In the rapidly evolving digital landscape of this year, Voice Search Optimization 2026 has shifted from a forward-looking trend to an immediate necessity for brand survival. We have entered the era of “Answer Engine Optimization” (AEO), where the goal is no longer to simply rank on a page, but to be the single, spoken result delivered by an AI assistant.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the exact strategies you need to dominate this voice-first landscape, ensuring your brand is the one Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa choose to cite as the “source of truth.”
The Silent Revolution: Why Ranking #1 is No Longer Enough
Imagine a scenario that plays out millions of times a day: You are driving to a high-stakes client meeting in a city you don’t know well. Suddenly, your car creates a terrifying rattling noise. You don’t have the luxury to pull over to the shoulder, unlock your phone, open Google Chrome, type a query, and scroll through a list of ten blue links. You keep your hands on the wheel and shout at your dashboard:
“Hey Siri, find a mechanic that is open right now and has good reviews.”
In this moment, Siri does not offer you a menu of options. She does not give you a “Top 10” listicle. She gives you one result. She reads the name, tells you the rating, and asks if you want directions.
If you are the mechanic ranked #1 on Google Search, but you haven’t optimized for Siri’s specific data ecosystem, you are invisible. You effectively do not exist to that customer.
This is the reality of the market today. With over 8.4 billion voice assistants currently in use globally, outnumbering the human population, and 75% of local discovery searches being voice-initiated, optimizing for the spoken word is a survival mechanism. The “digital divide” in 2026 is no longer between those who have websites and those who don’t; it is between those who are conversation-ready and those who are silent.
The Ecosystem Divide: It’s Not Just Google Anymore
The single biggest mistake marketers make in 2026 is assuming that a “one-size-fits-all” SEO strategy covers all bases. It does not. Unlike the desktop era, where Google was the undisputed king with over 90% market share, the voice ecosystem is fragmented, tribal, and relies on different “reservoirs” of data.
When a user asks a question, the device they are using determines where the assistant looks for the answer. If you optimize perfectly for Google but ignore Apple’s data sources, you are invisible to over 1.5 billion iPhone users. You must understand the specific data pipelines that feed each major assistant.
The “Source of Truth” Matrix
To rank effectively, you need to know which database each assistant queries. Here is the breakdown for 2026:
| Feature | Google Assistant / Android | Siri / Apple Ecosystem | Amazon Alexa |
| Primary Search Index | Google Search Index | Google (via Gemini) & Apple Maps | Bing |
| Local Business Data | Google Business Profile (GBP) | Apple Maps Connect | Yext & Bing Places |
| Review Source | Google Reviews | Yelp & TripAdvisor | Yelp |
| Response Style | Reads “Featured Snippets” | Brief Answers or App Actions | Brief Answers |
| Map Engine | Google Maps | Apple Maps | Mapbox / Here |
| Priority Ranking Factor | Relevance & Proximity | Rating & Distance | Review Sentiment |
Strategic Takeaway: The table above reveals a critical gap in most SEO strategies. Most businesses obsess over their Google Business Profile. However, to rank for Siri, you must claim your listing on Apple Maps Connect and ensure you have a strong presence on Yelp, as Siri prioritizes these platforms heavily for local recommendations. If you have 500 reviews on Google but zero on Yelp, Siri may completely ignore you when an iPhone user asks for a recommendation.
From Keywords to “Conversational Queries” [NLP]
Robots speak in keywords; humans speak in sentences. In 2026, the era of “keyword stuffing” is definitively dead. Voice search relies on Natural Language Processing (NLP), which allows computers to understand the intent behind a user’s words, not just the words themselves.
Google’s algorithms, powered by advanced AI models like Gemini, and Apple’s upgraded Siri intelligence, have shifted from “lexical search” (matching exact words) to “semantic search” (matching meaning). This shift is profound because it changes how we must write content. We are no longer writing for a crawler that counts words; we are writing for an AI that “listens” to context.
The Evolution of the Search Query
To understand how to write, you must understand how users speak. The transition from typing to speaking adds layers of complexity and intent.
- Old Way (Typing): “Italian restaurant Boston gluten-free.”
- Analysis: This is robotic. It lacks urgency or specific context.
- New Way (Speaking): “Where can I get the best gluten-free pasta in Boston for dinner tonight?”
- Analysis: This query is rich with context. It tells the search engine the location (Boston), the product (gluten-free pasta), the intent (dinner), and the timeframe (tonight).
