Artificial intelligence is reshaping industries worldwide with rapid advancements. Four major players are competing for dominance: Meta’s “Llama-3.1-405B”, OpenAI’s “GPT-4o”, Alibaba’s “Qwen 2.5-Max”, and DeepSeek’s “DeepSeek-V3”.
These models bring distinct strengths to the table, from open-source accessibility to proprietary frameworks and cutting-edge algorithms.
Chinese AI firms like Alibaba and DeepSeek are investing heavily in innovation, with Qwen 2.5-Max using a Mixture-of-Experts design for unmatched performance in benchmarks like GSM8K (94.5).
Meanwhile, GPT-4o shines in multi-tasking tasks such as MMLU-Pro (77.0), backed by a $25 billion SoftBank investment under Stargate Initiative funding worth $500 billion.
Meta offers an affordable solution, empowering Llama-3.1 with just 20 billion active parameters per query for efficiency on Hugging Face platforms. DeepSeek-V3 focuses on solving specific problems while keeping costs low at only $5.6 million through student-driven research labs.
As global competition heats up between Chinese and Western AI developers, each contender targets different markets through unique technologies and strategies designed to lead innovation ecosystems worldwide.
But which one will define the future? Read on our comparison of Llama-3.1-405B vs. GPT-4o vs. Qwen 2.5-Max vs. DeepSeek-V3!
Overview of the Contenders
The AI landscape is crowded, but these models stand out with their unique technologies and goals. Each contender competes to redefine problem-solving, efficiency, and adaptability in artificial intelligence systems.
Llama-3.1-405B
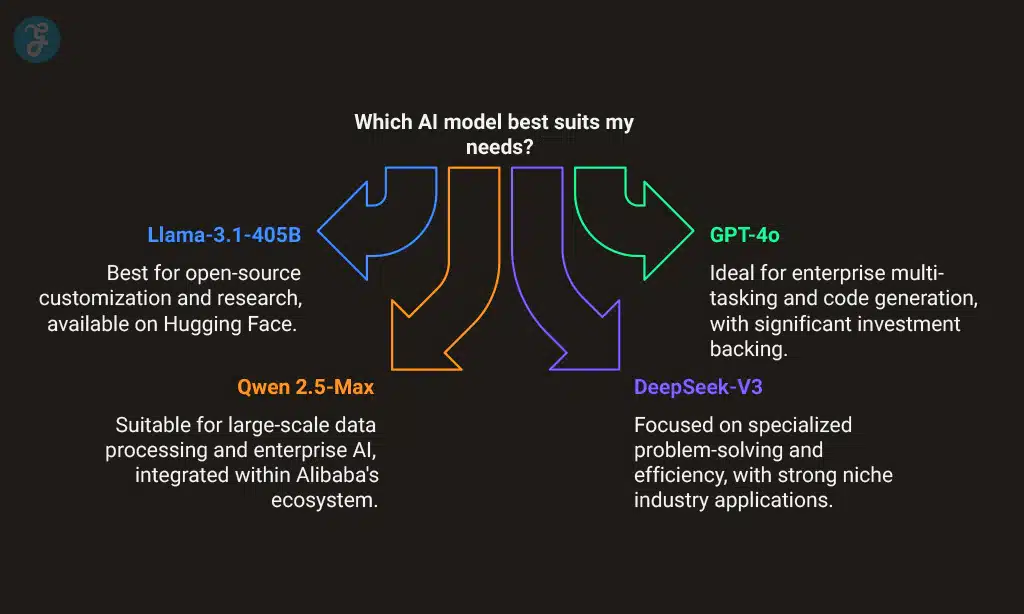
Llama-3.1-405B, released by Meta, operates as an open-source model available on Hugging Face. It activates only 20 billion parameters per query, making it more cost-efficient than competitors like GPT-4o and Qwen 2.5-Max.
Jefferies highlighted its reduced response times and operational costs compared to closed proprietary models in the AI market.
This large language model (LLM) competes directly with industry leaders in generative AI while benefiting from scalability through open-source accessibility. Its design supports reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), improving natural language understanding for practical applications such as AI assistants or business solutions.
GPT-4o
Unlike Llama-3.1-405B’s open-source focus, GPT-4o operates on a proprietary framework designed by OpenAI. This large language model (LLM) is recognized as an industry leader in artificial intelligence.
