Space is no longer a distant frontier that only a few superpowers visit once in a decade. In the last twenty years, space science innovations have moved faster than in the entire Cold War era.
Reusable rockets, deep space telescopes, lunar missions, private space stations, and quantum communication are changing how we explore, communicate, and even think about life beyond Earth. These space science innovations are not just about prestige. They connect directly to climate research, navigation, communication, disaster monitoring, new materials, and even global energy solutions.
In this article, we look at 12 game-changing space science innovations that are already shaping tomorrow. Each one is more than a headline. Together, they form a new infrastructure for the twenty-first-century space age.
Table: Overview Of Key Space Science Innovations
| Innovation | Main Impact Area | Short Description |
| Reusable rockets | Launch cost and access | Rockets that can land and be flown again |
| Deep space telescopes | Astronomy and cosmology | Telescopes like JWST are seeing the early universe |
| Lunar return and Artemis | Human exploration | Sustainable presence on the Moon |
| Planetary defense | Earth safety | Detecting and deflecting hazardous asteroids |
| Commercial space stations | Research and industry | Private orbital labs and habitats |
| Advanced propulsion | Deep space travel | Ion and electric engines for long missions |
| Mars and icy moon exploration | Life detection and geology | Rovers and probes on Mars, Europa, and Enceladus |
| Quantum communication satellites | Secure communication | Quantum key distribution from orbit |
| Space-based solar power | Clean energy | Power collected in space and beamed to Earth |
| In situ resource utilization (ISRU) | Off-world living | Using local materials on the Moon and Mars |
| Space manufacturing and 3D printing | New materials and logistics | Making products and parts in microgravity |
| Space data and AI | Earth observation and planning | Satellites plus AI for climate, farming, and security |
Here Are 12 Game-Changing Space Science Innovations of the Future
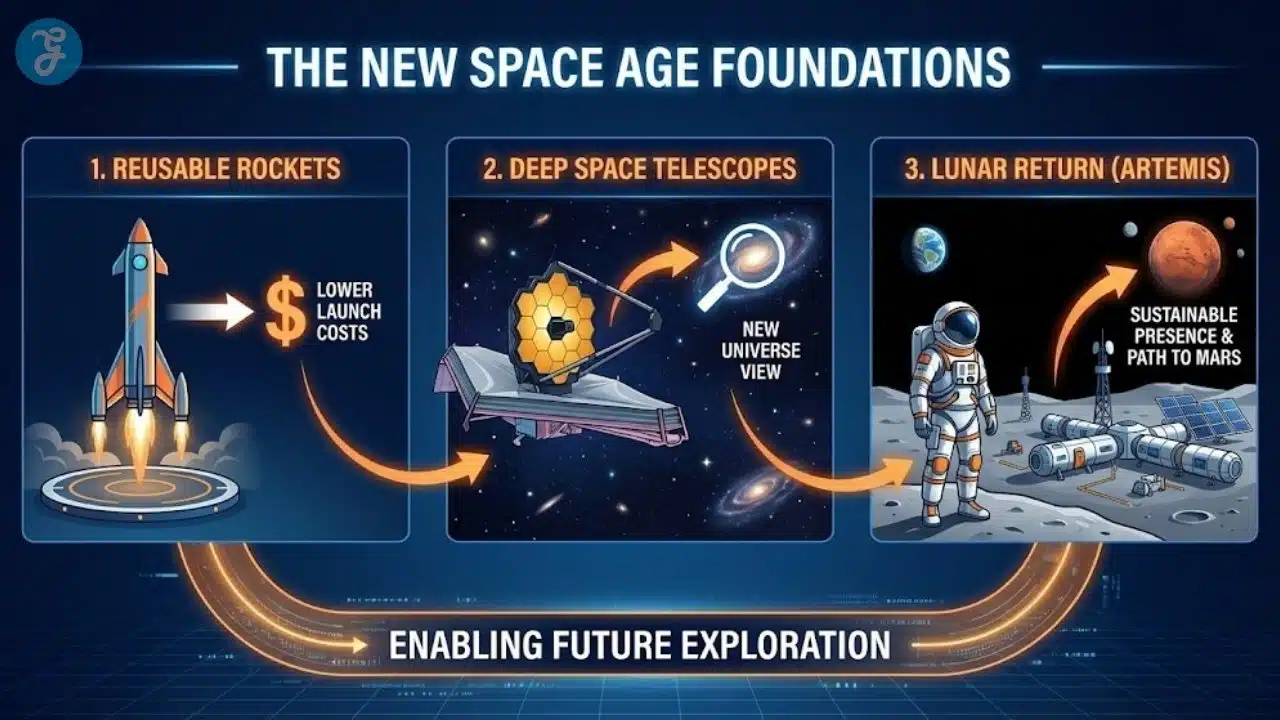
1. Reusable Rockets And Cheaper Access To Space
The first breakthrough that unlocked the modern space boom was the reusable rocket. Traditionally, rockets were used once and discarded. This was like throwing away a plane after a single flight. Companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin changed this model by building boosters that can guide themselves back to Earth and land vertically for reuse. This has cut launch costs and increased launch frequency.
Reusable rockets are a core example of space science innovations that act as enablers. Almost every other item in this list depends on cheaper, more reliable access to orbit. Lower costs encourage more satellites, more experiments, and more missions from universities and smaller nations.
Table: Key Points About Reusable Rockets
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Main benefit | Lower launch cost per kilogram | Reuse spreads hardware cost across many flights |
