In the digital age, small businesses face a constant battle to protect their online infrastructure from cyber threats. With limited budgets and resources, many small business owners fail to invest adequately in security measures, leaving their virtual private servers [VPS] vulnerable.
Cyberattacks targeting small businesses have increased significantly, and even a single breach can result in devastating consequences such as financial loss, damaged reputation, or legal action.
A VPS is an excellent choice for small businesses because it offers control over your environment while maintaining cost-efficiency. However, securing your VPS requires a comprehensive and proactive approach.
In this article, we will explore 10 Essential VPS Security Best Practices for Small Businesses that will help you fortify your infrastructure, minimize risks, and ensure business continuity in an increasingly hostile online environment.
Why VPS Security Matters for Small Businesses
Small businesses are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals because they often lack sufficient security measures. According to the 2020 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, nearly 28% of all data breaches involved small businesses, with many of these breaches resulting from outdated software, weak passwords, and insufficient protection measures.
In addition, a Ponemon Institute report reveals that small businesses are the most vulnerable to cyberattacks, with more than half of them reporting at least one attack in the last year. These attacks are often due to:
- Ransomware: Malware that locks down data and demands a ransom for its release.
- Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information through deceptive emails.
- DDoS Attacks: Overwhelming a server with traffic to render it inaccessible.
By following VPS Security Best Practices for Small Businesses, you not only protect your infrastructure but also ensure that your customers’ sensitive data remains secure, helping to build trust and loyalty.
Consequences of Poor VPS Security
Failure to secure your VPS can lead to severe consequences for your business. Here are some potential risks:
- Data Breaches: Exposing customer and business data can result in identity theft, fraud, and costly legal penalties under regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Financial Loss: Cyberattacks can lead to significant financial losses, both directly [through ransomware payments or stolen funds] and indirectly [through lost revenue and the cost of recovery].
- Reputation Damage: A breach can permanently harm your business reputation. Consumers and partners may lose trust in your ability to protect their data, which can have long-term effects on sales and business relationships.
- Compliance Issues: Many industries have strict data protection regulations. Failing to secure your VPS could result in compliance violations, leading to hefty fines or even lawsuits.
Given the stakes, it’s clear that small businesses must take VPS security seriously. Let’s dive into the 10 Essential VPS Security Best Practices for Small Businesses that will help you reduce vulnerabilities and safeguard your infrastructure.
10 Essential VPS Security Best Practices
When managing a VPS for your small business, security must be your top priority. Without robust security measures, your virtual private server can become a target for malicious actors, putting your business data, customer information, and reputation at risk.
By following these VPS Security Best Practices for Small Businesses, you can ensure your infrastructure remains safe, secure, and resilient against cyber threats.
These practices not only protect your server from external threats but also help establish a secure, trustworthy environment for your business operations.
1. Choose a Secure VPS Hosting Provider
Selecting the right VPS hosting provider is the first step in securing your infrastructure. Not all VPS providers offer the same level of security, so it’s essential to consider key features before choosing your provider.
| Feature | What to Look For |
| SSL/TLS Encryption | Ensures that all data transmitted between users and your VPS is encrypted, protecting it from being intercepted. |
| DDoS Protection | Shields your VPS from Distributed Denial of Service attacks that aim to overwhelm your server with malicious traffic. |
| Backup Services | Providers should offer regular, automated backups to ensur;;e data can be restored quickly in case of failure or attack. |
| Firewalls and IDS | A robust firewall and Intrusion Detection System [IDS] can block malicious traffic and alert you to potential threats. |
Example:
DigitalOcean offers a wide range of security features, including DDoS protection, firewall configuration, and automated backups, making it a reliable choice for small businesses looking to enhance their VPS security.
2. Regularly Update Your Software
Software vulnerabilities are among the most common ways attackers exploit servers. Running outdated software—whether it’s your operating system [OS], content management system [CMS], or other software—leaves your VPS exposed to known exploits.
Best Practices:
- OS Updates: Ensure your VPS’s OS is patched regularly. Linux distributions like Ubuntu and CentOS often release security patches automatically.
- CMS and Plugin Updates: If you’re running a CMS like WordPress, update both the platform and plugins regularly. An outdated plugin is often the entry point for attackers.