The “Who, What, Where, When, Why” Strategy
Voice queries are overwhelmingly question-based. To capture this traffic, your content must be structured to answer specific questions directly. You need to pivot your keyword research from “short-tail” to “long-tail conversational phrases.”
Actionable Steps for NLP Optimization:
- Target Long-Tail Keywords: Focus on phrases that are 5-8 words long. These mimic natural speech patterns. Instead of targeting “SEO Tips,” target “What are the best SEO tips for small businesses in 2026?”
- Conversational Tone: Write your content as if you are speaking to a friend. Use contractions (“you’re” instead of “you are”), simple sentence structures, and avoid corporate jargon. If a sentence is hard to say in one breath, it is too long for a voice assistant to read.
- Contextual Relevance: Google’s algorithms now look for “semantic relevance.” If you are writing about “Apple,” do you mean the fruit or the tech giant? Your surrounding content (words like “pie” vs. “iPhone”) clarifies this. You must build “topical authority” by covering a subject from every angle.
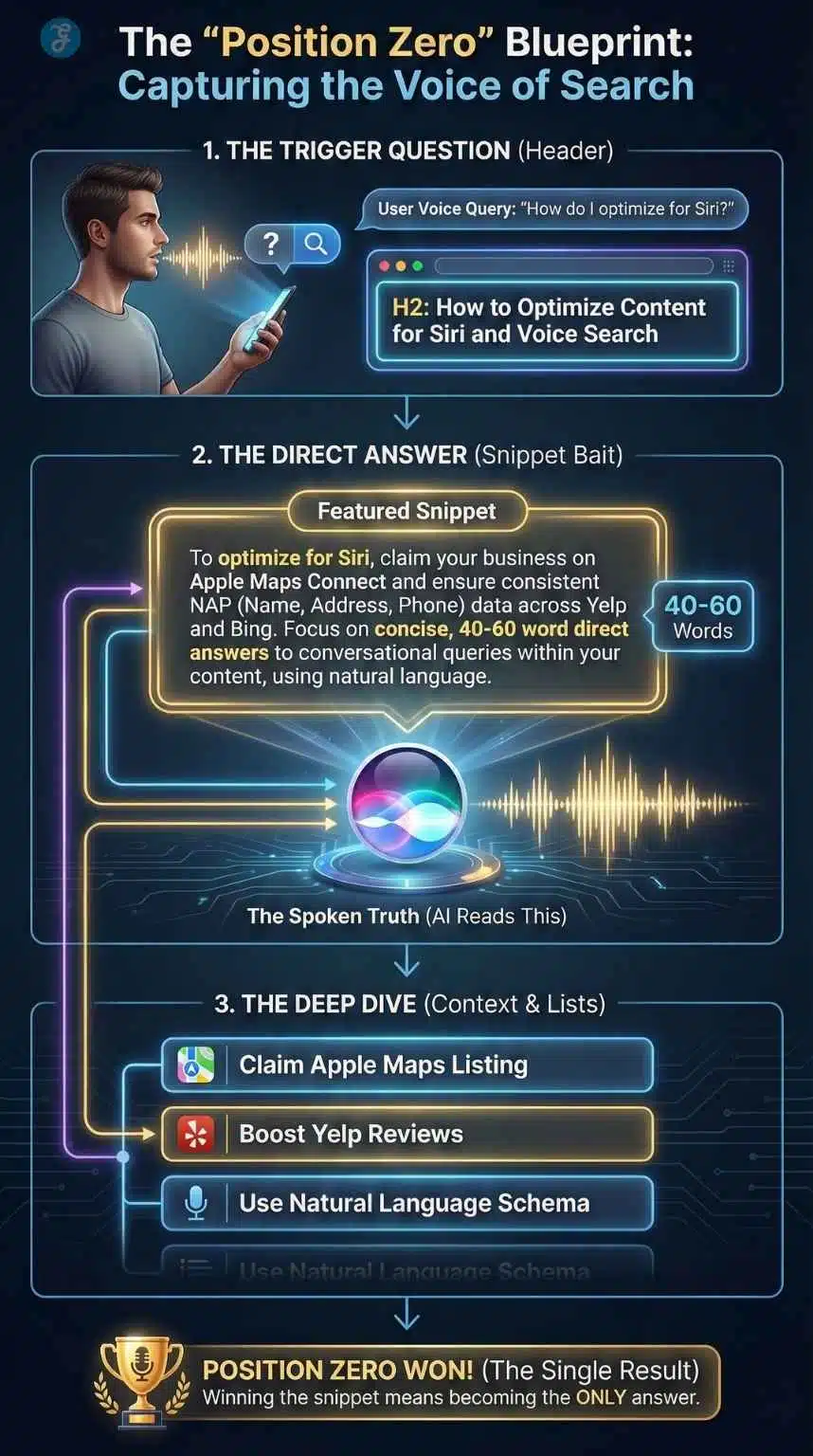
The “Position Zero” Content Formula
Voice assistants are impatient. They don’t read whole articles; they read snippets. Specifically, they read the Featured Snippet, the boxed answer that appears at the absolute top of Google’s search results.
