Today there is no way you can have effective workplaces and communications without using the new internet technologies. It means a lot for companies and entrepreneurs to have fiber optic internet for their premises. Even when you are not allowed to have more expenses for the internet, it’s better to save these dollars from some other activity than having something inferior to fiber optic internet technology.
Passing from the simple PSTN internet connection to the fiber optic one took many years and a lot of mindset changes. That is why you need to deeply understand what fiber optic technology means for the internet and how it can change the rules when speed increases.
What is the Fiber Optic Internet?
First, you need to understand what fiber optic internet technology stands for the average user. Even when you need a lower speed, you always have the chance to upgrade your internet experience and have the fiber optic to ensure that you get the most from the online servers that are close to your residence.
Optical fibers have been known for several decades, and they are like the glass where the data pass through as increments of pure light. That gives a chance to your data to move with the highest known speed in the universe, the one of the light. Using the fiber optic internet, you may theoretically connect two distant computers with the same software and have the fastest data transfer you can imagine.
It’s one of the new and revolutionary technologies for the internet these days and one that has made it possible to transfer a huge load of data in less than seconds.
How do FTTx and PON Work?
According to the different destinations of terminal devices, the fiber optic Internet is classified into Fiber to the Home (FTTH), Fiber to the Building (FTTB), Fiber to the Curb (FTTC), etc. All these are called FTTx.
There are two network systems of FTTx, including Active Optical Network (AON) and Passive Optical (PON). Generally, PON is preferred due to its high performance and low cost. It enables a single fiber to maintain an efficient broadband connection from a service provider to multiple end users.
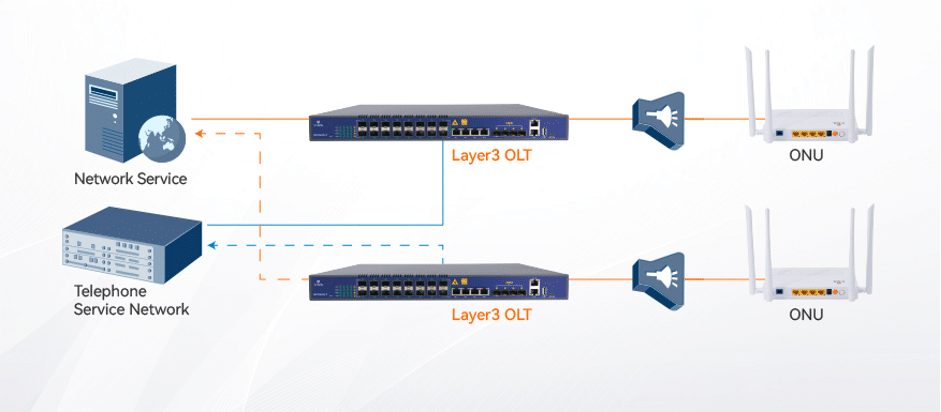
PON consists of an optical line terminal (OLT), optical distribution network (ODN) and optical network unit (ONU). The PON starts with the OLT at the ISP’s central office and connects to one or multiple ONUs via the optical fiber distribution with a passive optical splitter.
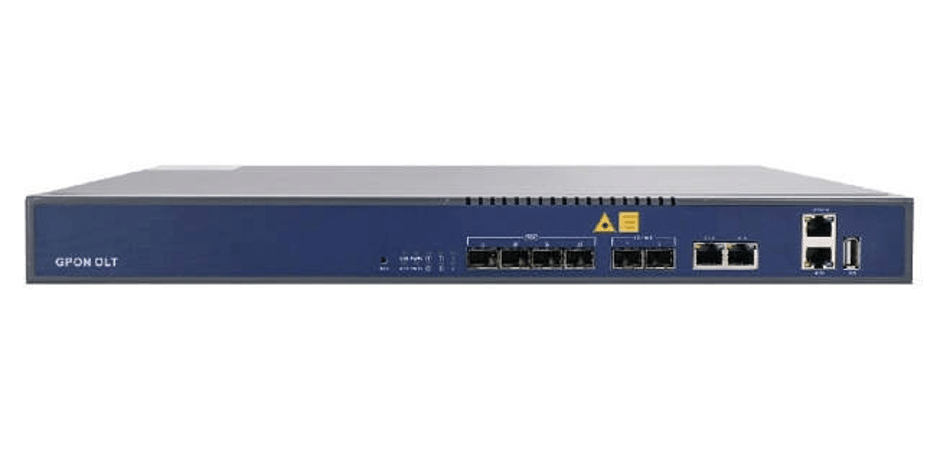
For example, as shown in the below image, it’s V-SOL 4 port GPON OLT. The uplink speed can reach up to 10Gbps and it’s empowered by cloud management.
