Sustainable waste management and recycling play a crucial role in addressing environmental challenges. But what is the process of sustainable waste management and recycling, and why is it essential in today’s world?
This comprehensive approach involves managing waste responsibly while promoting resource recovery to minimize environmental impact. Understanding this process empowers individuals, communities, and businesses to reduce waste, conserve resources, and support a circular economy.
Understanding Sustainable Waste Management
Sustainable waste management refers to the practices and strategies aimed at reducing the environmental impact of waste throughout its lifecycle. This approach prioritizes waste reduction, reuse, and recycling over traditional disposal methods like landfilling or incineration.
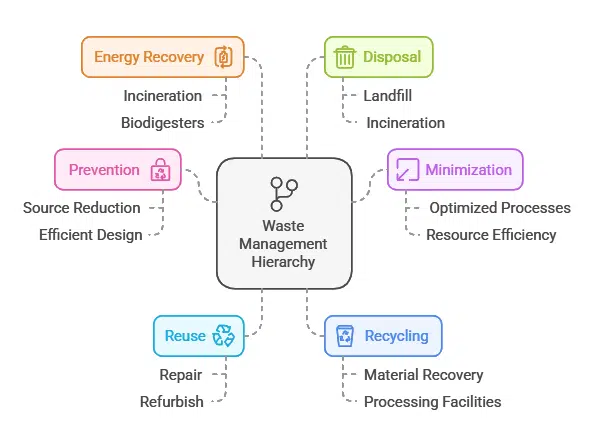
The Waste Management Hierarchy
At the core of sustainable waste management is the waste hierarchy, which outlines the preferred order of waste management options:
- Prevention
- Minimization
- Reuse
- Recycling
- Energy recovery
- Disposal
This hierarchy emphasizes the importance of avoiding waste generation in the first place, followed by reducing, reusing, and recycling materials before considering energy recovery or disposal options.
The Process of Sustainable Waste Management
1. Waste Generation and Prevention
The first step in sustainable waste management is to prevent or minimize waste generation. This involves:
- Designing products with minimal packaging
- Encouraging consumers to make environmentally conscious choices
- Implementing policies to reduce single-use items
2. Collection and Segregation
Once waste is generated, it needs to be collected and properly segregated. This step is crucial for effective recycling and resource recovery. Methods include:
- Curbside collection of separated waste streams
- Centralized collection points for different types of waste
- Use of color-coded bins for easy segregation
3. Processing and Treatment
After collection, waste undergoes various processing and treatment methods depending on its type:
- Organic waste: Composting or anaerobic digestion
- Recyclables: Sorting and preparation for recycling
- Non-recyclable waste: Energy recovery or safe disposal
4. Recycling
Recycling is a key component of sustainable waste management. It involves:
- Sorting materials by type (e.g., paper, plastic, glass, metal)
- Processing recyclables into raw materials
- Manufacturing new products from recycled materials
5. Energy Recovery
For waste that cannot be recycled, energy recovery methods can be employed:
- Incineration with energy capture
- Anaerobic digestion to produce biogas
- Landfill gas capture for energy production
6. Final Disposal
As a last resort, waste that cannot be recycled or used for energy recovery is disposed of in landfills or through other safe disposal methods.
The Importance of Recycling in Sustainable Waste Management
Recycling plays a crucial role in sustainable waste management by:
- Conserving natural resources
- Reducing energy consumption in manufacturing
- Decreasing greenhouse gas emissions
- Minimizing landfill space requirements
Recycling Rates and Statistics
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the recycling rate in the United States has increased significantly over the past few decades:
| Year | Recycling Rate |
| 1960 | 6.4% |
| 1990 | 16% |
| 2018 | 32.1% |
However, there is still room for improvement, as the majority of waste is still disposed of in landfills or through incineration.
Challenges in Sustainable Waste Management and Recycling
Despite the benefits, sustainable waste management and recycling face several challenges:
- Contamination of recyclable materials
- Lack of infrastructure in some regions
- Fluctuating markets for recycled materials
- Public awareness and participation
Innovative Approaches to Sustainable Waste Management
To address these challenges, innovative approaches are being developed:
1. Smart Waste Management Systems
IoT sensors and data analytics are being used to optimize waste collection routes and improve recycling efficiency. These systems have shown promising results:
- 15-23% increase in collection efficiency
- 10-17% rise in recycling rates
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
EPR policies hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal. This encourages the design of more sustainable and recyclable products.
3. Circular Economy Initiatives
The concept of a circular economy aims to keep materials in use for as long as possible, extracting their maximum value before responsible disposal. This approach promotes:
- Product design for longevity and recyclability
- Reuse and repair of goods
- Creation of new materials from recycled resources
Global Perspective on Waste Management and Recycling
Waste management practices vary significantly across countries and regions:
Developed Nations
Many developed countries have made significant progress in sustainable waste management:
- Germany achieved a 69% recycling rate for municipal waste in 2022
- Nine European countries, including Austria, Slovenia, and the Netherlands, achieved recycling rates of 50% or higher.
Developing Nations
Developing countries often face greater challenges in implementing sustainable waste management practices:
- In many low- and middle-income Asian countries, open waste dumping is still the most common method of disposal
- The World Bank estimates that urban areas of Asia produce about 760,000 tons of municipal solid waste per day.
The Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Recycling
As we move towards a more sustainable future, several trends are shaping the waste management and recycling landscape:
- Increased focus on waste prevention and reduction
- Advancements in recycling technologies
- Greater emphasis on the circular economy
- Integration of digital technologies for optimized waste management
Takeaways
To answer the question, “What is the Process of Sustainable Waste Management and Recycling?”, it is a comprehensive approach encompassing waste collection, segregation, recycling, and responsible disposal.
By adopting these practices, individuals and communities can reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and foster a healthier planet. The time to act sustainably is now, and understanding this process is the first step toward achieving a zero-waste future.