To win Voice Search Optimization 2026, you must win Position Zero. If you are in Position 1 (the first organic link) but not Position Zero, the voice assistant will likely skip you. Here is the proven formula for structuring your content to get picked up as the “spoken answer.”
Step 1: The Trigger Question (Header)
Use an H2 or H3 header to ask the exact question your user is asking. Do not be vague or “clever.” Be literal.
- Bad Header: Optimization Strategies
- Good Header: How do you optimize content for voice search in 2026?
Step 2: The Direct Answer (The “Snippet Bait”)
Immediately following the header, provide a concise, factual answer. This paragraph should be 40 to 60 words long, the average length of a voice assistant’s response.
Drafting Tip: Do not waffle. Start with “The best way to optimize…” or “Voice search optimization requires…” Avoid starting with “It depends” or “In this section, we will discuss…” The AI needs to be able to rip this paragraph out of your site and read it in isolation without losing meaning.
Step 3: The Deep Dive
After the direct answer, you can expand on the topic with detailed steps, examples, and nuance. This satisfies the user who clicks through to your website for more information, signaling to Google that your page is high-quality.
Step 4: List Formatting
Voice assistants love lists. If your answer involves steps, use bullet points or numbered lists.
- Example: “Here are the three steps to claim your Apple Maps listing:”
- Go to https://www.google.com/search?q=mapsconnect.apple.com.
- Sign in with your Apple ID.
- Verify your business phone number.
This structure is highly “parseable” for AI agents, making it more likely they will read your content aloud.
Technical SEO: The Backbone of Voice
You can have the best answers in the world, written by a Shakespearean scholar, but if your site is slow or technically flawed, voice assistants will skip you. Voice search is mobile-first, and speed is a critical ranking factor.
Speed is Survival
Voice searches are often performed on the go, sometimes on spotty 5G or 4G data connections. A user asking for a coffee shop doesn’t have time to wait 5 seconds for a script to load.
- The Benchmark: Your site must load in under 2.5 seconds.
- Core Web Vitals: Pay attention to LCP (Largest Contentful Paint). This measures how quickly the main content loads. If your LCP is poor, Google assumes the user experience is poor and will demote you in voice results.
- The Fix: Compress images to WebP format, minimize JavaScript execution time, and use a reliable Content Delivery Network (CDN) like Cloudflare to serve your content from a server closest to the user.
Schema Markup: Speaking the Robot’s Language
Schema markup is invisible code that tells search engines exactly what your content is. It is metadata that translates your human content into machine data. For Voice Search Optimization 2026, two types of schema are non-negotiable:
1. FAQPage Schema:
This tells Google, “Here is a list of questions and answers.” It is the most effective way to land in the “People Also Ask” boxes, which are prime territory for voice answers. When you implement this, you essentially spoon-feed the voice assistant the exact Q&A format it needs.
2. Speakable Schema:
This is a newer property that specifically identifies sections of an article that are suitable for text-to-speech playback. It essentially highlights the “read aloud” portion of your page for news assistants (like Google Assistant reading the daily news). While originally for news publishers, its application is broadening.
Implementation Tip: You don’t need to be a coder. Use plugins like RankMath or Yoast SEO for WordPress to automatically generate this schema for you.
Local SEO: Dominating the “Near Me” Search
“Near me” searches have evolved. Users are now hyper-specific. They don’t just ask for “restaurants.” They ask: “Find a coffee shop near me that has outdoor seating, free wifi, and is open right now.”
To capture this traffic, you must synchronize your N.A.P. (Name, Address, Phone Number) across the entire web. Even a slight discrepancy (e.g., “St.” vs. “Street”) can confuse the algorithms and lower your trust score.