| Technical feature | Vertical landing and propulsive descent | Rockets fire engines to slow down and land upright |
| Impact on cadence | Higher launch frequency | Easier to schedule missions and small payloads |
| Who uses them | Private firms and space agencies | Commercial launches, government missions, rideshares |
2. Deep Space Telescopes And A New View Of The Universe
The launch of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) gave astronomers a new set of eyes in the infrared spectrum. While the Hubble Space Telescope transformed visible and ultraviolet astronomy, JWST looks at light stretched by the expansion of the universe. It can see some of the earliest galaxies, study exoplanet atmospheres, and peer through dust clouds where stars are born.
JWST and other next-generation observatories are central space science innovations because they change our basic understanding of how the universe formed and how common habitable worlds might be.
Table: Deep Space Telescope Highlights
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Main example | James Webb Space Telescope | Infrared space telescope at–Sun-Earth L2 point |
| Core strength | Infrared sensitivity | Sees through dust and detects very distant galaxies |
| Science targets | Early galaxies, exoplanets, and star birth | Helps refine models of cosmic evolution |
| Broader impact | Public engagement and education | Stunning images inspire interest in science |
3. Lunar Return, Artemis, And The Road To Mars
For decades, the Moon was a symbol of a past achievement. Now it is turning into a future laboratory. Programs such as NASA’s Artemis aim to return humans to the lunar surface, establish a long-term presence, and test technologies that will later support missions to Mars. Other space agencies and private companies are planning landers, rovers, and mining experiments.
This new lunar push is one of the most strategic space science innovations. The Moon offers low gravity, local resources, and a close testing ground for habitats, life support systems, and in situ resource utilization.
Table: Artemis And Lunar Presence
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Main goal | Sustainable human presence on the Moon | Not just flags and footprints, but long-term bases |
| Key partners | International agencies and companies | Shared costs and technology through global alliances |
| Role for Mars | Test bed for deep space missions | Try habitats, ISRU, and logistics close to Earth |
| Science benefit | Study lunar geology and water ice | Helps understand solar system history and resource use |
4. Planetary Defense And Asteroid Deflection
For a long time, asteroid impacts were mostly the subject of disaster movies. Planetary defense changes that. Space scientists now track near-Earth objects and study their orbits. The DART mission (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) showed that a spacecraft can intentionally strike an asteroid and change its trajectory. This is a practical proof that humans can, in principle, reduce the risk from some future impact.
