Agriculture in New Zealand is undergoing a transformation, driven by the urgent need for sustainable and innovative solutions. Among the key advancements reshaping the industry are hydroponics and aquaponics.
These modern farming systems offer efficient, resource-conscious methods of growing food, making them increasingly popular among farmers, entrepreneurs, and policymakers. This article explores the growth of hydroponics and aquaponics in New Zealand, delving into their principles, current adoption, benefits, and future potential.
By the end, you’ll understand why these systems are hailed as the future of agriculture in this environmentally conscious nation.
Understanding Hydroponics and Aquaponics
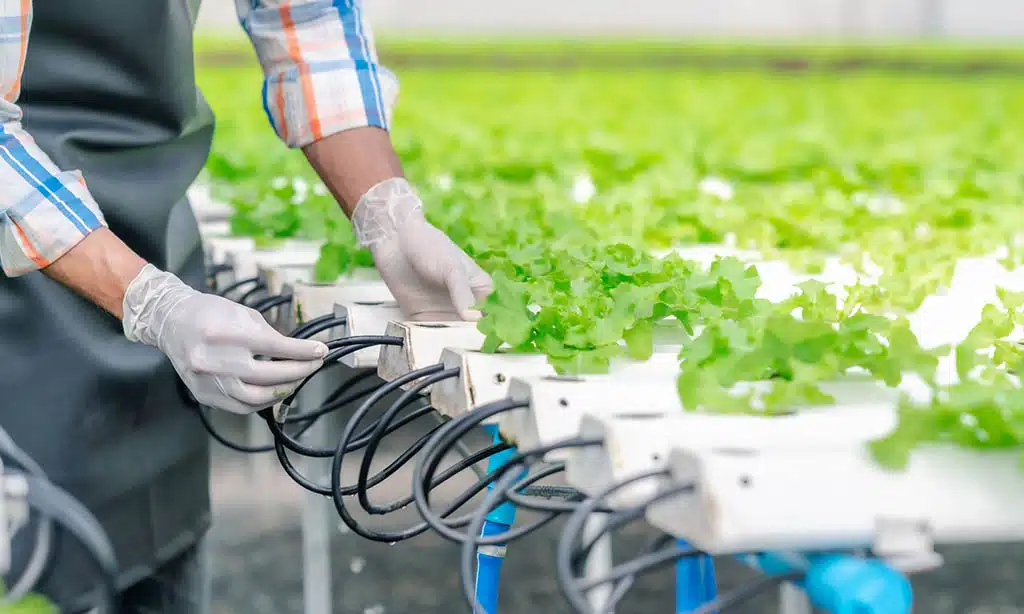
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead, it relies on nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots.
This technique allows for precise control over the growing environment, resulting in higher yields and faster growth rates compared to traditional farming methods. It is particularly suited for environments with limited arable land or adverse soil conditions.
Key Benefits of Hydroponics:
- Reduced water usage by up to 90% compared to soil-based farming.
- Eliminates the need for pesticides and herbicides.
- Enables year-round cultivation in controlled environments.
- Maximizes space utilization through vertical farming systems.
What Is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics. In this system, fish waste provides a natural source of nutrients for plants, while the plants filter and purify the water for the fish. This symbiotic relationship creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that minimizes waste and maximizes resource efficiency. It is an ideal solution for areas where water conservation is critical.
Key Features of Aquaponics:
- Dual production of fish and plants.
- Minimal water wastage due to continuous recirculation.
- Organic and chemical-free farming method.
- Offers a scalable solution from small household setups to large commercial farms.
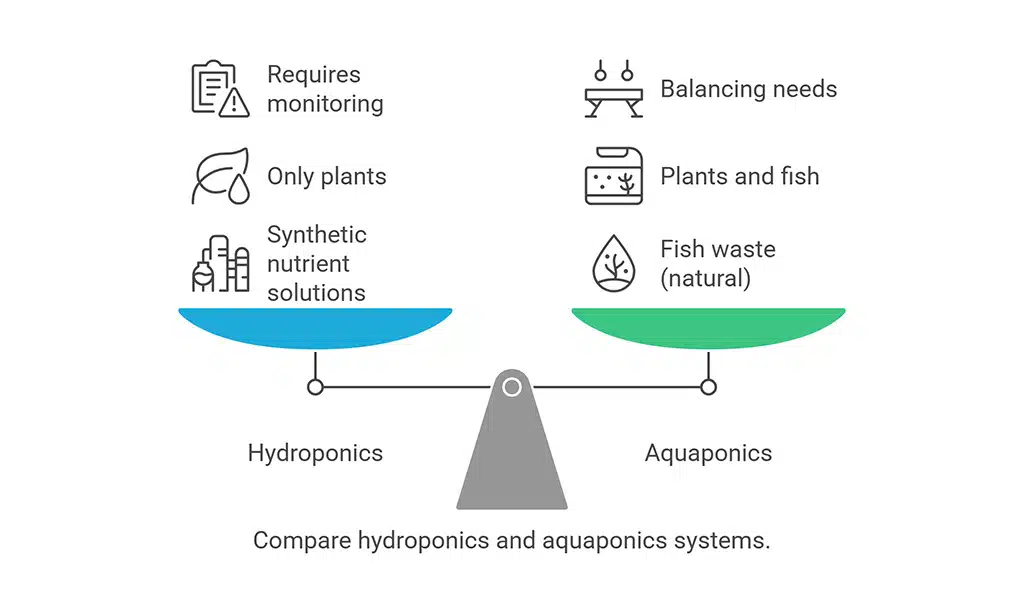
Key Differences Between Hydroponics and Aquaponics
| Feature | Hydroponics | Aquaponics |
| Nutrient Source | Synthetic nutrient solutions | Fish waste (natural) |
| Additional Output | Only plants | Plants and fish |
| Maintenance Level | Requires monitoring of nutrient solutions | Requires balancing fish and plant needs |
| System Complexity | Relatively simple | More complex |
| Sustainability | Resource-efficient but relies on chemicals | Fully organic with minimal external inputs |
Both systems have their unique advantages, but they share a common goal: increasing agricultural efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
Why New Zealand Is Embracing These Farming Techniques?
