Is your video meeting frozen or your stream glitchy? Many areas still lack real fiber broadband, and that can slow work or school. Fact: fiber connectivity moved from a fancy perk to a must-have for jobs, telehealth, smart homes, and more.
In this post, we map out key fiber broadband models shaping ISP Investment. We will cover open-access networks, public-private partnerships, passive optical network, last mile solutions, AI tools, and 5G backhaul.
You will find steps to help towns, schools, and providers bridge the digital divide and plan smart city upgrades. Keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- Open-access networks let multiple ISPs share a single fiber line, cut costs, and boost rural speeds. Cities can issue revenue bonds, and New York law lets networks drop providers under 20,000 users.
- Public-private partnerships unite city halls and tech firms to build fiber and gNodeBs in low-density areas. They mix public funds and private cash, use AI and cloud tools, and meet 2025 digital inclusion goals.
- 10G-PON and XGS-PON deliver 10 Gbps symmetrical speeds in 2025. Wi-Fi 7 approval in early 2024 paves the way for 2.1 billion devices by 2028 and powers telehealth, driverless cars, and city sensors.
- AI and automation cut network design times by up to 30%, speed site surveys by 20–25%, and speed permit approvals by 10–20%. A North American fiber firm saw rollout speeds rise 10% and cut costs with cloud services.
- On July 15, 2025, Memphis Light, Gas and Water and Nokia launched a $31 million private 5G backhaul for 420,000 users. After a 200% surge in fiber attacks in Missouri on July 20, 2025 that hit 148 links, ISPs added DDoS shields, encryption, and AI anomaly detection.
Open-Access Networks
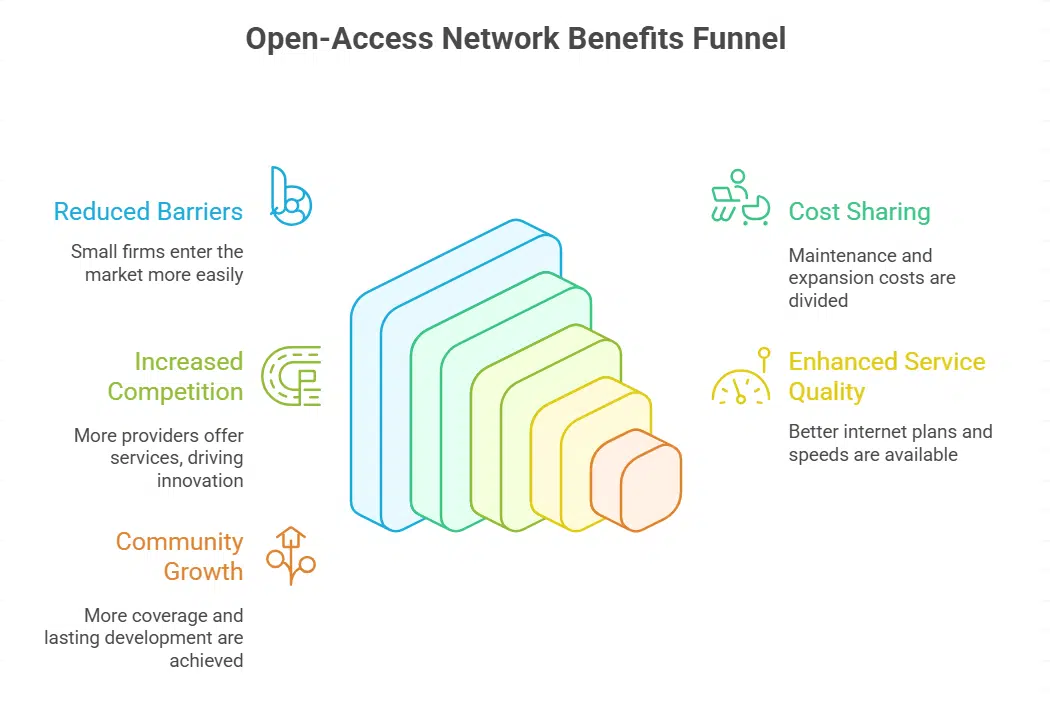
Open-access networks let many internet providers share one fiber line. This model will grow a lot in 2025, cutting barriers for small firms, spreading risk like butter on toast. Cities might tap public funding, issue revenue bonds for fiber-to-the-home links.
Broadband providers can then offer cheaper plans, boost service quality. Customers in rural zones get high-speed internet and narrow the digital divide. State law in New York even lets networks drop providers with fewer than 20,000 users, smoothing some rules.
Operators split maintenance tasks and expansion costs, sharing the load like a family pulling a wagon, which cuts big bills but needs careful deals. Competition springs up, pricing stays fair and speeds stay fast.
Public infrastructure teams often join, boosting energy efficiency in network infrastructure. Communities gain more coverage and lasting growth, and public value rises with each mile of fiber.
Stakeholders like policy makers, internet providers and municipal broadband groups work side by side, sharing gains and chores.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) feel like a handshake between city hall and a tech firm to fuel fiber projects. Officials pitch in funds and share budget goals. Tech firms bring new ideas and build fiber connectivity to bridge the digital divide.
Smaller towns get access points and gNodeB units with help. States often lack staff and cash. Private players shy from low-density areas due to ROI worries. Firms apply predictive maintenance tools and cloud computing to cut costs.
This moves broadband expansion in the US and beyond.