It excels in multi-tasking scenarios and has demonstrated exceptional natural language understanding and reasoning abilities. OpenAI developed it to handle complex tasks like JSON handling, data analysis, tool invocation, and code generation with high precision.
SoftBank recently announced plans to invest $25 billion into OpenAI through the $500 billion Stargate initiative. Such backing highlights both its scalability and strategic significance in Silicon Valley’s AI race.
Acknowledged by Sam Altman for its role against competitors like Qwen 2.5-Max and DeepSeek-V3, GPT-4o solidifies Western dominance over the growing field of AGI development while maintaining accessibility for enterprise adoption at scale.
Qwen 2.5-Max
Qwen 2.5-Max entered the market on January 29, 2025, through Alibaba’s ambitious AI initiatives. Its training set involved an impressive scale of 20 trillion tokens, making it a powerhouse in processing large-scale data.
The model employs Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture to optimize performance by assigning tasks to specialized nodes within its system. This approach enhances efficiency and scalability for complex computations.
Unlike open-source models like Llama-3.1-405B, Qwen 2.5-Max remains proprietary. This strategic choice allows Alibaba Group to maintain competitive control over this advanced artificial intelligence tool.
Industry experts note that this decision strengthens its position in markets requiring enterprise-focused solutions while leveraging China’s growing investments in cutting-edge AI development programs.
DeepSeek-V3
Released as an AI assistant on January 10, 2025, DeepSeek-V3 quickly gained attention for its problem-solving focus. Its Mixture of Experts (MoE) design allows it to allocate computing power efficiently.
This has made it highly effective in specialized tasks compared to general-purpose large language models like GPT-4o and Llama-3.1.
The open-source R1 model launched just days later, on January 20, 2025. Training the system cost $5.6 million but disrupted Silicon Valley by impacting tech shares significantly. Businesses have used DeepSeek-V3 for fine-tuning and scalable AI applications requiring advanced reasoning capabilities without relying on excessive computational resources.
Model Architectures and Technologies
Each model brings distinct design principles, showcasing unique strengths in artificial intelligence and pushing the boundaries of large language models (LLMs).
Llama-3.1-405B’s Open-Source Approach
Llama-3.1-405B stands out with its open-source AI model available on Hugging Face. It uses only 20 billion parameters per query, which reduces computational demand and energy use. This approach delivers competitive results while lowering costs and response times.
Reports by Jefferies highlight how this efficiency benefits businesses aiming for budget-friendly artificial intelligence solutions without sacrificing quality.
Its availability as an open-source model encourages collaboration across industries and researchers globally. Developers can access the base model to build innovative tools tailored to specific needs.
Unlike proprietary systems like OpenAI’s GPT-4o, Llama-3.1 balances accessibility with solid performance metrics, making it a favored option for startups or enterprises investing in large language models (LLMs).
GPT-4o’s Proprietary Framework
OpenAI developed GPT-4o as a powerful artificial intelligence model. Its proprietary framework ensures advanced multi-tasking capabilities and seamless integration across industries.
Unlike open-source models like Llama 3.1, GPT-4o operates on a closed ecosystem, allowing OpenAI to maintain tighter control over updates and data security.
This controlled approach enhances the model’s reliability for enterprise use. Recognized as an industry leader, GPT-4o delivers exceptional performance in natural language understanding, reasoning tasks, and AI-generated solutions.
Businesses often adopt it due to its robust support for code generation and detailed problem-solving processes.
Qwen 2.5-Max’s Mixture-of-Experts Design
Qwen 2.5-Max leverages a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, setting it apart from competitors like GPT-4o. This design improves scalability and efficiency during large-scale processing tasks.
The model trained on an impressive dataset of 20 trillion tokens—equivalent to about 15 trillion words—vastly enhancing its natural language understanding and reasoning capabilities.
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) fine-tune Qwen’s performance. These techniques help the model respond accurately while maintaining user-centric outputs.
Its MoE structure enables task-specific expertise by dynamically activating subsets of experts within the network, optimizing both processing speed and resource use at scale.
DeepSeek-V3’s Specialized Problem-Solving Algorithms
DeepSeek-V3 builds on its advanced Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, making it highly efficient. Each MoE model contains 200 billion parameters, enabling precise artificial intelligence (AI) problem-solving techniques.
