Agriculture has been at the heart of New Zealand’s economy and identity for centuries, shaping the nation’s landscapes, communities, and global reputation.
From rolling pastures dotted with sheep to expansive vineyards nestled in picturesque valleys, New Zealand’s agricultural landscapes are as stunning as they are productive.
Known for its high-quality produce, the country’s agricultural industry has evolved dramatically from indigenous practices to modern-day innovation.
In this article, we explore the evolution of agriculture in New Zealand by delving into its past, examining current practices, and looking ahead to the future.
The Evolution of Agriculture in New Zealand
Dr. Tim Mackle, CEO of DairyNZ, once said, “New Zealand’s agricultural journey is a testament to the innovation and hard work of its people. From humble beginnings to a global leader, we’ve always adapted to meet the challenges of the times.”
The story of the evolution of agriculture in New Zealand begins with the practices of the indigenous Maori people, who cultivated crops sustainably long before European settlers arrived. Over time, European farming techniques, technological innovations, and global trade revolutionized the agricultural sector, transforming it into the backbone of New Zealand’s economy.
This section explores the roots of this transformation and how early developments set the stage for modern advancements.
Pre-European Era
Before European settlers arrived, the indigenous Maori people practiced agriculture that was deeply rooted in sustainability. They cultivated crops such as kumara (sweet potato) and utilized natural resources to support their communities.
Their methods were environmentally conscious, relying on techniques like crop rotation and companion planting to maintain soil fertility and productivity.
European Settlement and Early Development
The arrival of European settlers in the 19th century marked a turning point for agriculture in New Zealand. Sheep farming quickly became a cornerstone of the economy, with vast tracts of land converted into pastures for wool production.
Wheat and dairy farming also gained prominence, supported by a growing population and increasing demand for food. The introduction of European farming techniques and livestock transformed the agricultural landscape.
Technological Advancements in the 19th and Early 20th Century
