In today’s data-driven and highly regulated environment, maintaining an unbroken chain of custody is critical for ensuring the integrity, security, and admissibility of evidence—whether physical, digital, or forensic. A single gap in documentation or handling can compromise an entire investigation, derail compliance efforts, or lead to costly legal disputes. Chain of custody compliance isn’t just a procedural formality; it’s a safeguard that protects authenticity, accountability, and trust.
This guide outlines seven proven techniques organizations can implement to strengthen their chain of custody processes—from secure tracking systems and digital audit trails to staff training and regulatory documentation. Whether your operations involve law enforcement evidence, clinical research samples, or digital forensics, these best practices will help you minimize risk, meet legal standards, and maintain full traceability across every transfer and transaction.
Key Takeaways
- Chain of custody compliance ensures that all evidence—physical, digital, or biological—remains authentic, traceable, and legally defensible.
- Documentation and traceability at every handoff are vital to prevent data tampering, contamination, or disputes in court or audits.
- Digital tracking systems and secure audit trails reduce human error, enabling accurate timestamping and automated recordkeeping.
- Access control protocols safeguard evidence by limiting handling to authorized personnel only.
- Regular training for employees reinforces proper handling, labeling, and documentation procedures.
- Compliance audits and spot checks help detect weaknesses in chain continuity before they become liabilities.
- Integration of technology—such as RFID tags, blockchain logs, or forensic management software—enhances transparency and accountability across the custody lifecycle.
Proper Evidence Collection and Packaging
Careful evidence collection sets the case on solid ground. Strong packaging keeps proof intact.
- Pick bags that meet tamper-evident and evidence packaging standards, with a serial-number seal, a clear label area, and a durable design. They catch any sign of tampering and lock in physical evidence like shell casings and fibers.
- Don full personal protective gear—gloves, mask, and gown—to shield crime scene items from contamination. This step saves fingerprints and DNA evidence from accidental mix-ups.
- Slide biological fluids and DNA evidence into sterile jars or swabs, seal them, then wrap to block any leak. A spill can ruin the integrity of key proof in a court of law.
- Write date, time, case ID, and collector initials in neat print on each package. Update the chain of custody log sheet or digital form right away for clear evidence documentation.
- Stick serial-number seals across bag seams and sign each seal broken line. Note the seal number on the evidence form and in the evidence management system for a solid audit trail.
- Stash computers, flash drives, and hard disks in static-free pouches with write-blockers attached, then drop them into a locked case. A breach in handling digital evidence can void admissibility in court.
- Move sealed packages to a locked evidence locker or tamper-proof box. Scan barcodes or swipe access cards to record each transfer in real time, guarding chain of custody compliance and evidence integrity.
How do you accurately label and document evidence?
Officers tag each sample with a barcode or serial number and stow it in a tamper-evident bag. Each label shows date, time, location and collector’s signature. Teams scan barcodes with a scanner and upload entries to a digital chain of custody form.
This audit trail blocks evidence tampering and proves evidence integrity in a court of law.
Analysts log witness names and site details on an evidence log sheet or within secure management software. Investigators stick to National Institute of Standards and Technology guidelines and use a barcode scanner and data encryption to lock sensitive information.
Supervisors enable role-based access control and run inspections on evidence lockers to shield items from contamination and breaches.
What are the best practices for secure storage and transportation?
Secure storage and transport sit at the core of evidence integrity. You need tight controls to stop tampering and data breaches.
- Lock items in a certified evidence locker with multi-factor authentication and audit trail software, like Fort Knox for proofs.
- Store packages in climate-controlled rooms to shield both paper files and storage discs from heat and moisture.
- Wrap each exhibit in evidence envelopes or rigid containers, then inspect seals before and after transport to spot any tampering.
- Write down every transfer in a chain of custody log and use digital tracking to get real-time updates on evidence location.
- Run background checks on staff who touch any piece and limit entry to trained experts to cut system vulnerabilities.
- Load packages into plain delivery trucks fitted with GPS trackers and sealed logs, then hand off keys at each checkpoint.
- Pair manual inspections with automated audits, tapping computer forensics tools to scan for data breaches or misplaced evidence.
