Toyota has once again captured global attention by unveiling a bold claim that could redefine the electric vehicle (EV) landscape for decades to come. The Japanese automaker, known for its conservative and research-driven approach, announced that its next-generation solid-state batteries could last up to 40 years — nearly three times the average lifespan of today’s passenger cars.
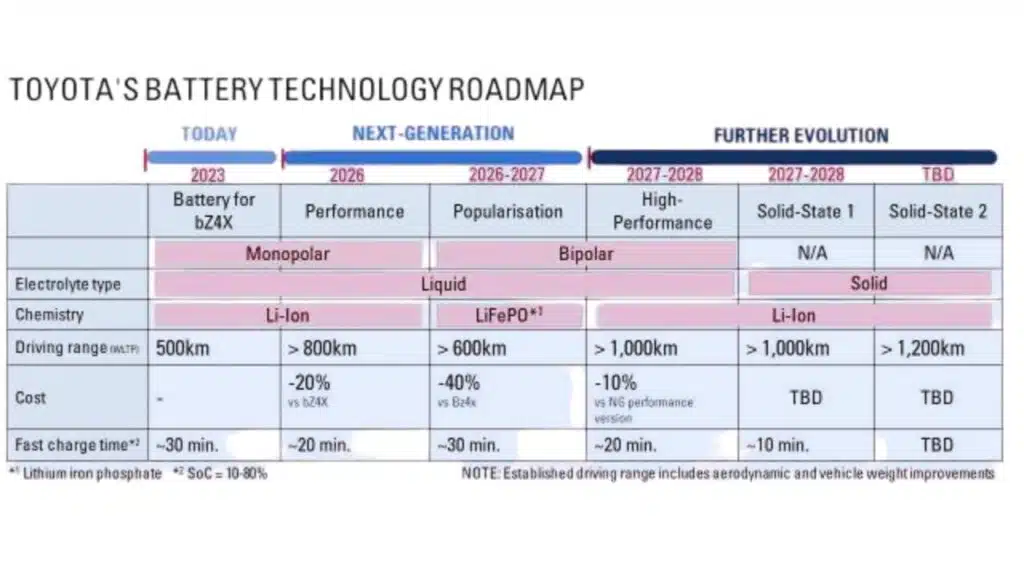
At the Japan Mobility Show, Toyota officials revealed that these upcoming solid-state cells are designed not only to dramatically improve driving range and charging speed but also to remain viable long after the vehicle’s lifespan has ended. This suggests a future where a single battery pack could outlive multiple vehicles, reshaping how consumers think about car ownership, sustainability, and long-term value.
Keiji Kaita, President of Toyota’s Carbon Neutral Advanced Engineering Development Centre, explained that current lithium-ion batteries typically retain about 90 percent of their capacity after 10 years, depending on usage. In contrast, the new solid-state batteries are expected to retain the same 90 percent capacity after an astonishing 40 years. If Toyota achieves this milestone, it would mark a monumental breakthrough — transforming how electric vehicles are designed, manufactured, and recycled.
The potential is staggering. Imagine an EV battery that remains efficient for four decades, reusable across generations of vehicles, and capable of being repurposed multiple times with minimal energy degradation. For an industry struggling with issues of cost, safety, and raw-material waste, this would represent a complete paradigm shift.
The Promise of Solid-State Batteries: Range, Speed, and Safety Redefined
To understand the magnitude of Toyota’s announcement, it is essential to grasp why solid-state batteries have long been called the “holy grail” of EV technology. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid electrolytes, solid-state batteries employ solid electrolytes — making them inherently safer, denser, and more efficient.
Toyota’s new generation of batteries promises several key benefits that could solve many of today’s EV pain points:
- Extended Range – By replacing the liquid electrolyte with a solid medium, energy density increases dramatically. This allows vehicles to travel significantly longer distances on a single charge, potentially crossing the 1,000-kilometre threshold that would remove most drivers’ “range anxiety.”
- Faster Charging – These batteries could charge to 100 percent in a fraction of the time current lithium-ion packs require. Early estimates suggest that a 10-minute full charge might soon be possible, making EVs more convenient than ever.
- Greater Safety – The solid electrolyte minimizes the risk of short circuits and thermal runaway, drastically reducing fire hazards that have plagued certain EV models.
- Lightweight and Compact – Solid-state cells are denser, which means they can deliver more power in a smaller and lighter package. This not only improves performance but also boosts vehicle efficiency and handling.
- Environmental Sustainability – With an expected 40-year life span, the environmental impact of battery production could be reduced dramatically. Fewer replacements would mean less mining, less waste, and lower emissions over time.
Toyota’s scientists believe that solid-state technology could eventually make electric vehicles cheaper to own over their lifetime, even if the initial purchase cost is higher. As Kaita noted, the upfront price of these advanced batteries might be steep at first, but their longevity would compensate for that investment many times over.