This system combines Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA), which improves task focus and result accuracy. Unlike broader-purpose models like GPT-4o or Llama-3.1-405B, DeepSeek-V3 prioritizes specialization for industry-relevant scenarios.
These algorithms excel in tackling specific challenges by focusing computational resources where needed most. Businesses benefit from this targeted approach, especially when addressing technical issues or logistical bottlenecks.
The integration of MLA ensures faster processing without sacrificing quality or scalability across tasks. Companies such as Tencent and Baidu find value in using DeepSeek-V3 to enhance enterprise solutions at scale while balancing cost-effectiveness with precision outcomes.
Performance Benchmarks
Performance tests highlight the strengths and specialized uses of each model. These results spotlight differences in adaptability, context handling, and task-specific success rates.
Qwen 2.5-Max’s Lead in General Performance
Qwen 2.5-Max demonstrates exceptional performance across benchmarks. It achieved a remarkable 94.5 score on GSM8K, showcasing its superior problem-solving abilities compared to DeepSeek-V3’s 89.3 and Llama-3.1-405B’s 89.0 scores.
This result highlights its capability in solving complex mathematical problems efficiently.
On the Arena-Hard benchmark, Qwen 2.5-Max recorded an impressive score of 89.4, outperforming DeepSeek-V3 at 85.5 and Claude 3.5 Sonnet at 85.2.
These outcomes establish its dominance in processing diverse tasks with high accuracy while maintaining reliable general-purpose performance for users globally, including business strategies or AI deployment scenarios like JSON handling and reasoning tasks by enterprises worldwide seeking robust solutions from Chinese AI investments like Alibaba’s innovative developments in artificial general intelligence tools driving market leadership effectively through advanced technologies.
GPT-4o in Multi-Tasking Scenarios
Building on Qwen 2.5-Max’s versatility, GPT-4o excels in handling multi-tasking scenarios. OpenAI’s model demonstrates strong adaptability across diverse tasks. It leverages its proprietary framework to balance performance and efficiency when addressing concurrent challenges.
For example, GPT-4o shows advanced reasoning abilities in academic contexts like the MMLU-Pro benchmark, scoring a competitive 77.0 against other base models like Qwen 2.5-Max (76.1) and DeepSeek-V3 (75.9).
This places it among top contenders for AI-based problem solving.
The model also outshines competitors in areas requiring natural language understanding and reasoning at scale while maintaining fairness assessments—a critical industry need today.
Its strengths include precise JSON handling for data-intensive workflows and robust code generation capabilities comparable to specialized tools such as DALL-E or DeepSeek-R1 algorithms from Alibaba’s ecosystem.
Businesses leveraging such capabilities see improved results with reduced manual oversight.
Llama-3.1-405B’s Strength in Open-Source Applications
Llama-3.1-405B stands out with its open-source availability on Hugging Face. This accessibility offers developers cost-effective solutions compared to proprietary models like GPT-4o.
Its reduced response times and competitive results make it a strong contender in the AI space, especially for budget-conscious projects.
The model supports diverse applications while maintaining high performance at lower costs. Jefferies has reported significant savings in operational expenses due to Llama’s efficiency.
Unlike closed ecosystems, this open approach fosters collaboration within the developer community, driving innovation forward rapidly.
DeepSeek-V3’s Problem-Specific Efficiency
DeepSeek-V3 thrives at solving specialized problems due to its advanced algorithms. It excels in targeted tasks, outperforming rivals like Qwen 2.5-Max and GPT-4o in niche scenarios.
On GPQA-Diamond, it scored an impressive 59.1, close to Qwen’s 60.1 but trailing Claude 3.5 Sonnet’s higher mark of 65.0. Its Arena-Hard performance reached 85.5, beating Claude but falling short of Qwen’s leading score.
Its efficiency shines in real-time benchmarks like LiveBench, scoring a strong 60.5 against Qwen’s dominating 62.2 and narrowly ahead of other contenders like Claude with its comparable result of 60.3 there too!
DeepSeek-V3 applies problem-specific optimization that appeals strongly to enterprise users needing precise solutions over general capabilities offered by players such as chatGPT or Google-backed tools similar competing ecosystem efforts globally dominate tech giants’ conversations today.
