The Web3 revolution represents a significant shift in how people interact with digital platforms, financial systems, and governance. By leveraging blockchain, cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi), and smart contracts, Web3 promises to decentralize control, eliminate intermediaries, and create a more transparent and user-centric internet.
However, this new paradigm brings with it challenges that governments around the world must address. As the Web3 landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial to understand how different countries are responding to these changes.
In this article, we will explore the 7 ways governments are responding to the Web3 revolution, diving deeper into each approach and providing examples of how nations are adapting to this technological shift.
From regulatory frameworks to innovation-driven incentives, governments are adopting diverse strategies to ensure the responsible growth of Web3 technologies.
Understanding the Web3 Revolution and Its Impact on Governments
Before we dive into the specifics of how governments are responding to Web3, it’s essential to understand the core concept of Web3 and why governments are prioritizing their engagement with these technologies. Web3 is fundamentally reshaping the way we interact with the internet by promoting decentralization, transparency, and user control.
In contrast to Web 2.0, where data and content are controlled by central entities, Web3 enables peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries, powered by blockchain technology.
For governments, the implications are significant. Web3 holds the potential to radically alter financial systems, public governance, and how governments interact with their citizens.
As blockchain technology underpins the decentralization of systems, governments must find ways to regulate this emerging technology while fostering innovation and minimizing risks such as fraud, money laundering, and cybersecurity threats.
What is Web3 and Why Should Governments Care?
Web3 refers to a decentralized digital ecosystem based on blockchain technology. It promises a future where data and digital assets are controlled by users, rather than centralized platforms or institutions. Here’s why governments must engage with Web3 technologies:
Definition of Web3: Beyond Blockchain
Web3 is more than just blockchain. It represents a new era of the internet where ownership of data, digital assets, and even governance is decentralized. Blockchain, the core technology behind Web3, allows transactions to be recorded securely and immutably across a network of computers without the need for a central authority.
While blockchain has become synonymous with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, Web3 encompasses a broader range of technologies, including smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Key Web3 Components:
| Component | Description |
| Blockchain | A decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. |
| Smart Contracts | Self-executing contracts with the terms of agreement directly written into code, removinBlockg intermediaries in transactions. |
| Decentralized Apps (dApps) | Applications that run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer network, allowing users to interact directly without central authorities. |
| DeFi (Decentralized Finance) | A financial ecosystem that operates on decentralized protocols, enabling services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. |
Key Characteristics of Web3 (Decentralization, Transparency, and Smart Contracts)
Web3 is defined by its three primary characteristics: decentralization, transparency, and smart contracts.
- Decentralization: Unlike Web 2.0, where data is stored on central servers controlled by corporations, Web3 eliminates centralized control by enabling distributed storage and decentralized decision-making.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology ensures that transactions are publicly recorded and traceable, which can significantly reduce corruption and increase trust in systems such as voting or public funds management.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts execute automatically when specific conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and cutting down costs and delays.
The Potential of Web3 in Transforming Global Economies
Web3 can potentially disrupt several industries by providing new ways to conduct financial transactions, establish identity systems, and improve public governance. For governments, this means creating new regulatory frameworks and innovative policies to facilitate Web3 adoption while safeguarding public interest.
| Sector | Web3 Impact |
| Finance | Web3 technologies like DeFi eliminate intermediaries, reduce transaction fees, and increase access to financial services for underserved populations. |
| Governance | Blockchain ensures transparent, tamper-proof systems for public recordkeeping, elections, and resource distribution. |
| Healthcare | Secure, transparent patient data management via decentralized networks can improve privacy, reduce fraud, and enhance accessibility to medical services. |
| Supply Chain | Blockchain’s immutable ledger can ensure transparency in product sourcing, logistics, and inventory management, reducing fraud and inefficiencies. |
Governments’ Role in Balancing Innovation with Regulation
Governments are tasked with ensuring that the innovations introduced by Web3 technologies do not outpace regulatory frameworks that protect consumers, maintain financial stability, and ensure national security. Balancing innovation and regulation will be crucial as Web3 technologies continue to evolve rapidly.
