As we move toward 2025, the pace of global business continues to increase. Companies are expected to not only meet customer demands faster but also react quickly to supply disruptions, market changes, and technological advancements.
Achieving supply chain agility—the ability to adapt quickly and efficiently—has become a vital strategy for companies aiming to stay ahead of the competition.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 10 strategies for enhancing supply chain agility in 2025, delving into practical, actionable insights that can be immediately implemented.
From leveraging technology and data analytics to fostering strong supplier relationships, each of these strategies will contribute to building a more resilient, flexible, and future-proof supply chain.
Strategy #1 – Embrace Digital Transformation
In today’s rapidly evolving market, digital transformation has become essential for supply chains aiming for agility. The adoption of new technologies allows businesses to streamline operations, enhance transparency, and respond more efficiently to market shifts. Embracing digital tools like IoT, cloud platforms, and AI can be the key to unlocking the next level of supply chain flexibility.
Implementing Advanced Technologies for Real-Time Data
Real-time data provides companies with up-to-the-minute insights into every facet of their supply chain. Technologies like IoT and RFID allow for real-time tracking of goods, inventory, and shipments. By integrating these technologies into their operations, businesses can monitor stock levels, anticipate delays, and make informed decisions on-the-fly, improving overall efficiency.
Example: Walmart uses RFID tags and IoT sensors in its supply chain to track inventory levels in real time, allowing it to streamline product restocking and reduce stockouts. This approach has allowed Walmart to maintain high levels of customer satisfaction, ensuring goods are available when customers need them.
| Technology | Benefit | Example |
| IoT | Tracks inventory in real-time, reducing stockouts and overstocking. | Walmart uses RFID and IoT sensors for inventory management. |
| AI & Machine Learning | Predicts demand fluctuations and optimizes delivery routes. | Amazon uses machine learning to predict customer demand and improve inventory management. |
How AI and Machine Learning Can Enhance Agility
AI and machine learning [ML] enable predictive capabilities, helping businesses foresee changes in demand or potential disruptions in supply. These technologies can optimize processes such as inventory management, routing, and customer demand forecasting. With AI, supply chains can anticipate changes and adapt in real time, making them more agile and responsive.
Example: Amazon’s ML algorithms help the company predict product demand at a granular level, adjusting stock levels accordingly. This proactive approach to inventory management ensures that Amazon maintains high customer satisfaction while minimizing wasted stock.
Building a Robust Digital Infrastructure
To fully capitalize on digital transformation, businesses must invest in a strong digital infrastructure. Cloud-based platforms that enable collaboration, real-time data access, and integrated supply chain management are crucial. This infrastructure enables companies to connect suppliers, warehouses, logistics providers, and other stakeholders seamlessly.
| Key Action | Outcome |
| Cloud Platforms | Facilitate seamless communication and data sharing across departments and suppliers. |
| Real-time Integration | Ensure synchronization across the entire supply chain, improving decision-making speed and reducing errors. |
Strategy #2 – Leverage Data Analytics for Smarter Decisions
Data is now the backbone of modern supply chain management. With the right analytics tools, businesses can make smarter, data-driven decisions that increase efficiency and enhance agility.
The Power of Predictive Analytics in Supply Chain Management
Predictive analytics use historical data to forecast future events like demand surges, stock shortages, and potential supply chain disruptions. By leveraging these insights, businesses can proactively manage their resources, streamline operations, and avoid costly delays.
Example: Dell Technologies uses predictive analytics to optimize its supply chain. By analyzing historical order data and trends, Dell can predict customer demand, adjust production schedules, and ensure timely product deliveries.
| Tool | Benefit | Example |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasts demand and identifies potential disruptions. | Dell uses predictive analytics to adjust production schedules. |
| Dashboards | Allows decision-makers to monitor supply chain health in real-time. | Nike utilizes dashboards for better decision-making during product launches. |
Enhancing Decision-Making with Data Insights
Real-time data insights enable managers to make informed decisions quickly. Companies can use data analytics to optimize inventory levels, supplier management, and distribution channels, improving supply chain responsiveness.