- Automate Updates: Use automation tools [e.g., unattended-upgrades for Linux] to ensure your VPS stays updated even if you’re busy.
| Tool | Purpose | Benefits |
| UptimeRobot | Monitors uptime and alerts on downtime | Ensures your site stays online, notifying you of potential attacks or server issues. |
| Unattended-Upgrades | Automates security updates on Linux | Minimizes the risk of running outdated software by automatically installing patches. |
3. Use Strong Passwords and Authentication
One of the simplest and most effective ways to secure your VPS is by using strong, unique passwords for all accounts. Weak passwords remain one of the easiest ways for attackers to gain unauthorized access to your system.
Key Recommendations:
- Strong Passwords: Avoid using common passwords like “password123” or “admin. Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
- Two-Factor Authentication [2FA]: Enable 2FA for all critical accounts, including your VPS control panel and any SSH access. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring both a password and a second verification method [e.g., SMS code or app-based token].
- SSH Keys: Instead of using password-based authentication for SSH, consider using SSH key pairs. They are much more secure and harder to crack.
Example:
Google’s 2FA system and SSH key authentication offer an excellent way to ensure that only authorized users can access your VPS.
| Authentication Method | Advantages | Common Use Cases |
| Password | Simple, but vulnerable to brute-force attacks. | Best for lower-risk systems, but combined with 2FA. |
| 2FA | Adds an extra layer of security. | Used on critical accounts like control panels or databases. |
| SSH Keys | Extremely secure, eliminates password vulnerabilities. | Recommended for server access via SSH. |
4. Configure Your Firewall Properly
A properly configured firewall is essential to secure your VPS from unwanted traffic and potential attacks. Firewalls can block malicious IP addresses and ensure only authorized traffic can reach your server.
Best Practices:
- Limit Open Ports: Only allow traffic through ports that are necessary [e.g., HTTP, HTTPS, and SSH].
- Block Malicious IPs: Use a tool like Fail2Ban to automatically block IP addresses that make repeated failed login attempts, which may indicate a brute-force attack.
- Web Application Firewall [WAF]: A WAF sits between your server and the web, filtering out potentially malicious traffic before it reaches your server.
| Firewall Configuration | Recommended Action | Benefits |
| Restrict Incoming Traffic | Only open essential ports [e.g., 80, 443 for web traffic] | Minimizes attack surface by closing unnecessary ports. |
| Block Suspicious IPs | Use Fail2Ban to block brute-force attack IPs | Protects against repeated login attempts. |
| WAF | Implement a WAF for extra layer of protection | Filters out common web-based threats like SQL injection. |
5. Implement Regular Backups
Even with all the security measures in place, accidents happen. Cyberattacks, system failures, or human error can lead to data loss. Having a reliable backup system is essential for minimizing downtime and recovering data quickly.
Best Practices:
- Automated Backups: Set up automatic backups to run at regular intervals [e.g., daily or weekly].
- Offsite Backups: Store backups offsite [e.g., on cloud storage] to ensure data can be restored if the primary server is compromised.
- Test Backups: Regularly test your backup system to verify that data can be restored without issues.
Example:
AWS Backup is a cloud-native backup service that integrates with your VPS, offering seamless backup and restore capabilities.
| Backup Strategy | Action Required | Benefits |
| Automated Backups | Set up regular automated backup intervals | Ensures that no critical data is missed during backups. |
| Offsite Backups | Store backups in cloud or remote storage | Provides an additional layer of safety in case of physical server failure. |
| Test Backups | Regularly verify backups by restoring data | Confirms the integrity and effectiveness of backups. |
6. Use Encryption for Sensitive Data
Encryption plays a critical role in securing sensitive data stored on your VPS. Without encryption, sensitive business and customer data is vulnerable to theft or misuse. Encrypting data ensures that even if attackers gain unauthorized access, the data remains unreadable and protected.
Best Practices for Encryption:
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Use SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data between your VPS and your customers. This is particularly crucial for websites that handle payment information, login credentials, or any sensitive personal data.
- Encrypt Data at Rest: Encrypt any data stored on your VPS, such as customer databases, financial information, and employee details. Tools like LUKS [Linux Unified Key Setup] provide a strong encryption layer for data storage.