Did you know that New Zealand was the first country to export frozen meat to the UK? This groundbreaking achievement in the late 19th century revolutionized global trade and firmly established New Zealand as a major player in the agricultural industry.
Refrigerated shipping enabled the country to transport high-quality meat and dairy products to markets thousands of miles away, creating new opportunities for growth. Fertilizers, irrigation systems, and mechanization further enhanced productivity, laying the groundwork for a robust agricultural industry.
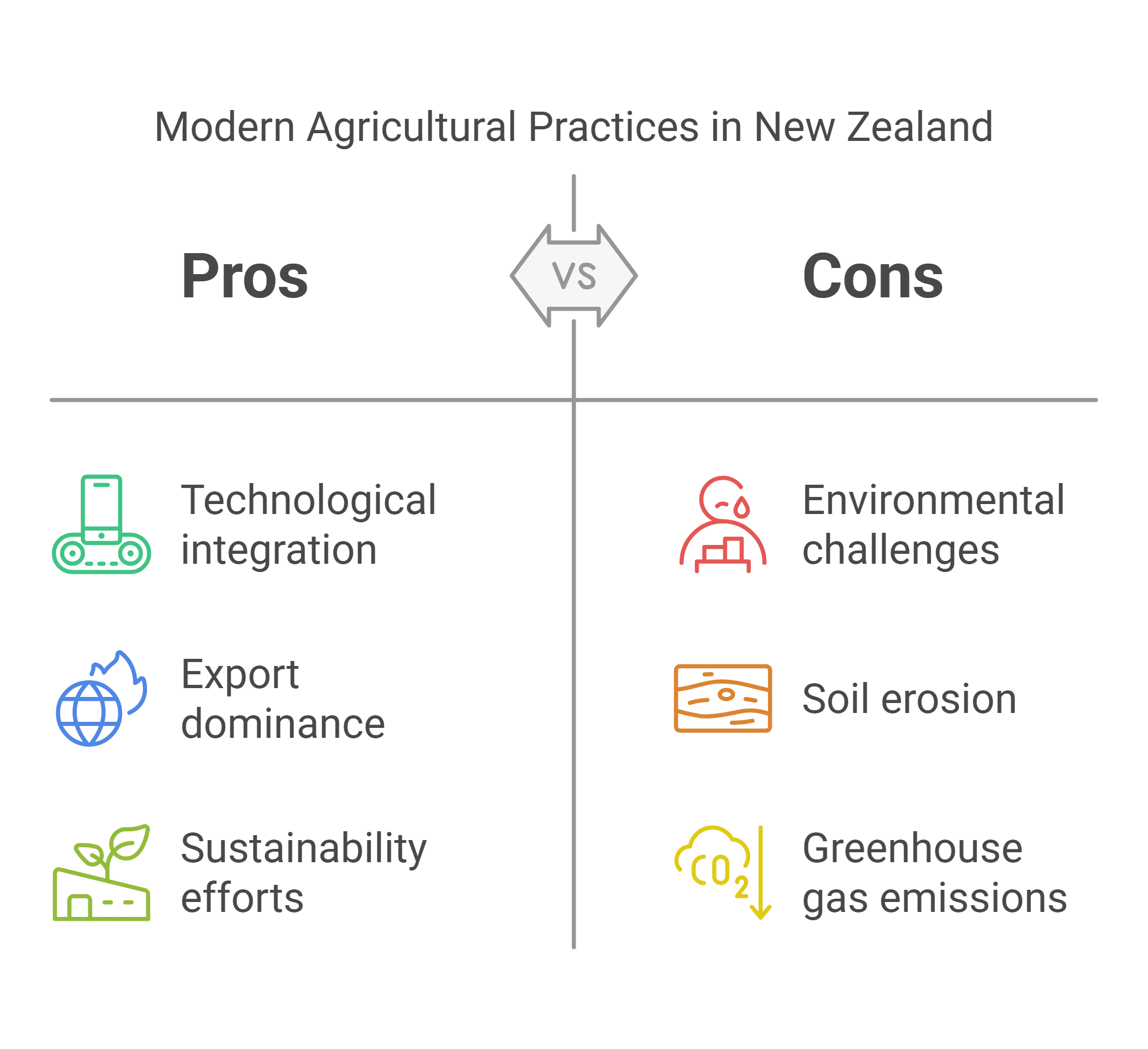
The Present – Modern Agricultural Practices
The evolution of agriculture in New Zealand has reached an era defined by cutting-edge technologies, global market leadership, and a growing focus on sustainability.
Today’s agricultural practices blend innovation and tradition, making New Zealand a global benchmark for efficiency and quality in farming.
This section delves into the modern techniques, challenges, and sustainable practices shaping the industry today.
Technological Integration
Today, New Zealand’s agriculture is synonymous with cutting-edge technology. Farmers use precision agriculture tools, including GPS-guided machinery, drones for crop monitoring, and advanced irrigation systems. These innovations have improved efficiency, reduced waste, and optimized yields while addressing environmental concerns.
Export Dominance
New Zealand’s lush green hills and pristine farmland are not just a feast for the eyes—they’re also the backbone of its thriving export economy. The agricultural industry contributes approximately 65% of the country’s total export earnings, and the iconic dairy farms scattered across the countryside account for nearly 35% of these exports.
With scenic vineyards producing world-class wines and fertile orchards yielding premium fruits, the agricultural landscapes embody the country’s global reputation for quality and excellence. Free trade agreements and access to international markets have enabled the country to thrive as a key supplier of premium produce, driving its economic success.
New Zealand is a global leader in agricultural exports, with the industry contributing approximately 65% of the country’s total export earnings. Dairy products alone account for nearly 35% of these exports, making New Zealand one of the top dairy exporters worldwide.