Creating Actionable Dashboards and KPIs
Dashboards give managers immediate visibility into key supply chain metrics such as lead times, stock levels, and transportation efficiency. By having this information at their fingertips, managers can quickly identify problems and take corrective actions to maintain agility.
| KPI | Purpose | Example |
| Lead Time | Monitors time from order to delivery. | FedEx uses lead time metrics to streamline delivery operations. |
| Inventory Turnover | Measures how often stock is sold and replaced. | Zara uses this KPI to ensure quick restocking and stock freshness. |
Strategy #3 – Foster Stronger Supplier Relationships
Building strong supplier relationships is crucial for maintaining flexibility in the supply chain. Collaborative, long-term partnerships can help businesses respond quickly to changes in demand or supply, creating a more agile and resilient supply chain.
Building Collaborative Partnerships for Flexibility
Working closely with suppliers ensures both parties can react to changing market conditions and adjust production or delivery schedules as needed. These partnerships also promote greater transparency and smoother communication.
Example: Toyota’s famous “just-in-time” [JIT] manufacturing system is built on strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers. This system allows Toyota to minimize inventory while meeting fluctuating demand without disruptions.
| Strategy | Benefit | Example |
| Collaborative Planning | Helps adjust production schedules and inventory based on demand. | Toyota uses JIT to collaborate closely with suppliers. |
| Supplier Risk Sharing | Allows companies to mitigate risks together. | Apple partners with suppliers to share risks related to material shortages. |
Sharing Data with Suppliers for Better Visibility
Sharing relevant data with suppliers can improve coordination and reduce delays. Information on sales forecasts, stock levels, and production schedules can help suppliers plan their deliveries better, ensuring a smooth flow of goods through the supply chain.
Managing Risks with Multi-Supplier Networks
To mitigate risks, businesses should avoid relying on a single supplier for critical components. Instead, creating a network of multiple suppliers allows for greater flexibility and reduces the likelihood of disruptions.
Strategy #4 – Optimize Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is key to maintaining agility. Companies that can quickly adjust inventory levels in response to demand changes will stay ahead of competitors. By adopting the right inventory strategies, businesses can maintain flexibility while minimizing costs.
Moving Toward Just-in-Time [JIT] vs. Just-in-Case [JIC]
While the traditional approach has been to stockpile goods [JIC], modern supply chains are increasingly adopting JIT strategies, which focus on having the right products in the right quantities at the right time, with minimal inventory.
Example: Toyota has successfully implemented JIT manufacturing, reducing excess inventory costs and improving overall efficiency while maintaining the ability to respond quickly to demand fluctuations.
| Approach | Description | Example |
| Just-in-Time [JIT] | Minimizes inventory and aims to restock just as needed. | Toyota uses JIT to optimize production and minimize waste. |
| Just-in-Case [JIC] | Stockpiles inventory to prepare for potential disruptions. | General Electric often uses JIC in highly regulated industries. |
Real-Time Inventory Tracking with IoT
IoT-based inventory management solutions can provide real-time updates on stock levels, product location, and inventory conditions. This visibility helps businesses manage stock more efficiently and reduce overstocking or stockouts.
Example: Zara uses real-time inventory tracking in its stores, which enables the company to quickly restock and meet customer demand.
The Role of Demand Forecasting in Inventory Agility
Effective demand forecasting uses historical sales data and market trends to predict future demand. By understanding customer buying patterns, companies can adjust inventory levels proactively, ensuring they have enough stock to meet demand without overstocking.
Strategy #5 – Invest in Agile Transportation Networks
Transportation is one of the most critical aspects of supply chain agility. An agile transportation network allows businesses to adjust routes and methods quickly, ensuring that goods are delivered on time, even during disruptions.
Multi-Modal Transportation for Greater Flexibility
Adopting a multi-modal transportation system, which uses a mix of air, sea, rail, and road transport, allows companies to optimize cost, speed, and flexibility. Switching between modes depending on the situation ensures that goods can still be delivered efficiently.