Planetary defense is one of the most directly protective space science innovations. It links space research to public safety and global risk management.
Table: Planetary Defense Essentials
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Main focus | Detect and track near-Earth objects | Use telescopes and surveys to find hazardous asteroids |
| Test mission | DART impact on Dimorphos | Proved kinetic impact can alter an asteroid’s path |
| Follow up | Better surveys and impact modeling | Improve warning time and response options |
| Global role | International coordination | Planetary defense is a shared responsibility |
5. Commercial Space Stations And Private Orbital Labs
The International Space Station has been a joint laboratory for more than two decades. As it approaches the end of its life, private companies are designing commercial space stations. These platforms are planned to host research, manufacturing, tourism, and national astronaut programs.
This shift is a major space science innovation in terms of business model. Instead of only government-owned stations, orbit becomes a place where companies rent laboratory modules, test new drugs, grow crystals, or host paying visitors.
Table: Commercial Space Station Features
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Core idea | Privately run orbital platforms | Companies build and operate stations as services |
| Main customers | Space agencies, companies, and universities | Buy time, space, and support for experiments |
| Uses | Research, manufacturing, tourism | From materials science to media production |
| Long-term outcome | Continuous human presence in orbit | Low Earth orbit becomes a normal working environment |
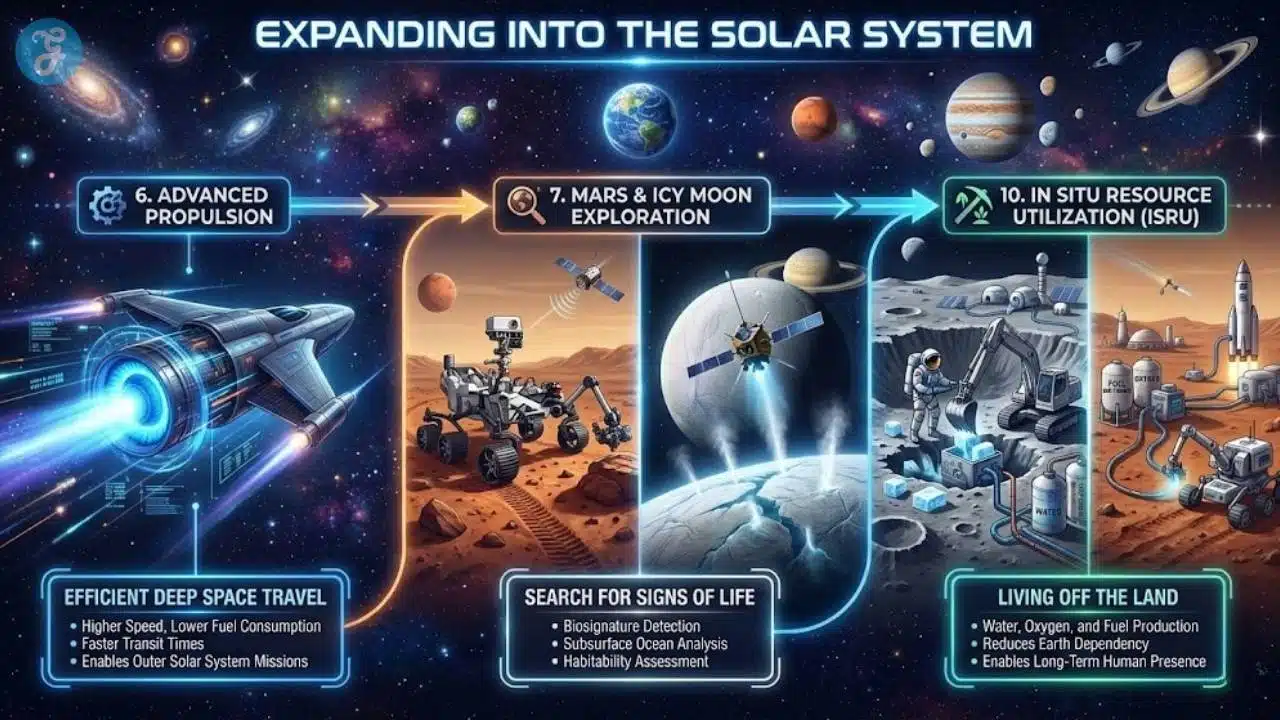
6. Advanced Propulsion For Deep Space Travel
Chemical rockets are powerful, but they are not efficient for long-distance missions. To explore the outer planets and beyond, space agencies and companies are developing ion engines, solar electric propulsion, and other advanced systems. These engines produce low thrust but can operate for months or years, slowly accelerating a craft to high speeds.