7 Ways Governments Are Responding to the Web3 Revolution
Governments across the globe have adopted a variety of approaches to harness the potential of Web3 while mitigating its risks. Let’s look at 7 ways governments are responding to the Web3 revolution.
1. Introducing Regulatory Frameworks for Cryptocurrencies and Tokens
As cryptocurrencies and tokens gain popularity, governments are introducing regulatory frameworks to ensure their responsible use. These frameworks aim to address issues such as fraud, money laundering, and consumer protection while promoting transparency and growth in the crypto market.
For example, the European Union has introduced the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, which provides a comprehensive legal framework for cryptocurrency assets. Similarly, the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been actively working on creating clearer guidelines for cryptocurrencies and tokens.
Key Points:
- EU’s MiCA Regulation: Provides legal clarity on cryptocurrencies, including rules for exchanges, stablecoins, and investor protection.
- US SEC: Focuses on securities regulation and ensuring compliance for cryptocurrency trading platforms.
- Asia-Pacific: Countries like Japan have implemented licensing systems for crypto exchanges to improve market integrity.
| Region | Regulatory Approach |
| Europe (MiCA) | Framework for crypto assets that enhances transparency, stability, and consumer protection. |
| United States | SEC and CFTC collaborate to regulate digital assets, focusing on fraud prevention and market manipulation. |
| Japan | Licensing requirements for exchanges to ensure consumer protection and prevent illegal activities. |
2. Developing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Many central banks are exploring the possibility of launching their own digital currencies to provide the benefits of digital currencies while maintaining control over their national monetary systems. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are essentially government-backed digital currencies that maintain the value of traditional fiat currencies.
Countries such as China and Sweden are already testing CBDCs. The Digital Yuan (China) and e-krona (Sweden) are some of the most notable examples of CBDC projects in development.
Key Insights:
- China’s Digital Yuan: China’s state-backed digital currency, the Digital Yuan, has been rolled out in several cities, offering a new method of payment for goods and services.
- Sweden’s e-krona: Sweden is testing the e-krona as a response to the decline of cash usage in society.
- Global Trends: The Bank of England, Federal Reserve, and European Central Bank are researching the feasibility of CBDCs.
| Country | CBDC Development |
| China | Digital Yuan in use for domestic payments, with plans for broader international adoption. |
| Sweden | Testing the e-krona, with a focus on maintaining the stability of Sweden’s monetary system amidst declining cash usage. |
| European Union | ECB exploring the digital euro as a means to ensure a stable, secure currency amidst growing competition from private stablecoins. |
3. Embracing Blockchain for Public Sector Transparency
Blockchain’s ability to provide transparent, immutable records has made it an attractive tool for governments looking to improve accountability and reduce corruption. Many governments are experimenting with blockchain to enhance transparency in elections, voting systems, and public records management.
For example, Estonia is one of the pioneers in blockchain implementation for public services. The country uses blockchain to secure digital identities, voting systems, and public registries, improving transparency and reducing the risk of fraud.
Key Examples:
- Estonia’s Blockchain-Based Voting: Estonia uses blockchain technology to secure e-voting systems, allowing citizens to vote from anywhere while ensuring the integrity of the process.
- Georgia’s Land Registry: The government of Georgia has adopted blockchain for land title registration, reducing fraud and streamlining land transactions.
| Country | Blockchain Application |
| Estonia | Blockchain-based digital IDs, e-residency, and e-voting systems to enhance transparency and streamline public services. |
| Georgia | Blockchain used to register land titles, reducing fraud and increasing trust in land ownership and transactions. |
| Dubai | Dubai is exploring blockchain for government services like licensing, real estate transactions, and supply chain management. |
4. Encouraging Innovation through Web3 Incubators and Grants
To foster innovation in Web3, many governments are providing funding, grants, and support for Web3 startups. These initiatives aim to create an environment where blockchain developers and Web3 entrepreneurs can thrive. Governments that promote Web3 innovation are setting up incubators, accelerators, and research programs.