The “Local Pack” Trifecta
You must view your local presence as a three-legged stool. If one leg is missing, the strategy collapses.
- Google Business Profile (GBP): This is the holy grail for Android users. Complete every single field. Upload photos of the interior, exterior, and products. Use the “Q&A” section of GBP to populate common voice queries like “Do you have parking?”
- Apple Maps Connect: Essential for Siri. Ensure your category is correct (e.g., “Vegan Restaurant” vs. just “Restaurant”). Siri relies on this specific categorization to filter results.
- Bing Places: Often powers the fallback results for Alexa and some vehicle voice systems (like BMW and Ford).
Reviews as Ranking Signals
Voice assistants trust what other humans say. Siri, in particular, will often read out your star rating from Yelp before even giving your address.
- The Yelp Factor: For iPhone users, Yelp is the engine of trust. You cannot ignore it.
- Review Velocity: Getting 10 reviews in one day and then zero for a month looks suspicious. Aim for a steady stream of reviews.
- Sentiment Analysis: AI now reads the text of reviews, not just the stars. If people constantly mention “great cheesecake” in your reviews, and a user asks Siri for “best cheesecake near me,” you are more likely to rank, even if “cheesecake” isn’t in your business name.
Content Strategy for Voice: Beyond the Blog
Text is not the only way to rank. In 2026, we are seeing a convergence of media formats where voice search pulls results from video and audio sources.
Video Optimization for Voice
YouTube is the second-largest search engine in the world. Often, when a user asks “How do I tie a tie?”, Google Assistant will not read a blog post; it will display a video segment.
- Video Chapters: Break your videos into clearly labeled chapters. This allows Google to jump directly to the relevant part of the video (e.g., “The Knot”) and serve it as a voice/visual answer.
- Transcripts: Always include a full transcript of your video. This makes the audio searchable by text-crawling spiders.
Podcast and Audio SEO
With the rise of smart speakers, audio content is becoming searchable. Google is now indexing podcasts.
- Clear Titles: Use descriptive titles for podcast episodes that match user queries.
- Show Notes: Treat your show notes like a mini-blog post, optimized with headers and keywords.
Future-Proofing: The Rise of AI Agents
As we look toward the latter half of 2026, we are seeing the rise of AI Agents. These are advanced assistants that don’t just retrieve information but act on it. This is the shift from Large Language Models (LLMs) to Large Action Models (LAMs).
- Current Voice Search: “What is the phone number for Tony’s Pizza?”
- AI Agent Request: “Book a table for two at Tony’s Pizza for 7 PM, but only if they have patio seating available.”
To be the restaurant that gets booked, your site needs to be “machine-readable.” This means having clear, structured data for your menu, opening hours, and reservation policies. If an AI agent cannot easily parse your reservation page because it’s buried in a PDF menu or a Flash animation, it will move on to a competitor that is easier to interact with.
The “Entity” Strategy
You must establish your brand as a known “Entity” in the Knowledge Graph. This means having a clear About page, linking to your social profiles, and getting cited by other authoritative sources. When Google understands who you are, it is more confident in recommending you.
Implementation Checklist for 2026
To make this actionable, here is your 30-day sprint plan to overhaul your Voice Search Optimization strategy.
| Phase | Action Item | Priority |
| Week 1 | Claim and verify the Apple Maps Connect listing. | Critical |
| Week 1 | Audit Google Business Profile for completeness. | Critical |
| Week 2 | Implement the FAQ Schema on your top 5 landing pages. | High |
| Week 2 | Run a PageSpeed Insights test and fix LCP issues. | High |
| Week 3 | Rewrite top blog posts to follow the Position Zero Formula. | Medium |
| Week 4 | Launch a campaign to generate Yelp Reviews. | Medium |
Final Thoughts: Voice is the Interface of the Future
Voice search is not a fad; it is the natural evolution of human-computer interaction. It removes the friction of typing and allows for immediate, on-demand answers. It is the most “human” way to interact with the digital world.
By shifting your strategy from “keywords” to “conversations,” and by treating Apple Maps with the same respect as Google, you position your brand to be the one voice that cuts through the noise. In the coming years, the “digital divide” won’t be between those who have websites and those who don’t. It will be between those who are conversation-ready and those who are silent.
In 2026, the winner isn’t the one with the most backlinks; it’s the one that provides the best answer, the fastest, in the language your customer actually speaks.