New Zealand’s natural environment and commitment to sustainability make it an ideal location for hydroponics and aquaponics. The country’s abundant water resources and temperate climate support the adoption of these systems.
Additionally, rising energy efficiency in controlled environments has made them more economically viable. These factors align with the national strategy to reduce carbon emissions and protect biodiversity.
Consumer Demand for Sustainable Produce
With an increasing number of consumers seeking organic, pesticide-free food, hydroponics and aquaponics align perfectly with market demand. New Zealand’s export markets, particularly in Asia and Europe, are also driving growth by prioritizing sustainably produced goods.
According to a 2024 market report, demand for hydroponic and aquaponic produce has increased by 25% year-over-year, reflecting the growing consumer preference for sustainable food.
The Current State of Hydroponics and Aquaponics in New Zealand
Across the country, farmers are turning to hydroponics and aquaponics to address challenges like soil degradation and water scarcity. For example, Pure Hydroponics, a leading New Zealand-based company, supplies advanced hydroponic systems to local growers, enabling them to produce high-quality lettuce and herbs with minimal water use.
Another success story comes from Oamaru, where a family-run aquaponics farm produces fresh vegetables and fish for local markets.
Government Support and Initiatives
The New Zealand government has introduced policies and funding programs to encourage sustainable farming practices. Grants for research and development in hydroponics and aquaponics are helping farmers transition to these advanced systems, further accelerating their adoption. The Sustainable Food & Fibre Futures fund, for instance, provides financial assistance to projects aimed at improving resource efficiency in agriculture.
Emerging Technologies in Hydroponics and Aquaponics
Advancements in technology, such as IoT (Internet of Things) sensors and AI-driven monitoring systems, are enhancing the efficiency of hydroponics and aquaponics.
Farmers can now track nutrient levels, water quality, and plant health in real time, optimizing their operations and reducing labor costs. In addition, automated climate control systems ensure ideal growing conditions, further boosting productivity.
| Technology | Application | Benefits |
| IoT Sensors | Real-time monitoring of water and nutrients | Prevents waste and ensures crop health |
| AI Systems | Predictive analysis for farm management | Reduces operational inefficiencies |
| Automated Systems | Climate control and irrigation management | Maximizes yield and reduces labor |
Advantages of Hydroponics and Aquaponics for New Zealand
The adoption of hydroponics and aquaponics is rapidly redefining agriculture in New Zealand, offering a range of advantages that make them invaluable for a sustainable future.
Environmental Benefits
- Water Efficiency: Both systems use significantly less water than traditional farming. For example, aquaponics recycles water through its closed-loop system, minimizing wastage.
- Reduced Land Use: Since plants can be grown vertically or in small spaces, these systems reduce the need for large agricultural land.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: By enabling local production of food, hydroponics and aquaponics reduce the environmental impact of transporting produce over long distances. According to a 2023 study, hydroponic systems in New Zealand emit 30% fewer greenhouse gases than conventional farming methods.
Economic Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Although the initial setup costs can be high, the long-term savings from reduced resource use and higher yields outweigh the investment.
- Export Opportunities: New Zealand’s reputation for quality produce can be bolstered by the adoption of innovative, sustainable farming methods. The global hydroponics market, valued at USD 10 billion in 2023, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.3% through 2030, offering significant export potential.
Health and Nutritional Benefits
- Produce grown in hydroponic and aquaponic systems is often fresher and richer in nutrients due to controlled conditions.
- The absence of chemical pesticides and herbicides ensures food safety and consumer trust. Aquaponics, in particular, supports fully organic production, meeting global standards for organic certification.
Challenges and Future Potential
Barriers to Wider Adoption
- Initial Costs: Setting up hydroponic or aquaponic systems requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology. The average cost for a small-scale hydroponic farm in New Zealand starts at NZD 50,000.
- Technical Knowledge: Farmers need specialized training to operate these systems effectively. Without proper knowledge, issues like nutrient imbalances or water quality problems can arise.
- Market Awareness: While demand is growing, many consumers are still unfamiliar with the benefits of hydroponically and aquaponically grown produce. Education campaigns are needed to build trust and awareness.
Addressing These Challenges
- Training Programs: Government and private organizations can offer workshops and resources to educate farmers. For example, Massey University offers short courses on hydroponic and aquaponic farming.
- Collaborations: Partnerships between technology companies, researchers, and farmers can drive innovation and reduce costs. Companies like Autogrow are working with local farmers to implement cutting-edge solutions tailored to New Zealand’s needs.
The Future of Hydroponics and Aquaponics in New Zealand
As New Zealand continues to prioritize sustainability, the growth of hydroponics and aquaponics is expected to accelerate. Innovations in automation, renewable energy integration, and consumer awareness campaigns will play crucial roles in shaping their future.
By 2030, it is projected that hydroponic systems will account for 15% of the country’s horticultural production.
Takeaways
The growth of hydroponics and aquaponics in New Zealand represents a significant leap toward sustainable agriculture. These systems not only address pressing environmental and economic challenges but also align with consumer demand for healthier, eco-friendly food options.
By embracing these technologies, New Zealand is setting an example for the world, demonstrating how innovation can transform agriculture and ensure food security for generations to come.
Detailed insights, practical examples, and cutting-edge technologies highlight why these farming systems are more than just a trend—they are the future of agriculture.