For example, Singapore and Estonia have established themselves as Web3 hubs, offering tax incentives, grants, and support to blockchain startups. Singapore’s Blockchain Innovation Program is a notable example of a government-backed initiative that helps Web3 startups scale and innovate.
Key Examples:
- Singapore’s Blockchain Innovation Program: Offers funding and resources for Web3 startups to explore blockchain use cases in finance, supply chain, and more.
- Estonia’s E-Residency Program: Allows entrepreneurs to register businesses in Estonia and access digital services from anywhere in the world.
| Country | Government Support for Web3 |
| Singapore | Blockchain Innovation Program funds Web3 startups, especially those developing solutions in finance, governance, and more. |
| Estonia | E-Residency program offers international entrepreneurs access to Estonia’s digital services for business management. |
| Switzerland | Switzerland’s Crypto Valley in Zug is home to numerous Web3 and blockchain startups, supported by favorable tax laws. |
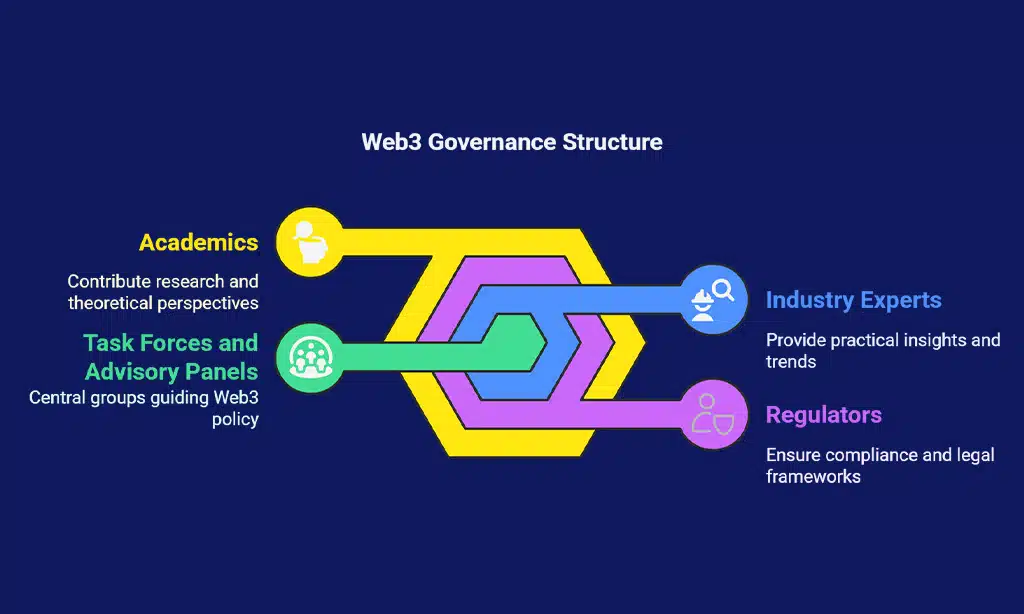
5. Setting Up Web3 Task Forces and Advisory Panels
Governments are also setting up specialized task forces and advisory panels to guide their responses to Web3 technologies. These groups bring together industry experts, regulators, and academics to provide recommendations on policy development and ensure that governments are informed about emerging Web3 trends.
Key Insights:
- US Crypto Task Force: In 2021, President Biden signed an executive order creating a task force to address the regulatory framework for digital assets in the US.
