The question “What’s the difference between machine and AI subtitle translation?” has become increasingly crucial as content creators seek the most effective translation solutions for their global audience. While both approaches aim to break down language barriers, the underlying technology, translation quality, and practical applications differ significantly. Understanding these distinctions is essential for making informed decisions about subtitle translation strategies.
Understanding Machine Translation: The Foundation of Language Technology
Machine translation represents the foundational approach to automated language translation, relying on predetermined rules and statistical models to convert text from one language to another. Traditional machine translation systems, including early versions of Google Translate and Microsoft Translator, operate through direct word-to-word or phrase-to-phrase conversion based on linguistic rules and pattern matching.
How Traditional Machine Translation Works
Machine translation technology processes source language input through several systematic steps:
- Rule-Based Processing: Early translation engines relied on grammatical rules and dictionaries to translate words and phrases from one language to their target language equivalents.
- Statistical Analysis: More advanced machine translation systems analyze massive datasets of parallel texts to identify language patterns and improve translation accuracy.
- Pattern Matching: Machine-translated subtitles emerge from comparing input text against existing translation databases and selecting the most statistically probable matches.
The process means that traditional machine translation often struggles with context, cultural references, and idiomatic expressions that don’t translate literally between language pairs.
AI Translation: The Evolution of Language Processing
AI translation represents a fundamental advancement in translation technology, leveraging artificial intelligence, neural machine translation, and deep learning to understand context and produce high-quality translations. Unlike traditional machine translation, AI translation tools analyze entire sentences and paragraphs to grasp meaning before generating translated text.
Neural Machine Translation Architecture
Modern AI translation systems, particularly neural machine translation platforms, process language through sophisticated artificial intelligence networks:
- Contextual Understanding: AI makes translation decisions based on comprehensive sentence and paragraph context rather than isolated words or phrases.
- Deep Learning Models: Advanced systems learn from massive datasets containing millions of translation examples across multiple languages.
- Natural Language Processing: AI translation incorporates sophisticated natural language processing to understand nuance, tone, and cultural context.
This technological advancement enables AI-powered translations to handle complex scenarios that traditionally required human translator intervention.
Key Differences in Translation Quality and Accuracy
Accuracy Comparison: Machine vs. AI Translation
The most significant difference between machine and AI subtitle translation lies in translation quality and accuracy:
Machine Translation Limitations:
- Literal word-for-word translation often loses meaning
- Struggles with context-dependent phrases and idiomatic expressions
- Limited ability to adapt to cultural references
- Inconsistent quality across different language pairs
- Frequent mistakes in grammar and sentence structure
AI Translation Advantages:
- Contextual understanding produces more accurate translations
- Better handling of cultural references and local expressions
- Improved grammar and natural language flow
- Consistent quality across multiple languages
- Reduced need for human oversight and intervention
Real-World Translation Examples
Consider translating the Spanish phrase “estar en las nubes” (literally “to be in the clouds”):
Machine Translation Output: “To be in the clouds” AI Translation Output: “To be daydreaming” or “To have one’s head in the clouds”
This example illustrates how AI translation tools understand idiomatic expressions and cultural context, while traditional machine translation provides literal but meaningless results.
