identity items in NFT marketplaces.
Taxation adds another layer of complexity, with profits often treated as capital gains but varying by location. Rising fraud cases amplify these concerns—examples include fake sales of popular NFTs like Snoop Dogg’s creations or Bored Ape tokens without proper rights authentication through smart contracts or blockchain technology audits.
Future Trends in NFTs and Digital Rights Management
NFTs may soon blend with AI to improve content tracking. They could also reshape virtual spaces like the metaverse, creating new ways to manage rights.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
AI boosts NFT marketplaces by making processes smarter. Tools like DeepArt.io and RunwayML help create high-quality digital art quickly. They use giant datasets to generate fresh designs, adding value for creators and buyers alike.
It also strengthens security. AI detects scams in digital assets, cutting down fraud risks. Personalized recommendations improve customer experience, showing users the right content based on their interests.
This technique creates smoother transactions in virtual environments while protecting intellectual property rights through advanced verification systems.
Expansion into the Metaverse
The metaverse is reshaping digital ownership and revenue streams. By 2025, it’s set to generate billions annually through virtual goods, gaming, and education. NFTs play a key role by authenticating digital assets like art or collectibles in these virtual worlds.
Fashion brands now use NFTs to sell exclusive outfits for avatars. NFT interoperability allows creators to profit across platforms while offering users true control over their digital identity.
Play-to-earn games let gamers earn cryptocurrency through activities tied to non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Major businesses, including entertainment companies and institutions, adopt blockchain technology for applications in this expanding space.
Improved smart contracts enhance licensing agreements within the virtual economy without middlemen slowing deals down. This shift bridges traditional markets with decentralized ecosystems built on transparency and blockchain innovation.
Takeaways
NFTs are rewriting the rules for digital ownership. They give creators more control, protect their rights, and open new revenue streams. Digital art, music, and even virtual real estate now have stronger safeguards.
Challenges remain, but the potential is massive. The future of managing digital assets looks brighter with non-fungible tokens in play.