Llama-3.1-405B vs. GPT-4o vs. Qwen 2.5-Max vs. DeepSeek-V3
Here’s a comparative table summarizing the key differences between Llama-3.1-405B, GPT-4o, Qwen 2.5-Max, and DeepSeek-V3 based on your content:
| Feature | Llama-3.1-405B (Meta) | GPT-4o (OpenAI) | Qwen 2.5-Max (Alibaba) | DeepSeek-V3 (DeepSeek) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Type | Open-source | Proprietary | Proprietary | Open-source (R1) & Proprietary |
| Parameters (Active per Query) | 20B | Not disclosed | Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) | 200B (MoE) |
| Architecture | RLHF, Open-Source | Proprietary, Multi-tasking | Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), 20T tokens trained | Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) |
| Best For | Open-source customization, research | Enterprise, multi-tasking, code generation | Large-scale data processing, enterprise AI | Specialized problem-solving, efficiency |
| Performance Benchmarks | GPQA-Diamond: 59.1 | MMLU-Pro: 77.0 | GSM8K: 94.5, Arena-Hard: 89.4 | GSM8K: 89.3, Arena-Hard: 85.5 |
| Cost Efficiency | Low-cost, open-source | Expensive, enterprise-grade | Scalable for large enterprises | Low-cost, targeted solutions |
| Investment & Funding | Supported by Meta | $25B SoftBank investment (Stargate Initiative) | Alibaba-backed, China’s AI expansion | $5.6M investment from student-driven labs |
| Market Position | Research & open-source developers | Enterprise AI, dominant in Silicon Valley | China’s AI leader, enterprise & cloud integration | Cost-effective solutions for businesses |
| Access & Deployment | Available on Hugging Face | Limited API access, enterprise-focused | Proprietary, Alibaba ecosystem | Open-source R1, available for customization |
| Multilingual Capabilities | Strong, global accessibility | High, excels in diverse language understanding | Advanced NLP for Chinese and global markets | Strong in niche industry-specific applications |
| Scalability & AI Usage | Developer-friendly, scalable | Large-scale enterprise applications | Cloud AI, scalable in business & government sectors | Problem-specific AI, used in research labs |
Key Features and Capabilities
Each AI model excels in unique tasks, showcasing distinct advantages. Their capabilities stretch across areas like reasoning, language comprehension, and data processing efficiency.
Tool Invocation and Code Generation
Qwen 2.5-Max dominates code generation with a HumanEval score of 73.2 and MBPP at 80.6. Its seamless integration via Qwen Chat and Alibaba Cloud Model Studio API ensures developers can invoke tools efficiently for complex tasks.
These high benchmarks highlight its Mixture-of-Experts design, built for intelligent decision-making.
GPT-4o also excels in multi-tasking scenarios, leveraging proprietary advancements to generate robust code templates on demand. Llama-3.1-405B appeals to open-source enthusiasts by enabling customizable tool use without licensing restrictions, while DeepSeek-V3 focuses its algorithms on domain-specific tool applications where precision is key.
Each caters uniquely to developer needs in modern AI development workflows.
Natural Language Understanding and Reasoning
Tool invocation and code generation rely on a model’s ability to comprehend language deeply. Advanced natural language understanding (NLU) and reasoning push this capability further by interpreting complex texts, context, and user intent.
Models like GPT-4o excel in multi-tasking scenarios, efficiently handling tasks that span various domains.
Qwen 2.5-Max demonstrates enhanced efficiency in large-scale processing by leveraging supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Its reasoning shows precision when solving intricate text-based problems at scale.
DeepSeek-V3 applies specialized algorithms for problem-solving but focuses primarily on niche applications instead of broad conversational AI tasks.
JSON Handling and Data Analysis
Natural language reasoning plays a critical role in understanding structured formats like JSON. Models such as GPT-4o and Qwen 2.5-Max excel at managing JSON due to their advanced parsing capabilities.
They quickly interpret nested data and extract key information for analysis, making them effective in real-time scenarios.
DeepSeek-V3 focuses on problem-specific tasks, giving it an edge in analyzing large datasets stored in JSON. Its specialized algorithms process complex relationships within the data faster than general-purpose models.
Llama-3.1-405B prioritizes open-source adaptability, letting developers customize its functionalities for unique use cases involving JSON handling or analytics pipelines. This versatility benefits industries looking for cost-effective yet customizable solutions.
Market Position and Accessibility
Open-source models like Llama-3.1-405B are reshaping accessibility for developers worldwide. Proprietary options, such as GPT-4o, focus on enterprise-grade features to dominate commercial applications.