- Use Full Disk Encryption: Consider enabling full disk encryption for your VPS to prevent unauthorized access to data in case the server is physically compromised.
| Encryption Type | Use Case | Tools/Recommendations |
| In-Transit Encryption | Secure communication between users and the VPS | Use SSL/TLS certificates from providers like Let’s Encrypt or Comodo. |
| At-Rest Encryption | Protect stored data from unauthorized access | Use LUKS for Linux servers or BitLocker for Windows-based VPS. |
| Full Disk Encryption | Safeguard the VPS from physical compromise | Implement full disk encryption during OS installation [e.g., LUKS]. |
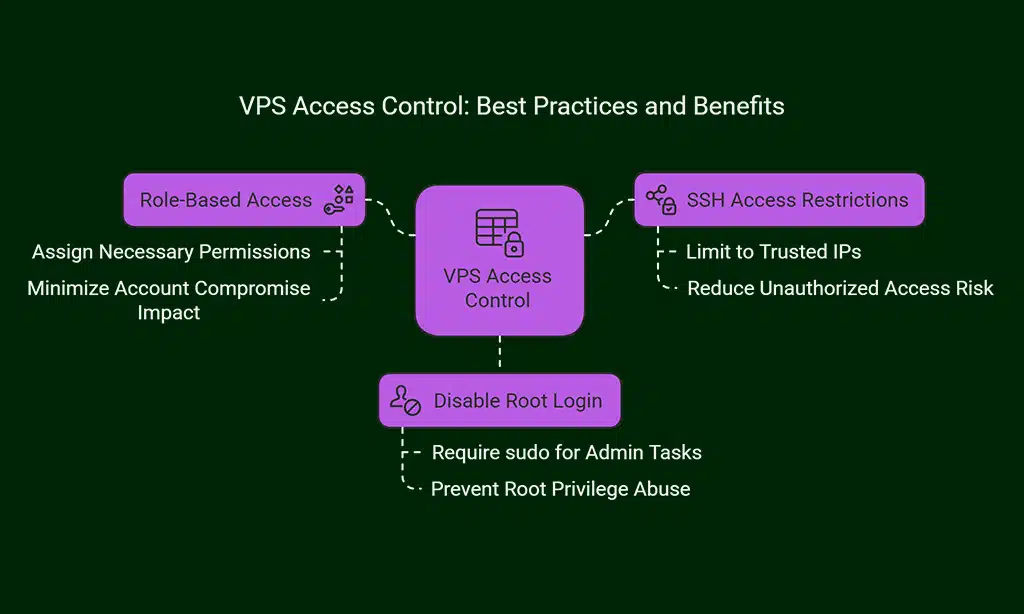
7. Limit Access to Your VPS
Limiting who can access your VPS and the level of access they have is crucial to minimizing potential attack surfaces. By enforcing strict access controls, you can reduce the chances of unauthorized entry into your system.
Best Practices:
- Use Role-Based Access: Assign different levels of access to different users based on their roles within the organization. The principle of least privilege [PoLP] ensures that each user only has the necessary permissions to perform their tasks.
- Limit SSH Access: By restricting SSH access to specific IP addresses or using two-factor authentication [2FA] for all logins, you further reduce the chances of an attacker gaining unauthorized access.
- Disallow Root Access: Disable direct root login through SSH. Instead, log in as a regular user and escalate privileges using sudo for administrative tasks.
| Access Control Method | Recommended Action | Benefits |
| Role-Based Access | Assign users only the permissions they need | Minimizes the impact of compromised accounts. |
| SSH Access Restrictions | Limit SSH access to trusted IP addresses only | Significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. |
| Disable Root Login | Require sudo for administrative access | Prevents attackers from easily gaining root privileges. |
8. Monitor VPS Performance and Security Logs
Continuous monitoring is essential to detect any unusual activity or potential threats. By regularly reviewing your VPS’s performance and security logs, you can identify early signs of an attack and take appropriate action before it escalates.
Best Practices:
- Use Log Management Tools: Implement tools like Logwatch or GoAccess to monitor server activity and generate alerts for suspicious behavior.
- Monitor System Resources: Keep an eye on CPU, RAM, and disk usage to identify any sudden spikes that could be indicative of a DDoS attack or malware infection.