Internet service providers (ISPs) win stable user bases and steady income. Budget risks shrink when funds mix comes from public and private sides. Projects meet coverage targets and fit tight budgets.
Tie-ups hit national digital inclusion goals for 2025. Rural spots see faster upgrades. Providers layer in security architectures like encryption and smart sensors for IoT links. Fiber lines grow in a step-by-step, flexible way.
Stakeholders reduce each loan burden and build trust in local markets.
Gigabit and Multi-Gigabit Network Expansion
Demand will skyrocket in 2025, thanks to video streaming, remote work, gaming, telemedicine, I tell you. 10G-PON and XGS-PON deliver 10 Gbps symmetrical speeds. Internet service providers will race to offer top quality, bundles, rock-solid reliability.
Smart cities rely on multi-gigabit broadband to power traffic sensors, telehealth kiosks, environmental monitors.
Fiber connectivity feeds Wi-Fi 7 growth, as the Wi-Fi Alliance approved that standard in early 2024. Analysts expect 2.1 billion Wi-Fi 7 gadgets by 2028. This surge helps driverless cars, remote surgery, virtual tours.
Broadband expansion shrinks the digital divide, boosting quality-of-service for homes, offices, hospitals.
AI and Automation for Network Optimization
AI tools run network management tasks. They use machine learning algorithms to spot faults and schedule predictive maintenance before links fail. Automation of network design cuts timelines by up to 30 percent, letting isps speed fiber connectivity builds.
Site survey software, digital tools for internet access projects, speeds up work by 20 to 25 percent. Permit center automation clears approvals 10 to 20 percent faster and snaps up permits 15 percent sooner.
A North American fiber network firm saw rollout speed climb by nearly 10 percent, slicing costs with cloud services.
Real time monitoring frees managers to tackle complex deployment challenges. Automation in construction management trims 5 to 8 percent off fiber broadband builds. GenAI platforms parse market segments and user engagement to spot low cost, high penetration areas.
That tactic helps internet service providers push broadband expansion and bridge digital divide gaps. Mobile data and IoT connections flow smoother, so streaming content gains less buffering.
Integration with 5G and IoT Technologies
Fiber links feed 5G nodes on poles and rooftops. They act like a highway for data and shave off delays. They serve as solid backhaul for busy cells. Memphis Light, Gas and Water teamed up with Nokia on July 15, 2025.
They built a private 5G system worth $31 M for over 420,000 customers. Internet service providers can now pair fiber connectivity with novel wireless cells. This duo handles video streams, smart devices, and public safety radios.
It helps close the digital divide in cities and towns.
Cities tie water meters, traffic signals, and emergency radios into one circuit. A single fiber link and 5G unit carries all in real time. I once saw a traffic light reboot in a blink.
This blend powers smart grid functions and advanced monitoring. Builders use micro-trenching or aerial fiber to slash costs and speed installs. Utilities like Utopia Fiber adopt these methods citywide.
Factories push internet of things data from robots, while retailers track stock live at checkout. The approach boosts citizen engagement and backs public safety alerts on a dime.
Advanced Cybersecurity Models for Fiber Networks
Charter Communications saw a 200% jump in fiber attacks in Missouri on July 20, 2025. The surge knocked out 148 connections, hitting hospitals, emergency services, bank systems hard.
Internet service providers now pour cash into DDoS shields and anti-ransomware tools. EU GDPR rules tighten privacy at every glass strand. AI anomaly detection scans traffic in real time, big operators flip that switch this year.
Research teams trial quantum key distribution over fiber connectivity to seal data with entangled photons. Google’s quantum computer chip may ride alongside cable cores and scramble packets on the fly.
PPP models fund defense grants and spur broadband expansion, they share threat intel and trim spending gaps. This drive shrinks the digital divide, it keeps IoT meters and smart grids safe.
Legislators spark debates on infrastructure protection and domestic terrorism.
Takeaways
Fiber models shape ISP plans this year. ISPs apply open access network tools like AI platforms. Public-private partnerships cut costs and boost rollout speed. Investors ride the fiber wave to tackle the digital divide.
5G backhaul links with IoT sensors for smart city apps. Security layers guard against DDoS with encryption protocols. These six paths give providers a solid, flexible base.
FAQs on Key Fiber Broadband Models Shaping ISP Investment
1. What are the six key fiber broadband models shaping ISP investment in 2025?
They include basic fiber, open access networks, public-private partnerships, fiber as a service, tax-efficient models, and orbit-based broadband that taps low earth orbit relays. For ISPs it builds out their internet services map.
2. How can internet service providers tap public-private partnerships for broadband expansion?
They team up with local funders, pool capital investment, cut red tape, speed up broadband expansion, shape business strategies, and win nods from policy makers.
3. How do open access networks and basic fiber links help close the digital divide?
They offer shared lines to many providers, boost internet connectivity, support the affordable connectivity program, and lift low-income or rural zones.
4. How does fiber connectivity support IoT and data centers in an urbanizing world?
It gives fast, stable links to smart sensors and heavy data loads, it drives energy conservation, and it makes utility grids smarter.
5. What finance and tax tools make fiber projects more sustainable for ISPs?
They use tax-efficient bonds, property tax relief, green finance, each save money, boost sustainability, and shape long-term finance plans.
6. Where do orbit-based broadband and copper-based service fit in this landscape?
Fiber is king, but orbit-based broadband and copper-based service fill gaps when straight fiber can’t reach, like an old school safety net.