Features:
Compact design is beneficial for applying in various scenarios
The compact design of 4 port GPON OLT makes it well being applied in many scenarios including low-density areas, remote areas, sparsely-populated areas and industrial parks.
Small and lightweight
The OLT device is small and light, which helps deliver and install easily. It supports multiple installation modes such as limited room space, basement, low-voltage room and small rack or cabinet.
Carrier-class security protection
The device supports the dynamic routing protocol RIP&OSPF, ensuring the safe operation of the network. It also provides uplink redundancy protection including LACP STP, RSTP and MSTP.
Lower TCO
Dramatically saves on investment fees in trunk fibers, pipe engineering, and facilities. Effectively reduce CapEx and OpEx.
How V-SOL POL Solutions Enhance the Internet Speed?
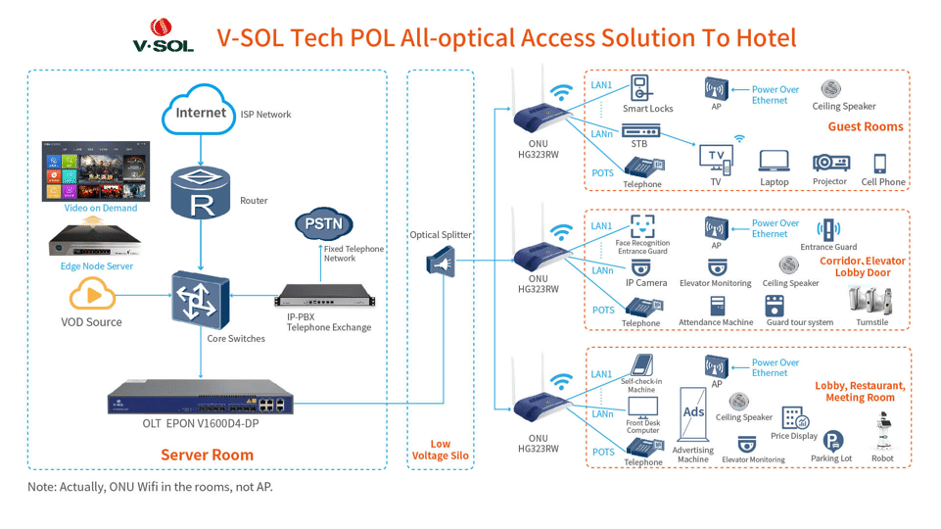
It’s the passive optical LAN (POL) that is given as a solution from V-SOL that makes it possible to have the best speeds at the lowest cost. With the passive LAN, the total network structure will be flatter and more concise. V-SOL has provided many POL solutions for different scenarios such as campus, hotel, highway tunnels and so on. The fiber optic network is with low-latency, high reliability, and anti-electromagnetic interference, which promises the best Internet speed in the application of live stream, video meetings, monitoring, AR/VR, etc.
Just like the V-SOL POL solution for hotels, with 1 fiber for 1 room and 1 terminal device equipped in one room, 1 network can be used in many scenarios like guest rooms, corridors, elevators, lobbies, and restaurants. 1 converged gateway can provide services like enterprise routing, Internet logging, and IPTV.
Fiber optic Internet is developing rapidly. Lots of ISPs are transferring their market from aging DSL networks to fiber optic networks. With the demands of different fields increasing, the fiber optic Internet gets improved in all aspects. It’s believed that there is still huge market potential for fiber optic Internet and it will not be outdated.