- Set Up Security Alerts: Configure alerts for any changes to critical files or configurations, such as modifications to firewall settings or login attempts from unauthorized IPs.
| Monitoring Tool | Purpose | Benefits |
| Logwatch | Reviews system logs and sends reports | Detects unusual activity and helps identify threats. |
| GoAccess | Real-time log analyzer for web traffic logs | Provides actionable insights into web server activity. |
| Syslog-ng | Centralized logging system | Helps aggregate logs from multiple sources for easier analysis. |
9. Install Security Plugins and Tools
Using security plugins and specialized tools can automate much of the monitoring and protection of your VPS. These tools are designed to detect vulnerabilities, block attacks, and provide real-time security updates.
Recommended Tools and Plugins:
- Malware Scanners: Tools like ClamAV or Imunify360 can scan your server for malware and viruses, helping to prevent malicious code from infiltrating your system.
- Security Plugins for CMS: If you run a CMS like WordPress, install security plugins like Wordfence or Sucuri Security to monitor traffic, prevent SQL injections, and perform regular vulnerability scans.
- Antivirus Software: On Linux or Windows VPS, using antivirus software [e.g., Sophos or Kaspersky] can help detect and quarantine viruses before they cause significant harm.
| Tool/Plugin | Purpose | Benefits |
| ClamAV | Open-source antivirus for Linux servers | Scans and removes malware on your VPS. |
| Imunify360 | Proactive security suite for Linux servers | Provides advanced malware detection and mitigation. |
| Wordfence | Security plugin for WordPress | Monitors site traffic, blocks threats, and prevents hacking attempts. |
10. Set Up Security Alerts and Notifications
Setting up security alerts ensures that you’re notified whenever suspicious activity occurs. Alerts can help you respond quickly to potential attacks, reducing the likelihood of significant damage.
Best Practices:
- Failed Login Attempt Alerts: Configure your system to notify you if there are multiple failed login attempts from the same IP address, as this could indicate a brute-force attack.
- File Integrity Monitoring: Use file integrity monitoring tools [e.g., AIDE] to detect unauthorized changes to critical system files.
- Suspicious Activity Alerts: Set up alerts for any unusual or suspicious activity, such as sudden spikes in traffic or changes to firewall rules, which may indicate an attack in progress.
| Alert Type | What It Tracks | Tools/Services Recommended |
| Login Failures | Multiple failed login attempts from the same IP | Fail2Ban, OSSEC |
| File Integrity Changes | Unauthorized changes to key system files | AIDE [Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment] |
| Suspicious Network Activity | Unusual traffic spikes or DDoS attempts | UptimeRobot, Cloudflare |
Advanced Security Measures for Small Businesses
For businesses that lack the resources or expertise to manage VPS security, managed security services provide an excellent solution. These services offer 24/7 monitoring, threat detection, and incident response, ensuring your VPS is protected round the clock.
Benefits of Managed Security Services:
- Proactive Threat Hunting: Managed services often include proactive monitoring to identify potential threats before they cause damage.
- Compliance Assistance: These services can also assist with ensuring your VPS complies with industry-specific regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Security Audits: Managed services frequently conduct security audits to identify weaknesses and implement best practices.
| Managed Service Provider | Features | Benefits |
| Cloudflare | DDoS protection, WAF, CDN services | Secures websites against attacks and improves performance. |
| AWS Managed Security | Continuous threat monitoring, automated patching | Ensures comprehensive security management for your VPS. |
| Rackspace | 24/7 monitoring, incident response | Provides hands-on security expertise for critical infrastructure. |
Secure Your VPS Against DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are a growing threat to VPS-hosted websites. These attacks flood your server with traffic, making your website or services inaccessible. Protecting your VPS against DDoS requires proactive defense measures.
Key Defenses Against DDoS Attacks:
- Cloud-Based DDoS Protection: Utilize services like Cloudflare or AWS Shield to block malicious traffic before it reaches your server.
- Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting for incoming traffic to ensure that your VPS can handle the load without being overwhelmed.
- Geofencing: Restrict access to your server from specific geographical regions where attacks are likely to originate.
Takeaways
Securing your VPS is one of the most critical steps in protecting your small business from cyber threats. By following the 10 Essential VPS Security Best Practices for Small Businesses, you can drastically reduce the risk of data breaches, downtime, and reputational damage.
The key to maintaining strong VPS security lies in proactive measures, regular monitoring, and ensuring your systems are always up to date.
No security strategy is foolproof, but by adhering to these best practices and investing in the right tools and services, you’ll create a robust defense against cyberattacks, allowing your business to operate securely and with confidence.