Environmental Challenges
The environmental impact of agriculture remains a pressing issue. According to Hon. Damien O’Connor, New Zealand’s Minister of Agriculture, “The industry’s future depends on our ability to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability. It’s about finding smarter ways to farm.” Despite its successes, New Zealand faces significant environmental challenges.
Soil erosion, declining water quality, and greenhouse gas emissions from livestock are pressing concerns. The government and industry stakeholders are working together to implement policies that promote sustainable farming practices.
Shift Toward Sustainability
There is a growing movement towards organic farming and regenerative agriculture, which prioritize soil health and biodiversity. Many farmers are adopting low-carbon technologies and exploring ways to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining productivity.
The Future – Trends and Innovations Shaping Agriculture
The evolution of agriculture in New Zealand continues to unfold as the nation strives to balance innovation, sustainability, and global leadership. With a strong agricultural foundation, New Zealand is uniquely positioned to embrace emerging technologies and climate-smart practices.
This section explores how advancements in sustainability, technology, and shifting consumer demands will shape the future of agriculture in the country.
Sustainability and Climate Change Adaptation
Maori leader Mike Smith highlights the importance of sustainability in modern agriculture: “Our relationship with the land is sacred, and our practices must reflect respect for future generations.
As the impacts of climate change become more pronounced, New Zealand’s agricultural sector must adapt to ensure resilience. Future policies are expected to focus on carbon-neutral farming, efficient water usage, and climate-smart practices.
Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and vertical farming are poised to revolutionize agriculture. Genetic engineering and advanced pest control methods will further enhance productivity while minimizing environmental harm.
Shifting Consumer Trends
Global demand for plant-based products and alternative proteins is rising, and New Zealand is well-positioned to capitalize on this trend. Export markets are evolving to cater to diverse dietary preferences, offering opportunities for innovation in product development.
Global Leadership
New Zealand has the potential to lead the world in sustainable agricultural practices. By leveraging its expertise and embracing innovation, the country can set an example for environmentally conscious farming on a global scale.
How People Can Support Sustainable Farming Practices
- Buy Local and Organic Products: Support farmers who prioritize sustainable practices by choosing locally grown, organic produce. This reduces carbon footprints and promotes environmentally friendly agriculture.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about sustainable farming techniques and share that knowledge with your community. Awareness is key to fostering support for eco-friendly practices.
- Participate in Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA): Join CSA programs to directly support small-scale farmers who focus on sustainable farming.
- Reduce Food Waste: Be mindful of food consumption to minimize waste, which indirectly supports the sustainability of agricultural resources.
- Advocate for Policy Changes: Encourage policymakers to support legislation that promotes sustainable farming and environmental conservation.
How Businesses Can Contribute to the Industry’s Future
- Invest in Sustainable Practices: Businesses can adopt regenerative farming techniques, reduce emissions, and prioritize eco-friendly technologies.
- Collaborate with Research Institutions: Partner with universities and research centers to develop and implement innovative agricultural solutions.
- Promote Agri-Tourism: Create opportunities for people to experience sustainable farming practices firsthand through tours and educational programs.
- Adopt Renewable Energy Sources: Use solar, wind, or bioenergy in farming operations to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Foster Fair Trade Practices: Ensure farmers receive fair compensation, encouraging them to maintain sustainable and ethical farming methods.
While agriculture in New Zealand faces challenges such as labor shortages, market volatility, and climate risks, it also presents immense opportunities. Agri-tourism, innovation hubs, and global partnerships could drive growth and sustainability in the sector. By addressing these challenges head-on, New Zealand can ensure a prosperous future for its agricultural industry.
Takeaways
The evolution of agriculture in New Zealand reflects a journey of innovation, resilience, and sustainability. From the indigenous practices of the Maori to modern technological advancements, agriculture has been the backbone of the nation’s economy and culture.
As New Zealand looks to the future, embracing sustainable practices and cutting-edge technology will be key to ensuring a thriving agricultural sector that benefits both the environment and future generations.