Example: FedEx uses a combination of air and ground transportation to optimize delivery times. During peak periods, FedEx switches to air transport to avoid congestion and speed up delivery.
| Mode | Benefit | Example |
| Air | Fast and ideal for high-value, time-sensitive goods. | FedEx uses air shipping to deliver packages faster. |
| Ground | Cost-effective for large shipments over longer distances. | UPS relies on ground transport for domestic deliveries. |
| Sea | Low cost for bulk goods, but slower. | Maersk uses sea shipping for large-scale goods distribution. |
Using Real-Time GPS and Telematics to Improve Delivery
GPS and telematics allow companies to track the exact location of their shipments. With this information, businesses can reroute shipments in real time, avoid delays, and communicate better with customers about estimated delivery times.
Example: Amazon’s use of real-time tracking and delivery routing through GPS enables it to fulfill orders faster and more efficiently.
Overcoming Transportation Bottlenecks with Agile Strategies
Transportation bottlenecks, whether due to traffic, weather, or logistics failures, can significantly delay the movement of goods. By maintaining flexible transportation options, businesses can quickly adjust routes or transportation methods to avoid disruptions.
Strategy #6 – Adopt a Resilient Risk Management Framework
Risk management plays a central role in supply chain agility. Companies must be proactive in identifying risks and building resilience into their supply chains to ensure they can continue operating during unexpected disruptions.
Building Contingency Plans for Unforeseen Disruptions
Developing a comprehensive risk management plan includes preparing for potential supply chain disruptions—whether from natural disasters, economic shifts, or geopolitical tensions. A well-designed contingency plan allows businesses to respond quickly and minimize downtime.
Identifying Key Vulnerabilities in Your Supply Chain
Conducting regular risk assessments helps businesses identify weak points in their supply chains, such as over-reliance on certain suppliers, single transportation routes, or limited stock at key points. Once vulnerabilities are identified, companies can work to strengthen these areas.
Leveraging Technology for Predictive Risk Assessment
Predictive risk management tools leverage historical data and AI to forecast potential risks. By utilizing these tools, businesses can anticipate and prepare for disruptions before they occur, enhancing supply chain resilience.
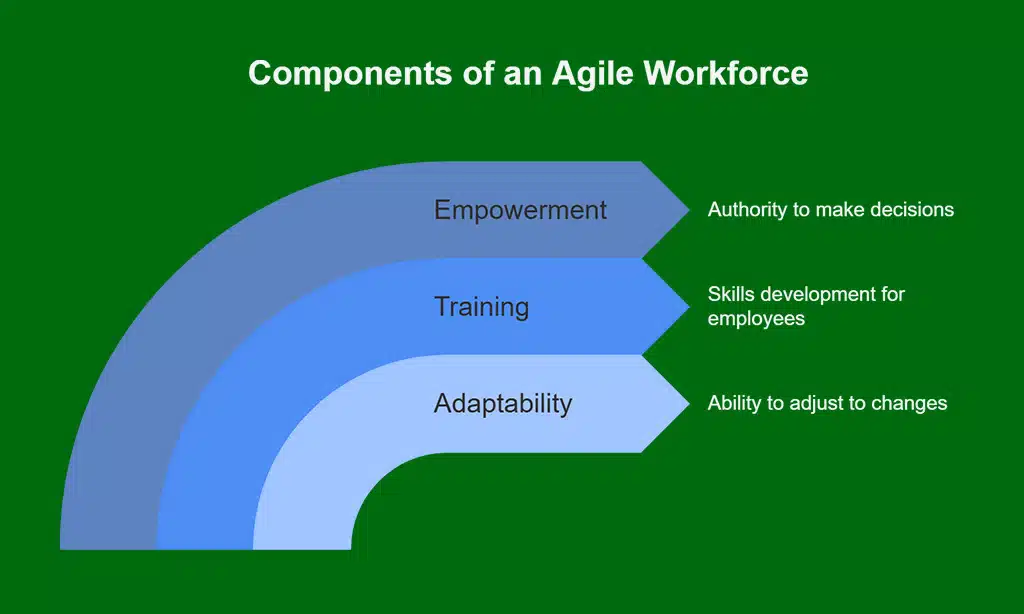
Strategy #7 – Strengthen Workforce Agility and Flexibility
An agile workforce is key to enhancing the overall flexibility of a supply chain. Employees who are adaptable, well-trained, and empowered to make decisions quickly help ensure that businesses can respond effectively to shifts in supply and demand.