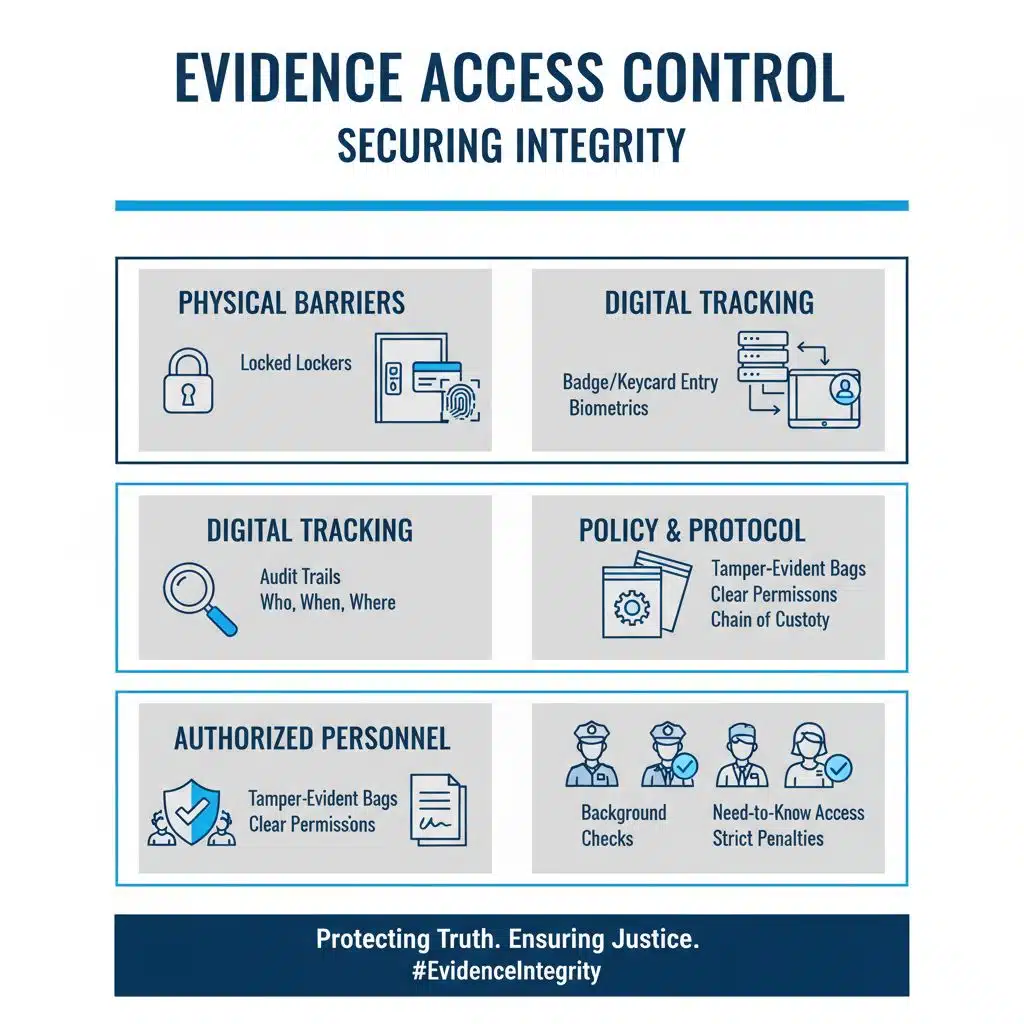
How can access to evidence be effectively restricted?
Law enforcement teams lock down evidence lockers. Badge readers, keycards, and biometric scanners guard storage doors. Each staffer passes a tough background check. Every swipe registers in an audit trail.
That record shows who enters, and when. Tamper-evident bags seal physical evidence in supply rooms.
Access control policies form a vital link in chain of custody, setting clear handling permissions for each item. Digital evidence management systems track file access. Lab techs, forensic analysts, and officers work only on cases they must handle.
Protocol breakers face strict fines or charges. This lockout of unauthorized hands guards evidence integrity.
Why is regular tracking and monitoring of evidence movement important?
Missing evidence can vanish faster than socks in a dryer. Organizational negligence and lack of tracking systems cause these slip-ups. A solid tracking system stops losses, by adding barcodes or RFID tags to each item.
This tech ties digital evidence and physical items to a single audit trail. Data from barcode scanners and GPS tools pin down every move. Names, titles, dates, condition notes, and paper docs ride along in the log.
Each item sits in a tamper-evident bag inside an evidence locker until needed.
Regular spot checks and internal audits catch missteps. They flag any tampering or chain of custody breaks. Healthcare and manufacturing firms handle dozens of transfers every day.
Discrepancies may cost trials or regulatory fines in a court of law or hospital review. Strict monitoring guards evidence integrity and boosts admissibility. It also speeds up evidence handling and cuts down pain points in evidence management.
How can technology improve chain of custody processes?
Barcodes tag each item in the chain of custody at the crime scene. Staff scan tags with handheld RFID readers in web portals and mobile scanners. Digital forensics teams access digital evidence logs in secure online systems.
GPS tracking maps the van route for real time evidence movement. Handlers use cloud apps for evidence handling, documentation, and admissibility.
AI spots odd entries in the audit trail. Machine learning flags mismatches fast. Software like EOXS Reports locks every update with a time stamp. EOXS People verifies handler IDs before any pick up or drop off.
Labs see fewer lost items, stronger data security, and a rock solid paper trail for court.
Takeaways
Strong seals and clear logs guard your chain of custody from day one. Using radio tags, tracking stickers, and sealable bags, you lock each transfer in place. A secure locker and a clear record log form a solid backbone.
This saves time, cuts risk, and meets court rules for data security and evidence admissibility. Keep sharp eyes, stick to best practices, and let each handoff shine with evidence integrity.
FAQs on Techniques to Ensure Chain of Custody Compliance
1. What is the chain of custody and why is it key?
Chain of custody is the path evidence takes, from the scene to the court. It shows who touched the item, and when. A clear audit trail, solid evidence documentation, and strict evidence handling stop claims of tampering. If that link breaks, even strong proof can fall flat.
2. How do we manage physical and digital evidence?
We label each item at the time of evidence collection. Then we pack photos in tamper-evident bags, and store digital evidence, like hard drives, in sealed boxes. We log each evidence transfer in a tracking sheet. We keep items in a secure evidence locker. I once saw a drive go missing under a bench. That taught us to lock boxes fast.
3. What are best practices for evidence documentation?
We note time, date, and handler name at every step. We keep simple forms or digital logs. We cross the t’s and dot the i’s with clear notes. Good evidence management and tracking boost evidence admissibility. Judges love crisp docs.
4. How can we prevent evidence tampering and contamination?
We wear fresh gloves, change them between items. We clean tools like a chef wipes knives. We seal each item in tamper-evident bags. We store samples apart to avoid evidence contamination. These steps guard evidence integrity.
5. Why must we guard evidence integrity at every step?
A broken seal or wrong file can kill a case in a court of law. Evidence integrity is the glue that holds proof together. Secure storage, solid audit trails, and clear chain of custody form double locks judges admire.
6. How does secure transfer and tracking work?
We use barcode tags or RFID chips on bags and drives. We scan at handoff, we log who gives and who gets the evidence. We set alerts for gaps. A digital forensics log boosts data security, so no step slips through the cracks.