Technology Architecture: Deep Learning vs. Rule-Based Systems
Machine Translation Technology Stack
Traditional machine translation systems rely on:
- Static dictionaries: Predetermined word-to-word mappings
- Grammatical rules: Fixed linguistic patterns for each language
- Statistical models: Basic probability calculations for word selection
- Limited context analysis: Processing individual sentences in isolation
AI Translation Technology Innovation
Modern AI translation leverages:
- Neural networks: Complex artificial intelligence systems that learn language patterns
- Deep learning algorithms: Advanced machine learning that improves through experience
- Contextual analysis: Understanding entire documents and conversations
- Continuous learning: Systems that enhance the quality of translation through ongoing data analysis
Practical Applications in Subtitle Translation
Machine Translation in Subtitle Creation
Machine-translated subtitles typically exhibit several characteristics:
- Speed: Rapid processing of large volumes of content
- Basic accuracy: Adequate for simple, straightforward dialogue
- Limited context awareness: Struggles with character relationships and story context
- Inconsistent quality: Variable results depending on language pairs and content complexity
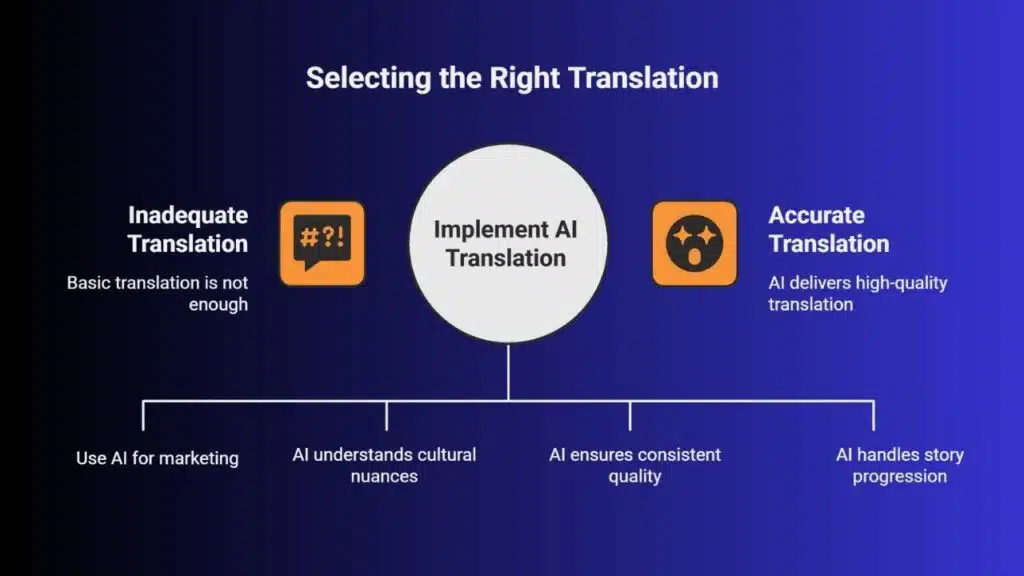
AI Translation for Professional Subtitles
AI-powered translations offer enhanced capabilities for subtitle creation:
- Contextual continuity: Understanding character development and story progression
- Cultural adaptation: Adjusting references and humor for target audiences
- Timing optimization: Better synchronization with audio and visual elements
- Quality consistency: Reliable performance across diverse content types
Rask.ai’s Advanced AI Translation Approach
Combining Best-in-Class Technologies
Rask.ai represents the cutting edge of AI translation technology, addressing the limitations of both traditional machine translation and basic AI systems. The platform’s approach demonstrates what’s possible when advanced artificial intelligence meets practical subtitle translation needs.
- Multi-Modal Processing: Rask.ai analyzes not just text but also audio context, speaker characteristics, and visual elements to produce more accurate translations.
- Cultural Intelligence: The system understands cultural references and adapts content appropriately for different target audiences while maintaining the original’s intent.
- Real-Time Optimization: Unlike static machine translation systems, Rask.ai continuously improves translation quality through machine learning and user feedback.
Professional-Grade Translation Solutions
Rask.ai’s AI translation capabilities address the specific challenges of subtitle translation:
- Speaker Recognition: The system identifies different speakers and maintains character voice consistency across translated subtitles.
- Contextual Continuity: Advanced AI understands story progression and character relationships, ensuring translated dialogue maintains narrative coherence.
- Technical Precision: The platform handles technical terminology, proper nouns, and industry-specific language with accuracy that rivals professional translators.
Industry Impact and Future Trends
The Translation Industry Transformation
The evolution from machine translation to AI translation has fundamentally transformed the translation industry:
- Accessibility: More people can now access high-quality translation services without the cost barriers of human translation.
- Speed and Scale: Content creators can translate subtitles for multiple languages simultaneously, reaching global audiences faster than ever before.
- Quality Standards: AI translation tools now achieve accuracy levels that approach human translator quality for many language pairs and content types.