Open-Source vs. Proprietary Models
Llama-3.1-405B and DeepSeek-V3 embrace open-source frameworks, offering transparency and collaboration. Developers can modify these models to suit specific needs without licensing restrictions.
DeepSeek-V3 particularly appeals to organizations needing cost-effective solutions for data-driven tasks like problem-solving or advanced analysis.
On the other hand, GPT-4o and Qwen 2.5-Max operate under proprietary systems. These models keep their architecture and training data locked away, ensuring control over product use while driving enterprise adoption.
Qwen 2.5-Max caters mainly to large businesses with its cutting-edge features but limited accessibility compared to alternatives like Llama-3.1’s economic flexibility in deployment scenarios.
Enterprise Adoption Rates
Enterprise adoption rates vary by model accessibility and cost-effectiveness. DeepSeek-V3, known for its specialized algorithms, offers affordable solutions tailored to enterprises.
This positions it as a strong choice for businesses seeking problem-specific AI tools without high expenses. Its focus on cost-efficiency attracts companies needing reliable yet budget-friendly systems.
Qwen 2.5-Max excels with faster response times and lower inference costs. These factors make it appealing to large-scale operations prioritizing speed and efficiency. Meanwhile, proprietary models like GPT-4o face barriers in price-sensitive markets despite their multi-tasking capabilities.
The open-source approach of certain models drives broader adoption in sectors requiring flexibility over licensing restrictions or financial investments.
Geopolitical and Industry Implications
China’s AI expansion accelerates with heavy investments in models like Qwen 2.5-Max and DeepSeek-V3. Meanwhile, Western companies focus on refining advanced systems such as GPT-4o and Llama-3.1 to maintain dominance.
Chinese AI Investments: Qwen and DeepSeek
China’s AI sector surged with Qwen 2.5-Max launching on January 29, 2025. Its mixture-of-experts design stands out as a key innovation, securing its place in high-demand areas like natural language understanding and reasoning.
DeepSeek also made waves by releasing an open-source R1 model on January 20, 2025, just days after introducing its assistant on January 10. The low-cost strategy disrupted Silicon Valley tech stocks, pushing global competitors to rethink pricing.
Qwen 2.5-Max focuses heavily on general performance benchmarks and enterprise applications, while DeepSeek’s models excel in specialized problem-solving tasks. These investments underscore China’s determination to lead the AI race amid rising competition against Western players like GPT-4o and Llama-3.1-405B.
Western AI Dominance: GPT-4o and Llama-3.1
Western companies continue to lead AI innovation with models like GPT-4o and Llama-3.1. OpenAI’s GPT-4o remains one of the strongest proprietary frameworks, with SoftBank announcing a $25 billion investment in its development.
This financial backing signals increasing confidence in Western AI technologies for enterprise applications.
Llama-3.1 carves out a prominent space as an open-source alternative, offering developers flexibility while adhering to global privacy standards. Its widespread accessibility attracts academic researchers and smaller organizations seeking cost-effective solutions without vendor lock-in.
Both models highlight the West’s strategy to dominate through technological advancement and market adaptability over time.
Predictions for the AI Industry’s Future Leader
Chinese firms like Qwen 2.5-Max and DeepSeek-V3 are rapidly advancing with significant investments in AI technology. These companies benefit from strong government backing, which accelerates their development cycles.
Qwen’s mixture-of-experts design positions it to excel in high-demand areas like data analysis and decision-making tools. DeepSeek-V3 focuses on problem-specific efficiency, making it appealing for industries requiring specialized solutions.
Competitive pressure is growing as U.S.-based models like GPT-4o face challenges maintaining dominance. GPT-4o holds its ground with enterprise adoption but sees threats from faster innovation abroad.
Llama-3.1-405B thrives due to accessibility through open-source support yet struggles against proprietary features by rivals overseas. Chinese giants could outpace Western counterparts if trends continue, reshaping global AI leadership within the next five years.
Takeaways
The battle for AI dominance is heating up between Llama-3.1-405B, GPT-4o, Qwen 2.5-Max, and DeepSeek-V3. Each model brings unique strengths, from open-source flexibility to cutting-edge architecture.
The winner will depend on market needs like cost efficiency, innovation scope, or enterprise applications. Consider how these advancements could reshape industries and global tech leadership.
Which contender aligns best with your goals?