Green energy has long been touted as the future of power generation, but concerns about its cost have persisted. Many wonder: Is green energy more expensive than traditional fossil fuels? The answer may surprise you.
Recent data and market trends reveal that renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly cost-competitive and, in many cases, are now cheaper than conventional power generation methods.
The Shifting Landscape of Energy Costs
Over the past decade, the renewable energy sector has experienced a dramatic transformation in terms of cost and efficiency. What was once considered an expensive alternative to fossil fuels has now become a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option for power generation.
Solar Power: A Shining Example of Cost Reduction
Solar energy has seen one of the most significant price drops among renewable sources. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global weighted average levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) projects fell by 85% between 2010 and 2022.
In 2022, the average cost of electricity from newly commissioned utility-scale solar PV projects was just $0.049 per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
Wind Power: Blowing Away Cost Expectations
Wind energy has also experienced substantial cost reductions. The global weighted average LCOE for onshore wind projects decreased by 69% between 2010 and 2022. In 2022, the average cost of electricity from new onshore wind projects was $0.033/kWh, making it one of the most competitive sources of new electricity generation.
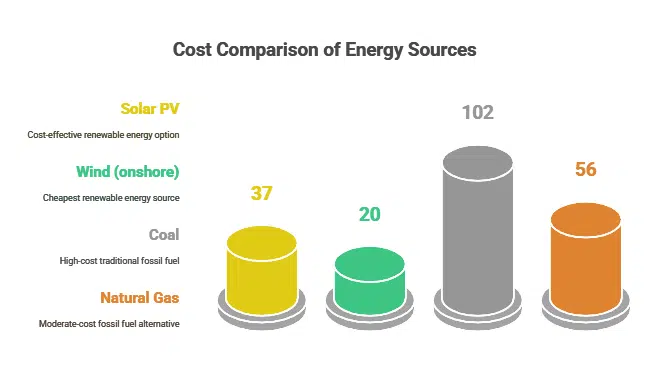
Comparing Costs: Renewables vs. Fossil Fuels
To truly understand whether green energy is more expensive, we need to compare it directly with fossil fuel alternatives. Here’s a breakdown of the average costs for different energy sources:
| Energy Source | Average Cost (USD/MWh) |
| Solar PV | $37 |
| Wind (onshore) | $20 |
| Coal | $102 |
| Natural Gas | $56 |
As we can see, both solar and wind power are now significantly cheaper than coal and even undercut natural gas in many cases.
Factors Driving the Cost Reduction in Renewable Energy
Several key factors have contributed to the decreasing costs of renewable energy:
- Technological advancements
- Economies of scale
- Improved manufacturing processes
- Learning curves in project development and operation
- Increased competition in the renewable energy sector
These factors have combined to create a virtuous cycle of cost reduction, making renewable energy increasingly attractive to investors and policymakers alike.
The Hidden Costs of Fossil Fuels
When considering the cost of energy, it’s crucial to look beyond just the price of generation. Fossil fuels come with significant externalities that are often not factored into their market price:
- Environmental damage and climate change impacts
- Health costs associated with air pollution
- Geopolitical risks and energy security concerns
When these factors are taken into account, the true cost of fossil fuels becomes much higher than their market price suggests.
The Economic Benefits of Green Energy
Investing in renewable energy doesn’t just reduce costs; it also brings significant economic benefits:
Job Creation
The renewable energy sector is a powerful job creator. According to IRENA, the renewable energy sector employed 12.7 million people globally in 2021, with solar PV being the largest employer.
Energy Independence
By developing local renewable resources, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, improving energy security and keeping energy dollars within the local economy.
Stable Energy Prices
Unlike fossil fuels, which are subject to price volatility, renewable energy sources offer more stable and predictable energy costs over the long term.
Challenges and Considerations
While the cost trends for renewable energy are promising, there are still challenges to consider:
Integration Costs
As the share of variable renewable energy (like wind and solar) increases in the power mix, there may be additional costs associated with grid integration and energy storage.
Initial Investment
While operational costs are low, the upfront capital costs for renewable energy projects can still be significant, especially for large-scale installations.
Geographic Variability
The cost-effectiveness of renewable energy can vary depending on location, as factors like solar irradiance and wind patterns play a crucial role in energy production.
The Future of Green Energy Costs
Looking ahead, the cost trajectory for renewable energy remains promising. Projections suggest that by 2025:
- The global average cost of electricity from solar PV could fall to $0.05-0.06 per kWh.
- Offshore wind costs could decrease by 35%.
- Battery storage costs are expected to continue declining, further enhancing the competitiveness of variable renewable energy sources.
Policy Implications and Global Trends
The increasing cost-competitiveness of renewable energy has significant implications for energy policy and global climate efforts:
- Many countries are accelerating their renewable energy targets, with the European Union aiming for 42.5% renewable energy by 2030.
- Developing countries are leapfrogging fossil fuel technologies and investing directly in renewables, driven by both economic and environmental considerations.
- Corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) for renewable energy are becoming increasingly common, as businesses seek to lock in low and stable energy prices.
Takeaways
So, is green energy more expensive? The evidence overwhelmingly suggests otherwise. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are now among the cheapest options for electricity generation worldwide. With continued technological advancements and supportive policies, green energy is poised to become even more affordable in the coming years.
Transitioning to renewables not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers significant economic benefits. By investing in green energy today, we can ensure a sustainable and cost-effective future for generations to come.