Overcoming the Challenges: From Research Lab to Real-World Deployment
Despite Toyota’s ambitious projections, experts caution that solid-state batteries are not yet ready for mass production. For years, the technology has remained elusive, with automakers and startups alike struggling to bring lab-scale prototypes to commercial viability. The obstacles are primarily tied to manufacturing complexity, cost, and durability under real-world conditions.
Solid-state batteries require highly stable materials that can maintain conductivity and structural integrity over thousands of charge-discharge cycles. This is a daunting challenge: ensuring that the solid electrolyte remains defect-free and interfaces seamlessly with electrodes without degrading performance. While many companies have made progress, none have achieved large-scale production at reasonable cost.
Toyota is well aware of these barriers. The company has spent over a decade refining its solid-state prototypes, investing heavily in materials research and advanced manufacturing techniques. It has partnered with Idemitsu Kosan to develop next-generation solid electrolytes and with Sumitomo Metal Mining to secure cathode materials optimized for these cells. This vertically integrated approach gives Toyota greater control over the supply chain — a crucial advantage as global demand for battery materials surges.
At present, Toyota plans to commercialize solid-state batteries by 2027–2028, possibly debuting them in both hybrid and high-performance electric vehicles. There have been indications that the first models to receive this technology could include a Lexus sports car, designed to demonstrate the system’s power and endurance, or a hybrid EV, which would allow Toyota to test longevity under mixed driving conditions.
How It Compares: Industry Race Toward Next-Generation Batteries
Toyota’s announcement doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Across the world, battery makers and automakers are locked in a race to conquer solid-state technology. Competitors like Solid Power (partnered with BMW), QuantumScape (backed by Volkswagen), and Samsung SDI are all pursuing similar breakthroughs. Each claims significant progress — yet none have reached Toyota’s level of confidence regarding lifespan and scalability.
Solid Power has reported experimental batteries capable of over 1,000 charge cycles, maintaining strong performance metrics. Harvard researchers have demonstrated a design retaining 80 percent of capacity after 6,000 cycles, while Samsung’s research division has projected a potential 20-year lifespan for its future solid-state cells.
Yet Toyota’s proposed 40-year life and 90 percent capacity retention stand apart — if achieved, it would be a monumental leap. For comparison, Tesla’s current lithium-ion batteries are estimated to last around 200,000 miles with 90 percent capacity retention, and most automakers only guarantee their battery packs for eight to ten years.
This development could spark a new phase of competition in the EV sector, reshaping the industry hierarchy. A durable, recyclable, and fast-charging battery would dramatically reduce ownership costs, extend vehicle lifespans, and reduce the environmental toll of battery production — potentially giving Toyota a formidable edge in the electric transition.
The Future of Mobility: Environmental, Economic, and Consumer Impact
If Toyota’s solid-state batteries meet even half their targets, the implications will be far-reaching. Environmentally, the shift toward long-lasting, reusable batteries would ease the pressure on mining industries responsible for lithium, nickel, and cobalt extraction — resources whose demand has surged alongside global EV adoption. Fewer production cycles would mean less energy consumption, lower carbon footprints, and reduced industrial waste.
Economically, Toyota’s strategy could redefine the resale and recycling value of EVs. A car might no longer be scrapped because its battery degraded; instead, the same energy pack could be reinstalled into a new vehicle, turning batteries into long-term assets. This would open a new secondary market for pre-used high-capacity batteries and potentially reshape automakers’ business models — from one-time sales to circular battery-leasing systems.
For consumers, the promise of a 40-year battery fundamentally changes the psychology of EV ownership. Range anxiety, charging anxiety, and depreciation anxiety could all diminish. Drivers could own vehicles that last as long as internal-combustion cars — or even longer — with lower maintenance and energy costs.
Toyota’s long-term approach also aligns with its broader carbon-neutral strategy. Instead of chasing quick adoption with mid-range lithium-ion models, Toyota aims for a sustainable and enduring technological foundation that can serve multiple generations of vehicles. It reflects the company’s belief that reliability, longevity, and safety remain core pillars of innovation — even in the electric era.
Toyota’s 40-year solid-state battery concept represents more than a technological milestone — it’s a vision for a new era of sustainable mobility. While many questions remain about scalability, cost, and real-world performance, the potential benefits are transformative. A single battery capable of powering several generations of vehicles could drastically cut waste, lower total ownership costs, and propel the EV industry toward true maturity.
Yet, the path forward remains challenging. Manufacturing consistency, material supply, and affordability must align before these batteries can move from prototype to production. The next few years will determine whether Toyota’s bold ambition becomes the foundation of a new energy age — or remains an unfulfilled promise in the long pursuit of the perfect battery.
The Information is Collected from Live Science and MSN.