- European Blockchain Observatory: The European Union has established the Blockchain Observatory to track and report on developments in the blockchain space, offering policy advice to the European Commission.
| Country | Task Force/Panel |
| United States | Crypto Task Force to regulate digital assets, focusing on preventing illegal activities like money laundering. |
| European Union | Blockchain Observatory tracks blockchain trends and provides advice on policy formulation to EU regulators. |
6. Promoting Digital Identity Solutions for Web3 Integration
Digital identity is a critical component of the Web3 ecosystem, enabling secure and decentralized identification for users without the need for traditional identity verification systems. Governments are actively exploring ways to integrate Web3-based digital identities to enhance privacy and security while ensuring that citizens retain control over their personal data.
For instance, Estonia’s e-Residency program allows global citizens to establish a digital identity in Estonia, granting access to a wide range of government services, business registration, and tax filings, all securely handled using blockchain technology.
Similarly, India’s Aadhaar digital identity system, although not based on blockchain, is one of the largest digital identity programs globally, and there is ongoing exploration into integrating Web3 technologies to further enhance data security and privacy.
Key Insights:
- Estonia’s e-Residency Program: Provides individuals from around the world with a digital identity to access Estonian government services, enabling a paperless experience for entrepreneurs globally.
- India’s Aadhaar System: With over 1.3 billion people registered, the Aadhaar system could see future upgrades integrating Web3 elements to provide secure, blockchain-backed verification of identity.
- Decentralized Identity Systems: Blockchain-based solutions like Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) allow users to control their own identity data, reducing reliance on central authorities and improving security.
| Country | Digital Identity Initiative |
| Estonia | e-Residency program allows citizens and non-citizens to access government services using secure blockchain technology. |
| India | Aadhaar, the world’s largest biometric database, may adopt Web3 technologies to decentralize data storage and enhance security. |
| United States | Projects like ID2020 are researching blockchain-based decentralized identities for individuals globally. |
7. Building Education and Training Programs for Web3 Technologies
To ensure that both governments and citizens are well-prepared for the Web3 revolution, many countries are introducing education and training programs specifically tailored to blockchain, cryptocurrency, decentralized applications, and other Web3 technologies.
These initiatives aim to equip individuals with the skills necessary to thrive in the rapidly changing digital economy.
Governments are collaborating with universities, tech companies, and international organizations to provide specialized courses, certifications, and workshops that can help build the Web3 talent pool.
These initiatives not only promote Web3 literacy but also help accelerate the adoption of Web3 technologies by creating a skilled workforce ready to embrace decentralized solutions.
Key Insights:
- Singapore’s Blockchain Literacy Programs: Singapore’s Blockchain Association offers a variety of blockchain training programs to help individuals and businesses understand Web3 technologies, aiming to position Singapore as a global leader in blockchain innovation.
- South Korea’s Blockchain Training: The South Korean government has set up multiple blockchain and cryptocurrency-related educational programs aimed at fostering local talent and boosting innovation.
- Blockchain Universities in Europe: Countries like Switzerland and Germany are home to universities offering blockchain-related courses to help students specialize in Web3 technologies and become the next generation of blockchain developers.
| Country | Education and Training Initiatives |
| Singapore | Blockchain literacy programs through public-private partnerships to prepare the next generation of blockchain professionals. |
| South Korea | The government has implemented blockchain-focused educational initiatives in collaboration with local universities and tech firms. |
| Switzerland | Universities such as the ETH Zurich offer advanced blockchain and Web3-focused programs for the digital economy. |
Wrap Up: The Importance of Government Adaptation in the Web3 Era
The Web3 revolution is well underway, and governments must adapt quickly to ensure they remain relevant in this rapidly evolving digital world. From regulatory frameworks to fostering innovation, ways governments are responding to the Web3 revolution will determine the pace at which these technologies are adopted and integrated into society.
By balancing regulation with innovation, governments can help ensure that Web3 technologies bring about positive change in governance, finance, healthcare, and more.
As Web3 technologies continue to mature, governments must maintain flexibility in their regulatory approaches while actively engaging with innovators to shape the future of the internet. The responses we see today will play a crucial role in determining how Web3 shapes the digital economies of tomorrow.