Investing in Cross-Training for Versatile Employees
Cross-training employees allows them to step into different roles across the supply chain. This strategy ensures that operations can continue smoothly, even if an employee is unavailable or if there is a sudden spike in demand in a specific area.
Example: Companies like Caterpillar have adopted cross-training programs that allow employees to move between roles in production, inventory management, and logistics. This not only reduces downtime but also increases the operational flexibility of the workforce.
| Training Strategy | Benefit | Example |
| Cross-Training | Employees can handle different roles, improving flexibility. | Caterpillar uses cross-training to keep operations running smoothly. |
| Employee Empowerment | Employees can make decisions, speeding up response times. | Toyota empowers its workforce to address issues on the production floor. |
Leveraging Digital Tools for Employee Collaboration
By utilizing communication platforms, project management tools, and collaboration apps, businesses can improve coordination among teams. This helps employees respond quickly to shifting priorities or unexpected issues, which enhances the overall agility of the workforce.
Example: Slack and Microsoft Teams have become critical tools in modern supply chains, facilitating seamless communication among remote and on-site teams, and speeding up decision-making processes.
Implementing Remote Monitoring Tools
The ability for employees to manage operations remotely provides greater flexibility. Remote monitoring of key performance indicators [KPIs], stock levels, and transportation can ensure that managers are in control even when they are away from the physical site.
| Tool | Benefit | Example |
| Collaboration Platforms | Enable better communication, allowing for quicker decision-making. | Slack and Microsoft Teams support remote collaboration. |
| Cloud-Based Monitoring | Provides real-time visibility into operations and inventory. | Oracle offers cloud-based tools that track workforce performance and inventory. |
Strategy #8 – Integrate Sustainability into Your Supply Chain
Sustainability has become an increasingly important aspect of supply chain management. Businesses are now realizing that agility is not just about responding to demand fluctuations, but also about building a supply chain that is environmentally and socially responsible, ensuring long-term viability.
The Role of Sustainable Sourcing
Sustainable sourcing ensures that businesses are using materials and resources that minimize environmental impact. By engaging with suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, companies can reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining a reliable and responsive supply chain.
Example: Patagonia has been a leader in sustainable sourcing, using recycled materials for its products. The company’s strong commitment to sustainability helps mitigate risks related to resource shortages and environmental regulations.
| Sustainability Initiative | Benefit | Example |
| Sustainable Sourcing | Ensures that resources are used efficiently and responsibly. | Patagonia uses recycled materials for production. |
| Carbon Footprint Reduction | Reduces environmental impact while maintaining supply chain flexibility. | Unilever is working to reduce its carbon emissions in supply chains. |
Green Logistics: Optimizing Transport for Sustainability
Optimizing transportation routes, using energy-efficient vehicles, and implementing packaging reductions are just a few ways businesses can make their logistics more sustainable. Green logistics not only reduces the carbon footprint but also improves efficiency, ensuring better resource use.
Example: DHL has made significant strides in sustainability by introducing electric vehicles into its fleet, thereby reducing carbon emissions and fuel costs. Their “GoGreen” initiative focuses on improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions in transportation.
| Strategy | Benefit | Example |
| Green Logistics | Reduces environmental impact and improves efficiency. | DHL has introduced electric vehicles in its logistics network. |
| Eco-Friendly Packaging | Minimizes waste and reduces costs. | IKEA uses sustainable packaging to reduce waste in supply chains. |
Circular Supply Chains for Long-Term Resilience
A circular supply chain focuses on reusing, recycling, and reducing waste at every stage of production and distribution. It ensures that resources are continuously cycled back into the system, making supply chains more sustainable and agile in the long run.