Emerging Technologies in Translation
The future of translation technology continues evolving beyond current AI capabilities:
- Real-Time Translation: Advanced systems that can translate and subtitle live content as it happens.
- Emotional Intelligence: AI that understands and preserves emotional context and tone across language barriers.
- Cultural Adaptation: Systems that don’t just translate language but adapt cultural context for local audiences.
Choosing Between Machine and AI Translation Solutions
When Machine Translation Suffices
Traditional machine translation may be adequate for:
- Basic content understanding: Simple informational content with straightforward language
- Internal communications: Draft translations for internal review and editing
- High-volume, low-stakes content: Large quantities of content where perfect accuracy isn’t critical
When AI Translation Becomes Essential
AI translation tools become necessary for:
- Professional content: Marketing materials, educational content, and public-facing communications
- Cultural sensitivity: Content that includes humor, cultural references, or emotional nuance
- Brand consistency: Materials where translation quality reflects on organizational reputation
- Complex narratives: Entertainment content with character development and story progression
Technical Considerations for Implementation
Input Quality and Processing Requirements
Both machine translation and AI translation systems depend on input quality, but they handle poor-quality source material differently:
- Machine Translation: Garbage in, garbage out—poor source language quality directly correlates with poor translated text quality.
- AI Translation: Advanced systems can often improve upon poor input quality by understanding context and correcting obvious errors during the translation process.
Integration with Existing Workflows
Modern translation solutions must integrate seamlessly with content creation workflows:
- API Accessibility: Both machine translation and AI translation services offer API access, but AI solutions typically provide more sophisticated integration options.
- File Format Support: AI translation tools often handle a wider range of input formats and maintain formatting during the translation process.
- Batch Processing: Advanced AI systems can process multiple files simultaneously while maintaining consistency across related content.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Machine vs. AI Translation
Economic Considerations
The cost difference between machine translation and AI translation often reflects the value difference in output quality:
Machine Translation Economics:
- Lower per-word processing costs
- Minimal setup and training requirements
- Suitable for large-volume, basic translation needs
AI Translation Investment:
- Higher initial costs offset by superior quality
- Reduced the need for human intervention and editing
- Better long-term ROI for professional content
Quality ROI Assessment
When evaluating translation solutions, consider the total cost of achieving acceptable quality:
- Machine translation + human editing: Often exceeds AI translation costs
- AI translation + minimal review: Typically provides better quality at lower total cost
- Professional human translation: Remains a premium option for the highest-stakes content
Future Implications for Content Creators
Democratization of Global Content
The advancement from machine translation to AI translation democratizes global content creation:
Accessibility: Smaller creators can now afford professional-quality translation services. Speed: Content can reach global audiences almost simultaneously with the original publication Quality: AI translation eliminates many barriers that previously made international content expansion difficult
Strategic Considerations
Content creators must consider how translation technology choices affect their long-term strategy:
Brand Reputation: Poor machine translation can damage brand perception, while quality AI translation enhances credibility.Better translation quality directly correlates with international audience engagement and retention Competitive Advantage: Early adoption of advanced AI translation tools provides market advantages in global content distribution
Conclusion: The Clear Choice for Modern Content Creation
Understandt the difference between machine and AI subtitle translation reveals why modern content creators increasingly choose advanced AI solutions like Rask.ai. While traditional machine translation served as an essential stepping stone in breaking down language barriers, AI translation represents the current standard for professional content localization.
The evolution from rule-based machine translation to context-aware AI translation reflects broader technological advancements in artificial intelligence and natural language processing. For content creators serious about global reach and professional quality, AI translation tools provide the accuracy, cultural sensitivity, and technical sophistication necessary for effective international communication.
As the technology continues advancing, the gap between machine translation and AI translation will only widen. Organizations that embrace advanced AI translation solutions today position themselves advantageously for tomorrow’s increasingly connected global marketplace, where quality translation isn’t just a nice-to-have feature—it’s essential for competitive success.
Rask.ai exemplifies the best of modern AI translation technology, combining technical innovation with practical usability to deliver translation solutions that genuinely serve the needs of today’s global content creators. The choice between machine and AI translation is ultimately a choice between basic functionality and professional excellence.