Advanced propulsion is one of the most enabling space science innovations for serious deep space exploration. It reduces fuel mass and allows missions that would be impossible or too expensive with conventional rockets alone.
Table: Advanced Propulsion At A Glance
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Main types | Ion and solar electric propulsion | Use electric power to accelerate charged particles |
| Strength | Very high fuel efficiency | Less propellant for the same change in speed |
| Best use cases | Long-distance robotic missions | Outer planets, asteroids, and cargo to Mars |
| Future directions | Nuclear electric and thermal systems | Higher power for crewed deep space missions |
7. Mars And Icy Moon Exploration For Signs Of Life
Rovers like Perseverance on Mars, along with orbiters and planned sample return missions, are part of a long campaign to understand whether life ever existed on the Red Planet. At the same time, missions are being designed to explore icy moons such as Europa and Enceladus, which have subsurface oceans that may be habitable.
These missions are among the most exciting space science innovations because they tackle a fundamental question: are we alone, or is life common in the universe?
Table: Life Focused Exploration Targets
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Mars | Ancient riverbeds and sedimentary rocks | Good places to search for past microbial life |
| Europa and Enceladus | Subsurface oceans beneath ice shells | Plumes and chemistry hint at possible habitable zones |
| Tools | Rovers, orbiters, landers, future drills | Combine remote sensing with on-site measurements |
| Long-term aim | Sample return and biosignature search | Bring material to Earth labs for detailed analysis |
8. Quantum Communication Satellites And Ultra Secure Links
Quantum communication satellites use the principles of quantum mechanics to enable very secure distribution of encryption keys. In practice, they support quantum key distribution, where any attempt to intercept the signal is detectable. Several nations have launched experimental quantum satellites to test this technology over long distances.
This is one of the most advanced space science innovations in the area of communication. It could underpin future secure networks for governments, finance, and critical infrastructure.
Table: Quantum Communication Highlights
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Core principle | Quantum key distribution | Uses quantum states of particles to share keys |
| Role of satellites | Long-distance secure links | Bridge ground stations separated by thousands of miles |
| Security advantage | Eavesdropping detection | Measurement disturbs quantum states |
| Future vision | Global quantum secure network | Combine space and ground fiber links |
9. Space-Based Solar Power As A Clean Energy Source
Space-based solar power is an idea that has existed for decades, but recent advances are turning it into a more serious field. The concept is simple. Solar panels in orbit receive sunlight almost all the time, without clouds or night. They convert this energy to microwaves or lasers and beam it to receiving stations on Earth. Early experiments are testing parts of this system.
As a space science innovation, space-based solar power connects orbital technology to global energy and climate goals.
Table: Space-Based Solar Power Basics
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Main advantage | Near continuous solar exposure | No night, no clouds in space |
| Energy transfer | Microwave or laser beams to the ground | Collected by rectennas or receivers |
| Technical challenges | Efficiency, alignment, safety | Need precise control and safe power densities |
| Potential impact | Large-scale clean energy supply | Could complement ground-based renewables |
10. In Situ Resource Utilization On The Moon And Mars
Sending everything from Earth is expensive. In situ resource utilization, often shortened to ISRU, is the practice of using local materials on other worlds. On the Moon, this could mean extracting oxygen from lunar regolith or using ice in shadowed craters for water and fuel. On Mars, it could involve making methane and oxygen from carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Among space science innovations, ISRU is crucial for long-term human presence. It turns distant worlds from pure destinations into places where people can live and work more independently.