Example: Nike’s “Reuse-A-Shoe” program takes worn-out sneakers and transforms them into new materials that can be used in manufacturing. This initiative not only reduces waste but also creates a more flexible, sustainable supply chain.
Strategy #9 – Enhance Customer-Centricity in Your Supply Chain
In an era where customer expectations are at an all-time high, businesses need to align their supply chain strategies with customer demands for faster delivery, higher-quality products, and personalized experiences. Customer-centric supply chains enhance agility by allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing consumer needs.
Personalizing the Customer Experience
Personalization is a key driver of customer satisfaction. By using data analytics and customer feedback, businesses can tailor their supply chain operations to provide faster, more efficient delivery of personalized products.
Example: Amazon leverages its vast customer data to deliver highly personalized recommendations and fast shipping. Its ability to customize customer experiences has made it a dominant player in the retail industry.
| Personalization Strategy | Benefit | Example |
| Customer Data Analytics | Tailors supply chain operations to meet specific customer needs. | Amazon offers personalized delivery based on customer preferences. |
| Last-Mile Delivery Optimization | Improves delivery efficiency and customer satisfaction. | FedEx optimizes last-mile delivery by analyzing real-time customer data. |
Fast and Flexible Delivery Systems
Customers now expect faster delivery times, with some even demanding same-day or next-day deliveries. To meet these expectations, supply chains must be able to adjust delivery schedules on the fly and employ multiple delivery methods to ensure timely arrivals.
Example: Zara has built a flexible supply chain that allows it to quickly adapt to shifting consumer demands. The company is able to introduce new styles into its stores on a weekly basis, ensuring it stays relevant and responsive to customer preferences.
Managing Customer Returns Efficiently
A responsive supply chain must also have the capability to handle returns efficiently. Easy returns processes improve customer satisfaction, while the ability to quickly restock returned items ensures that supply chains remain fluid and agile.
Example: Zara has an efficient return system that quickly processes returned items and reintegrates them back into stock, ensuring minimal disruption in the supply chain.
Strategy #10 – Invest in Agile Leadership and Decision-Making
Lastly, one of the most important elements of supply chain agility is leadership. Agile decision-making at the top level drives the entire supply chain to remain flexible, proactive, and adaptable to change.
Promoting a Culture of Agility
Leaders must foster a culture of agility, where quick decisions are encouraged, and employees are empowered to act independently when needed. A flexible leadership mindset enables organizations to remain competitive in rapidly changing environments.
Example: Tesla’s leadership is known for its quick decision-making and willingness to pivot quickly, whether in response to a production issue or market shift. This agile approach allows Tesla to scale rapidly while maintaining its competitive edge.
| Leadership Strategy | Benefit | Example |
| Decentralized Decision-Making | Promotes quick, localized responses to changes. | Tesla allows employees to make quick decisions at all levels of the supply chain. |
| Change Management | Helps the organization adapt to changes smoothly and quickly. | Google encourages agile leadership practices across its teams. |
Building Cross-Functional Teams
Agile leadership also means creating cross-functional teams that can tackle challenges from multiple perspectives. By combining expertise from different areas, such as procurement, logistics, and sales, businesses can respond to challenges more effectively and collaboratively.
Empowering Decision-Makers Across the Organization
Empowering decision-makers throughout the organization can eliminate bottlenecks and speed up response times. Whether it’s a supply chain manager or an inventory coordinator, providing them with the authority to make decisions on the ground level leads to faster responses and greater overall agility.
Takeaways: Preparing for the Future of Supply Chains
As we approach 2025, the ability to implement strategies for enhancing supply chain agility will be a key differentiator between successful companies and those that fall behind.
With technologies like AI, real-time data, and IoT, along with strong supplier relationships and flexible workforces, businesses can build supply chains that not only respond quickly to disruptions but thrive in the face of change.
By focusing on the strategies outlined above—from embracing digital transformation to investing in agile leadership—companies can future-proof their supply chains, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly complex and fast-paced global marketplace.
The time to act is now—integrate these strategies into your supply chain to ensure you’re prepared for the opportunities and challenges of 2025 and beyond.