Table: ISRU Key Elements
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Resources on the Moon | Regolith, metals, water ice | Use for construction, air, water, and propellant |
| Resources on Mars | CO2 atmosphere, water ice, soil | Make fuel and support agriculture |
| Main benefit | Lower launch mass from Earth | Fewer resupply missions needed |
| Long-term vision | Self-supporting off-world settlements | Local industry and infrastructure |
11. Space Manufacturing And 3D Printing In Microgravity
Microgravity provides a unique environment for manufacturing advanced materials. Certain crystals, fiber optics, and biological structures can form more perfectly in space than on Earth. At the same time, 3D printers on the International Space Station and future stations allow astronauts to produce tools and spare parts without waiting for resupply.
This area of space science innovations sits at the intersection of materials science, engineering, and logistics. It reduces dependence on Earth deliveries and creates products that may be valuable back on the ground.
Table: Space Manufacturing Summary
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Microgravity benefit | Fewer defects in some materials | Helps grow better crystals and fibers |
| On-orbit 3D printing | Make tools and parts on demand | Increases flexibility and reduces storage needs |
| Commercial products | Advanced fiber optics, medical materials | Potential high-value exports from orbit |
| Future extensions | Larger structures built in space | Build antennas and habitats too big for rockets |
12. Space Data, AI, And Better Decisions On Earth
Modern satellites collect enormous amounts of data about weather, climate, oceans, forests, cities, and more. Artificial intelligence and machine learning help process this data to spot patterns that humans would miss. This combination of satellites and AI drives better forecasts, smarter farming, improved disaster response, and more efficient use of resources.
Although it happens above our heads, this is one of the most practical space science innovations for daily life on Earth.
Table: Space Data And AI Use Cases
| Aspect | Key Point | Quick Explanation |
| Data sources | Earth observation satellites | Capture images and measurements across the globe |
| AI role | Pattern detection and prediction | Find trends in large datasets |
| Example uses | Weather, crops, deforestation, shipping | Support planning and risk reduction |
| Benefit | Better, faster, more informed decisions | Helps governments, businesses, and communities |
Pros And Cons Of Rapid Space Science Innovations
Like any major technological shift, the current wave of space science innovations comes with benefits and risks. On one hand, there are new jobs, new science, and new tools for climate action. On the other hand, there are concerns about space debris, militarization, inequality of access, and environmental impacts of launch activities.
Understanding both sides helps guide policy, investment, and public debate.
Table: Pros Versus Cons Of Space Science Innovations
| Pros | Cons |
| Better climate and Earth monitoring | More satellites increase the risk of space debris |
| Cheaper access to space for many actors | Potential militarization and strategic tensions |
| New industries and high-skilled jobs | Inequality between spacefaring and non-spacefaring nations |
| Improved global communication and security | Environmental impact from rockets and infrastructure |
| Path to long-term human presence off Earth | Ethical questions about mining and colonization |
Space Science Innovations And The Next Decade
The space science innovations shaping tomorrow are not isolated projects. Reusable rockets make launches cheaper. Cheaper launches support deep space telescopes, lunar bases, and quantum satellites. Data from these missions feeds AI systems that improve life on Earth. In situ resource utilization and space manufacturing prepare the ground for long-term human presence beyond our planet. Planetary defense protects the world, which makes all of this possible.
Taken together, these developments signal the start of a new space era that is more continuous, more commercial, and more connected to daily life than any previous phase of exploration. If guided well, they can support science, security, climate stability, and economic opportunity. The challenge is to manage them wisely so that the benefits of space science innovations are shared as widely as possible.